Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell (Photo from the New York Times.)
This afternoon, Wednesday, January 31, the Federal Reserve’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) held the first of its eight scheduled meetings during 2024. As we noted in a recent post, macroeconomic data have been indicating that the Fed is close to achieving its goal of bringing the U.S. economy in for a soft landing—reducing inflation down to the Fed’s 2 percent target without pushing the economy into a recession. But as we also noted in that post, it was unlikely that at this meeting Fed Chair Jerome Powell and the other members of the FOMC would declare victory in their fight to reduce inflation from the high levels it reached during 2022.
In fact, in Powell’s press conference following the meeting, when asked directly by a reporter whether he believed that the economy had made a safe landing, Powell said that he wasn’t yet willing to draw that conclusion. Accordingly, the committee kept its target range for the federal funds rate unchanged at 5.25 percent to 5.50 percent. This was the fifth meeting in a row at which the FOMC had left the target unchanged. Although some policy analysts expect that the FOMC might reduce its federal funds rate target at its next meeting in March, the committee’s policy statement made that seem unlikely:
“In considering any adjustments to the target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will carefully assess incoming data, the evolving outlook, and the balance of risks. The Committee does not expect it will be appropriate to reduce the target range until it has gained greater confidence that inflation is moving sustainably toward 2 percent.”
