Photo courtesy of Lena Buonanno.
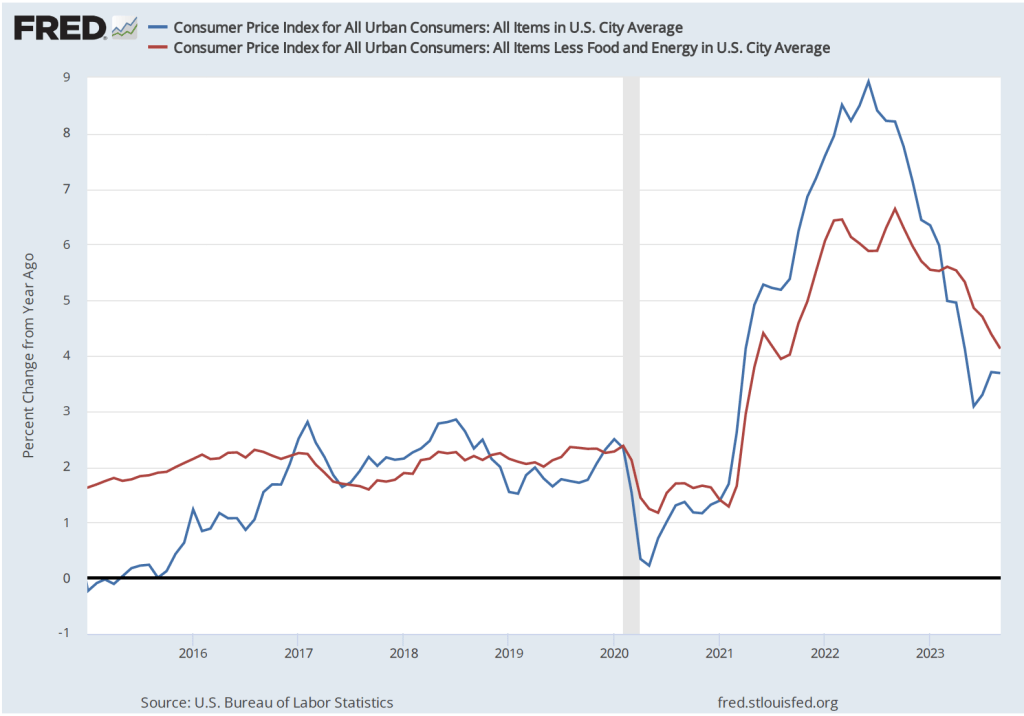
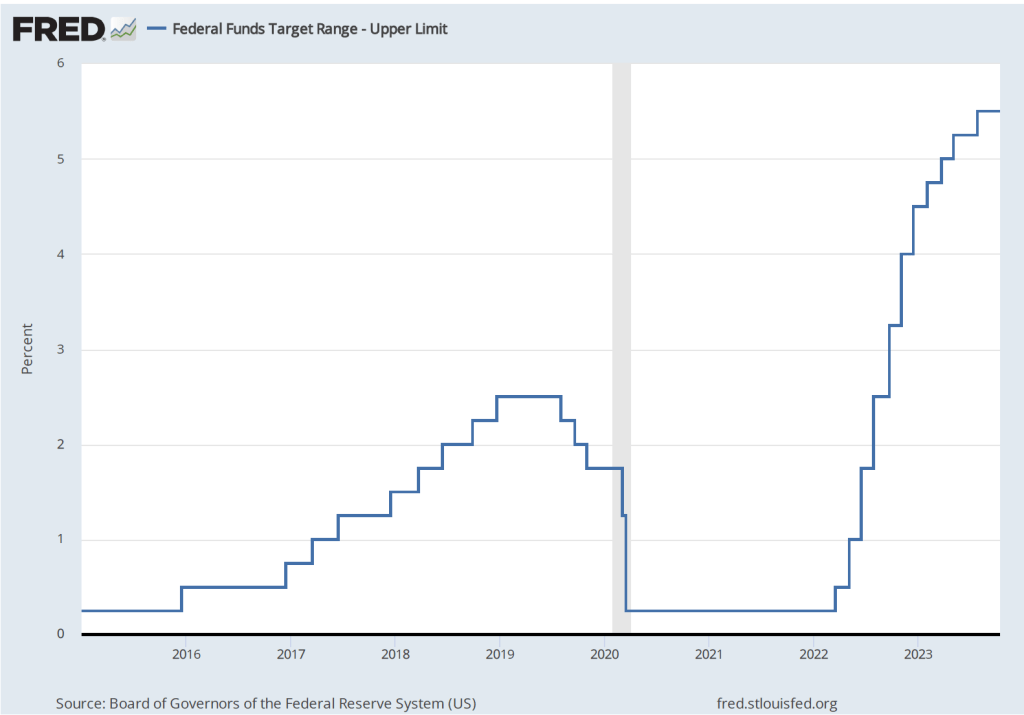
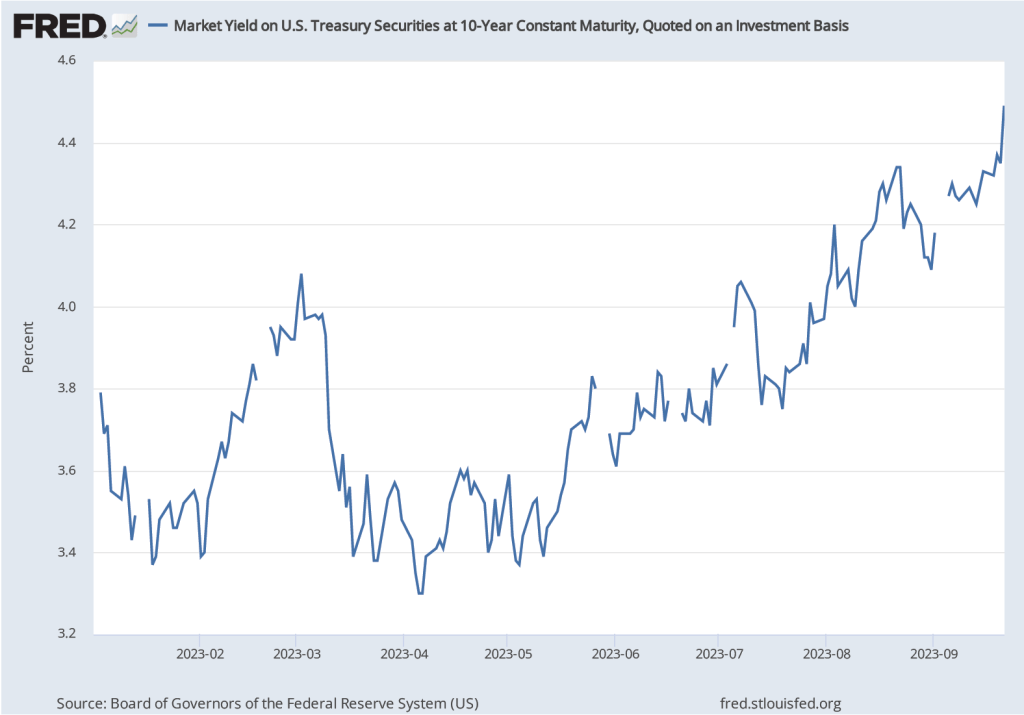
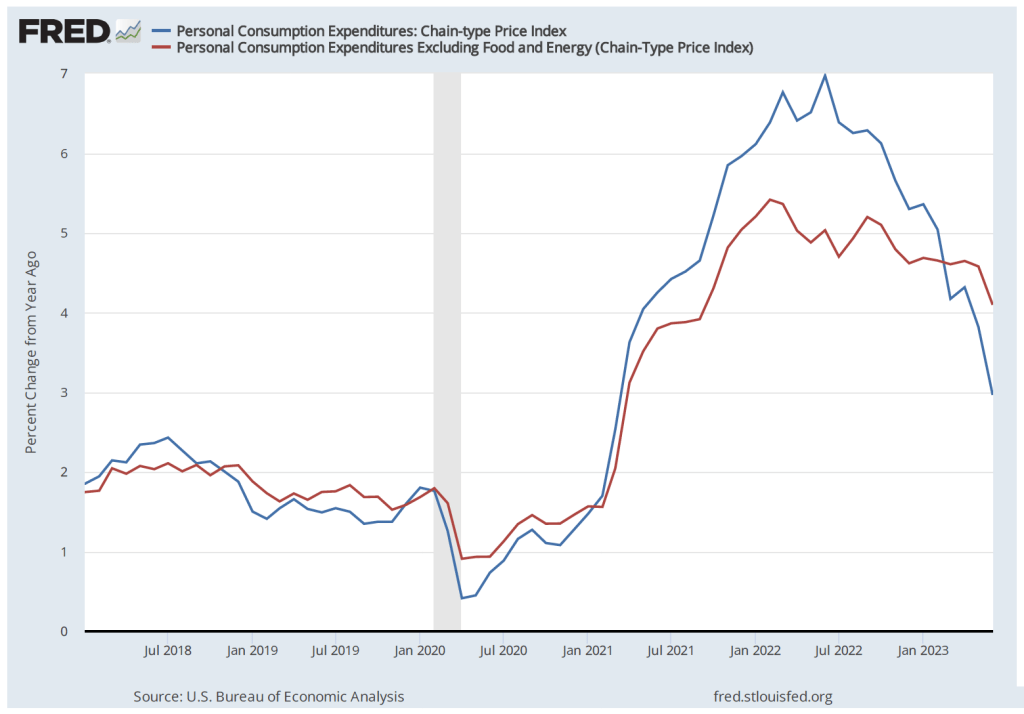
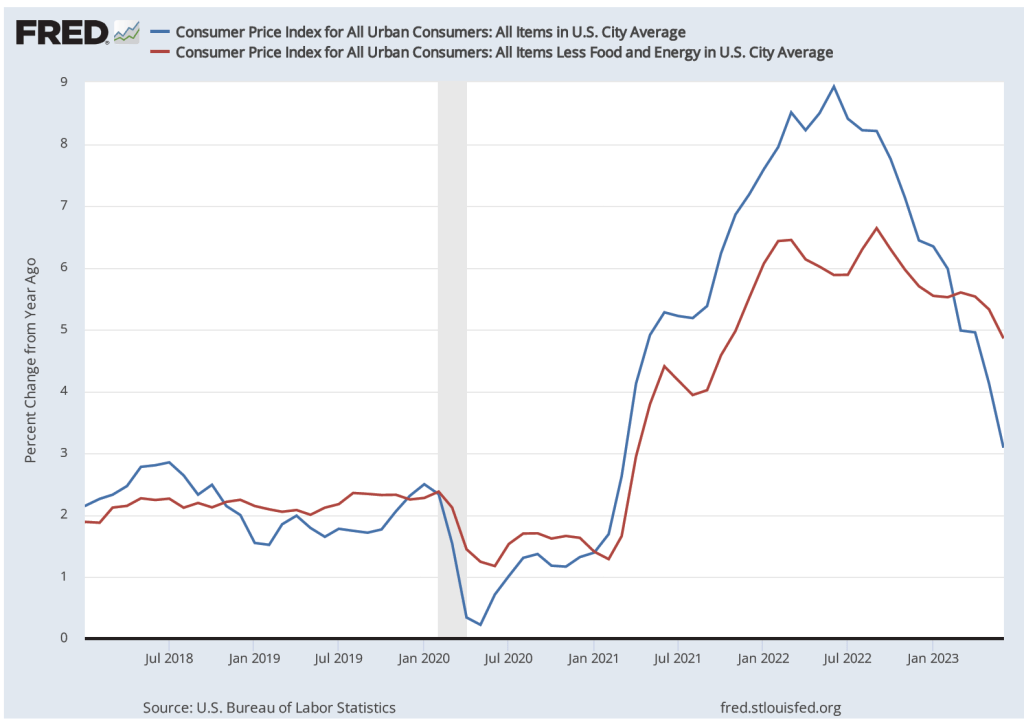
During the last few months of 2023, the macroeconomic data has generally been consistent with the Federal Reserve successfully bringing about a soft landing: Inflation returning to the Fed’s 2 percent target without the economy entering a recession. On the morning of Friday, January 5, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) issued its latest “Employment Situation Report” for December 2023. The report was generally consistent with the economy still being on course for a soft landing, but because both employment growth and wage growth were stronger than expected, the report makes it somewhat less likely that the Federal Reserve’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) will soon begin reducing its target for the federal funds rate. (The full report can be found here.)