Powell reinforced the point during his press conference by stating it was unlikely that the committee would cut the target rate at the next meeting. He noted that:
“The economy has surprised forecasters in many ways since the pandemic, and ongoing progress toward our 2 percent inflation objective is not assured. The economic outlook is uncertain, and we remain highly attentive to inflation risks. We are prepared to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate for longer, if appropriate.”
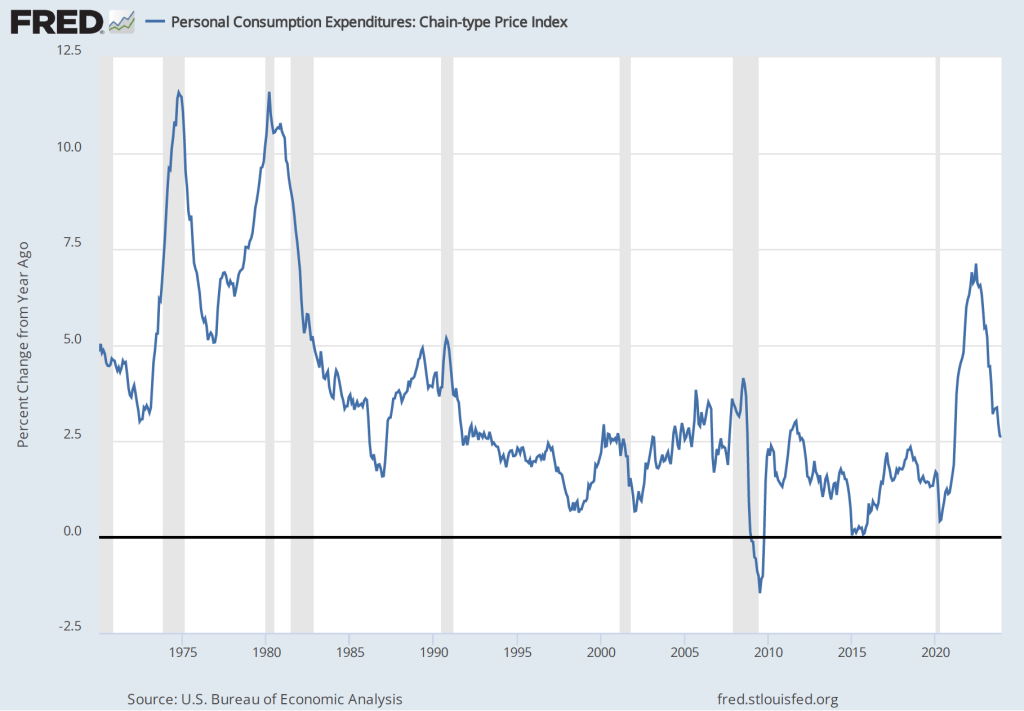
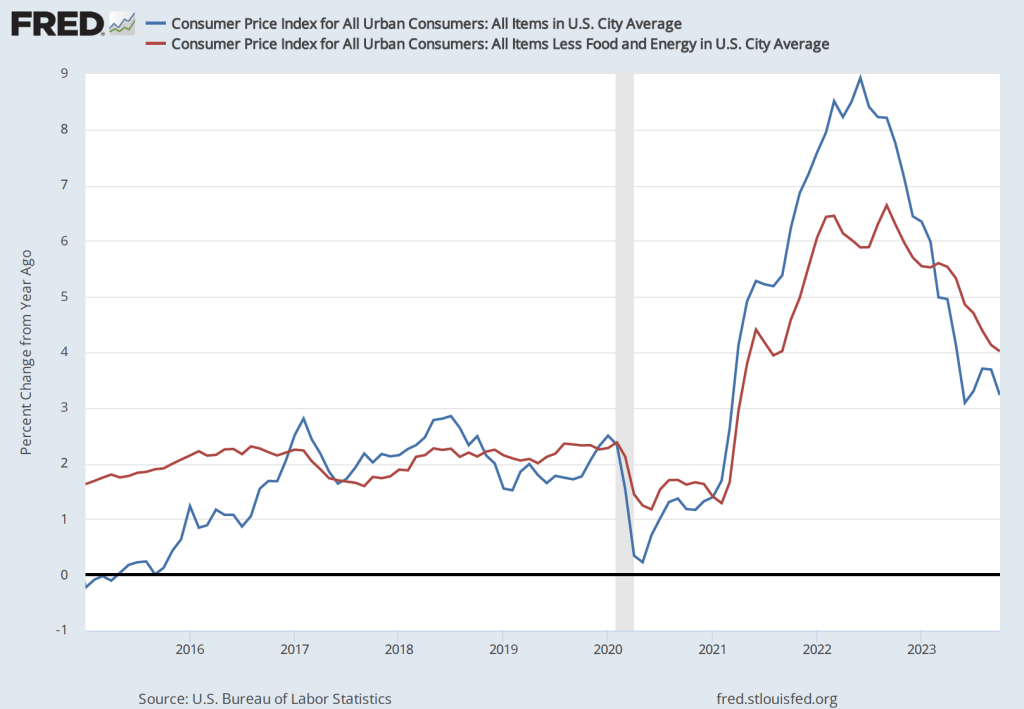
Powell highlighted a couple of areas of potential concern. The Fed gauges its progress towards achieving its 2 percent inflation goal using the percentage change in the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index. As we noted in a recent post, PCE inflation has declined from a high of 7.1 percent in June 2022 to 2.9 percent in December 2023. But Powell noted that PCE inflation in goods has followed a different path from PCE inflation in services, as the following figure shows.
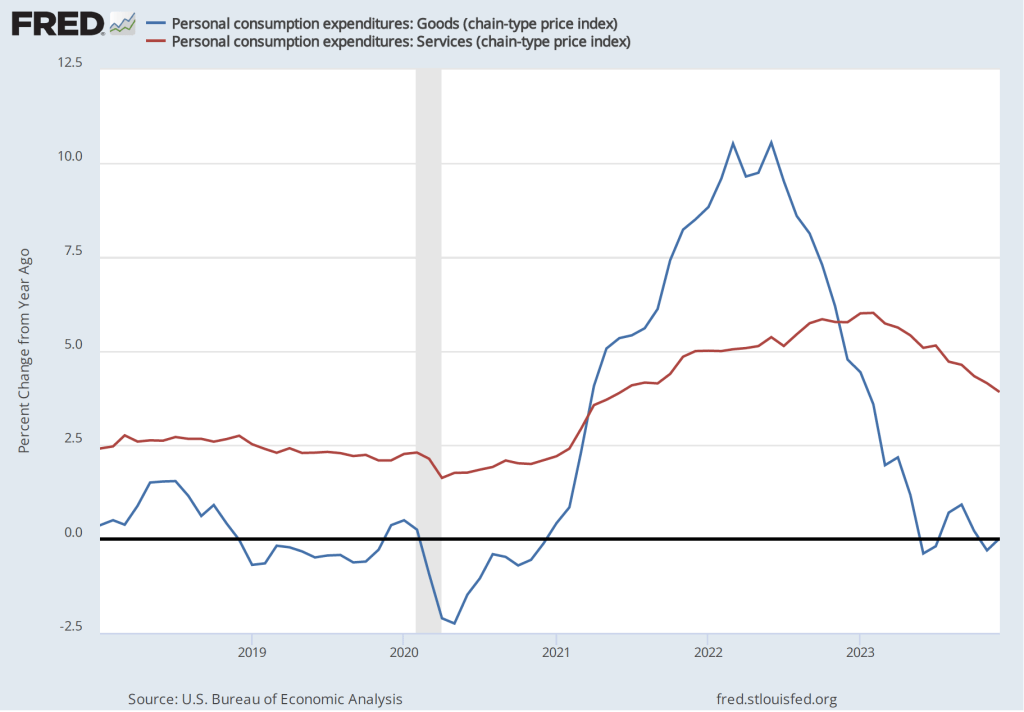
Inflation during 2022 was much greater in the prices of goods than in the prices of services, reflecting the fact that supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic had a greater effect on goods than on services. Inflation in goods has been less than 1 percent every month since June 2023 and has been negative in three of those months. Inflation in services peaked in February 2023 at 6.0 percent and has been declining since, but was still 3.9 percent in December. Powell noted that the very low rates of inflation in the prices of goods probably aren’t sustainable. If inflation in the prices of goods increases, the Fed may have difficulty achieving its 2 percent inflation target unless inflation in the prices of services slows.