Economists and policymakers—notably including the members of the FOMC—typically focus on the change in total nonfarm payroll employment as recorded in the establishment, or payroll, survey. That number gives what is generally considered to be the best gauge of the current state of the labor market.
The report indicated that during December there had been a net increase of 216,000 jobs. This number was well above the expected gain of 160,000 to 170,000 jobs that several surveys of economists had forecast (see here, here, and here). The BLS revised downward by a total of 71,000 jobs its previous estimates for October and November, somewhat offsetting the surprisingly strong estimated increase in net jobs for December.
The following figure from the report shows the net increase in jobs each month since December 2021. Although the net number of jobs created has trended up from September to December, the longer run trend has been toward slower growth in employment. In the first half of 2023, an average of 257,000 net jobs were created per month, whereas in the second half of 2023, an average of 193,000 net jobs were created per month. Average weekly hours worked have also been slowly trending down, from 34.6 hours per week in January to 34.3 hours per week in December.

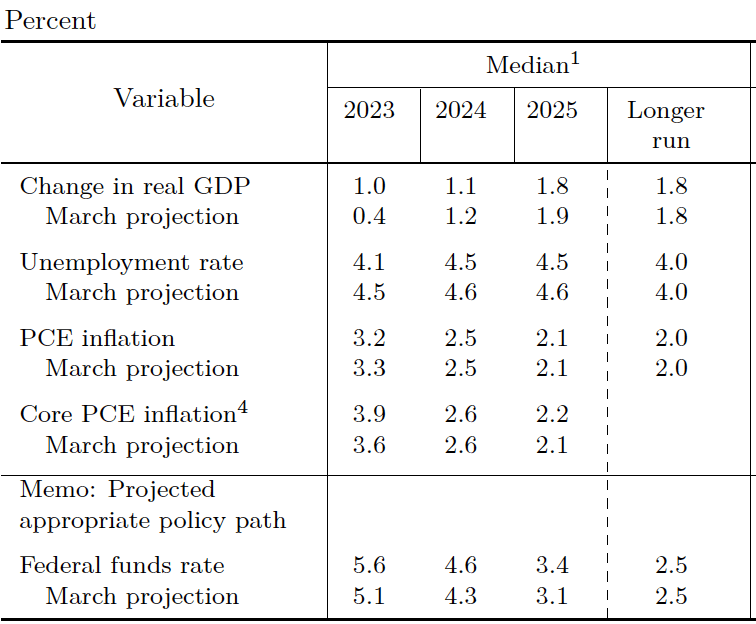
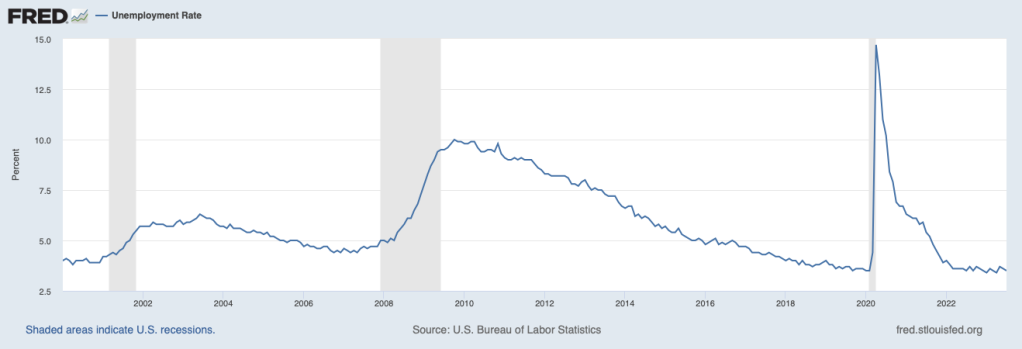
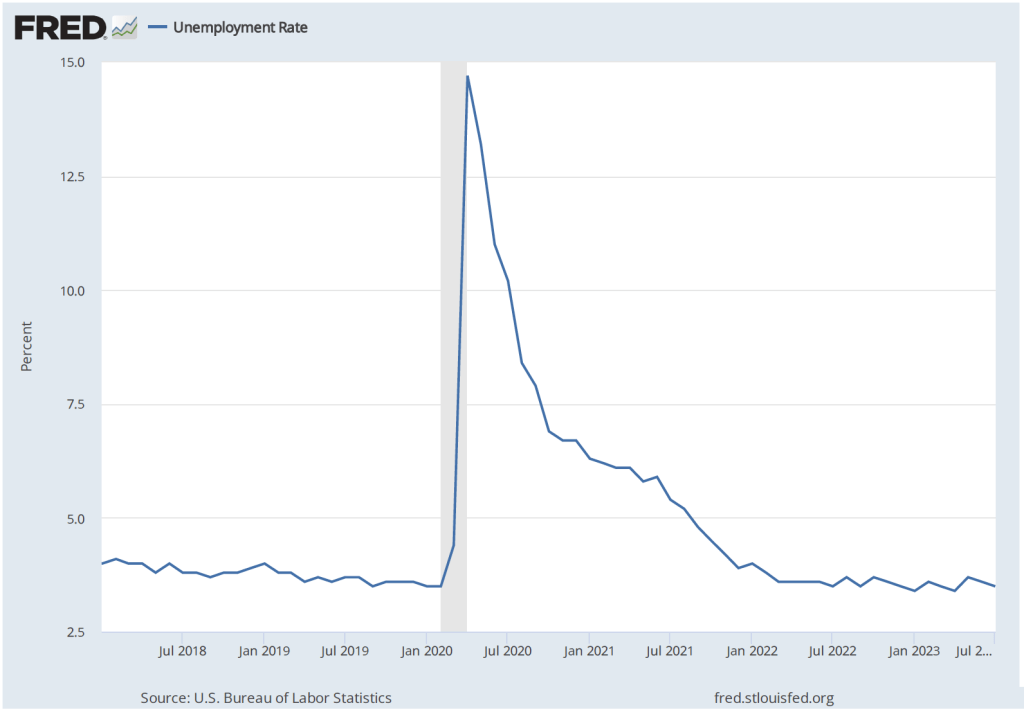
Economists surveyed were also expecting that the unemployment rate—calculated by the BLS from data gathered in the household survey—would increase slightly. Instead, it remained constant at 3.7 percent. As the following figure shows, the unemployment rate has been below 4.0 percent each month since December 2021. The members of the FOMC expect that the unemployment rate during 2024 will be 4.1 percent. (The most recent economic projections of the members of the FOMC can be found here.)