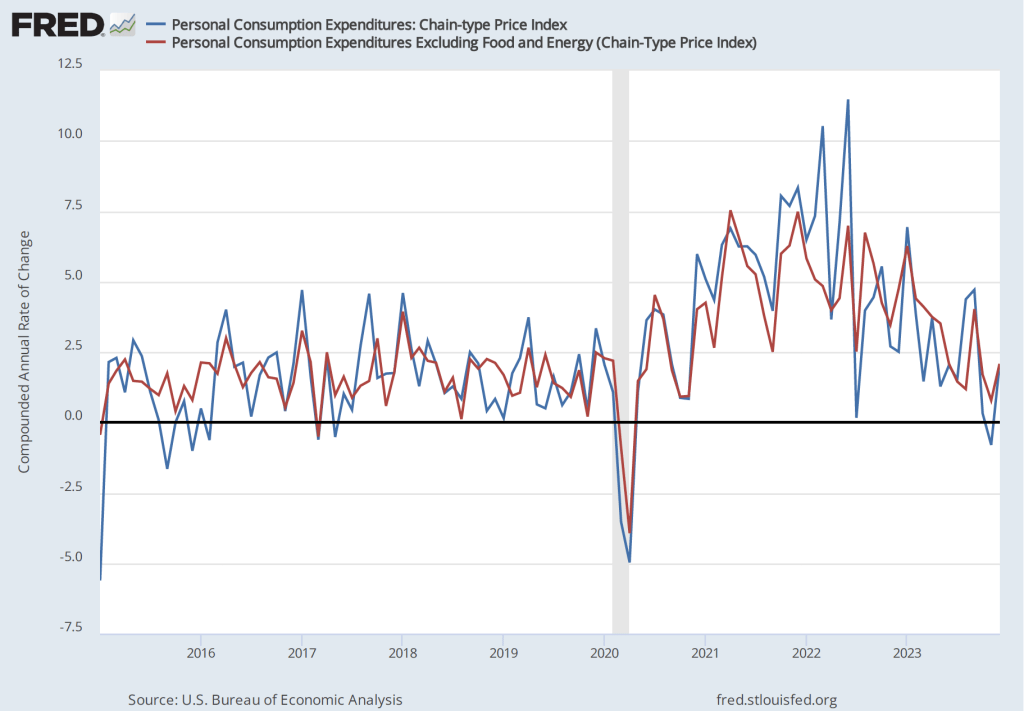
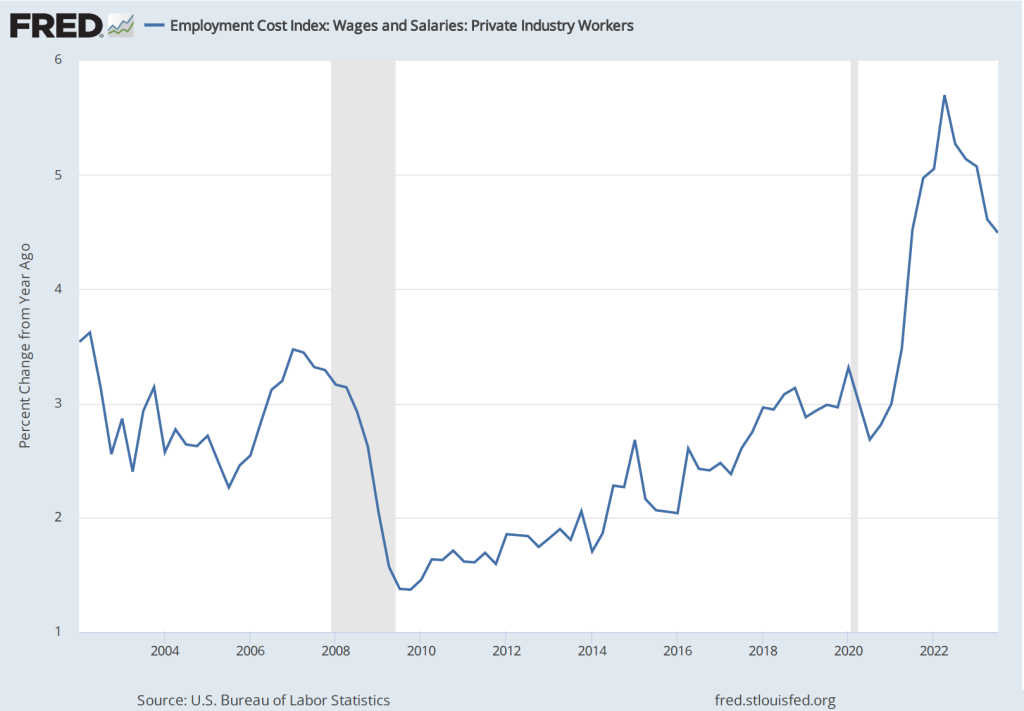
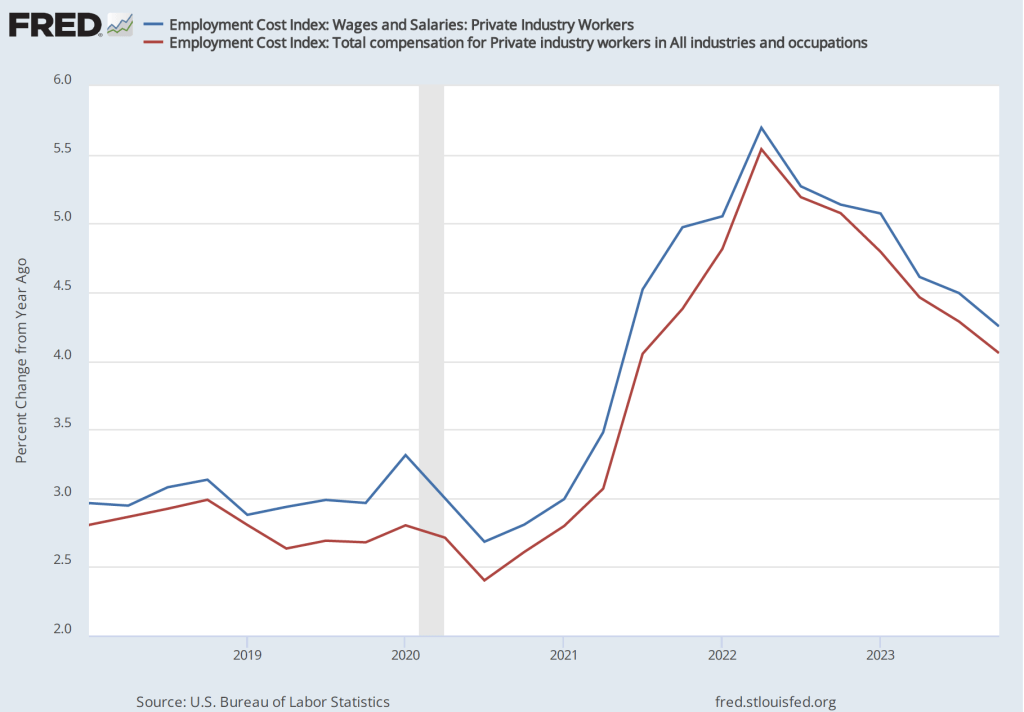
Powell also noted that the most recent data on the employment cost index (ECI) had been released the morning of the meeting. The ECI is compiled by the Bureau of Labor Statistics and is published quarterly. It measures the cost to employers per employee hour worked. The BLS publishes data that includes only wages and salaries and data that includes, in addition to wages and salaries, non-wage benefits—such as contributions to retirement accounts or health insurance—that firms pay workers. The figure below shows the percentage change from the same month in the previous year for the ECI including just wages and salaries (blue line) and for the ECI including all compensation (red line). Although ECI inflation has declined significantly from its peak in he second quarter of 2022, in the fourth quarter of 2023, both measures of ECI inflation were above 4 percent. Wages increasing at that pace may not be consistent with a 2 percent rate of price inflation.
Powell’s tone at his news conference (which can be watched here) was one of cautious optimism. He and the other committee members expect to be able to cut the target for the federal funds rate later this year but remain on guard for any indications that the inflation rate is increasing again.