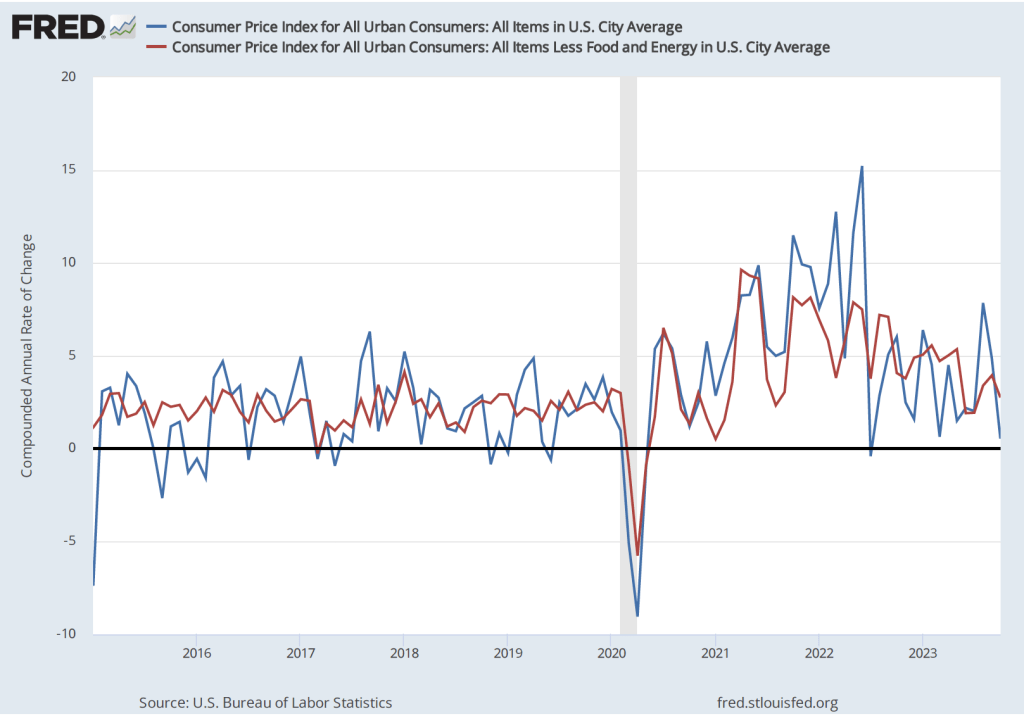
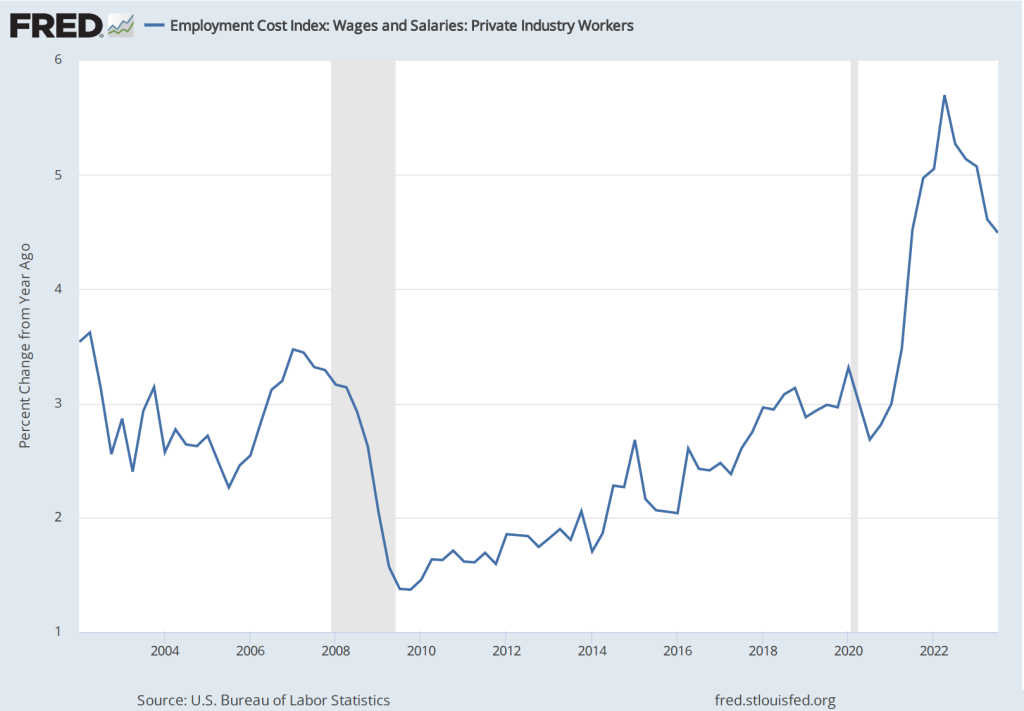
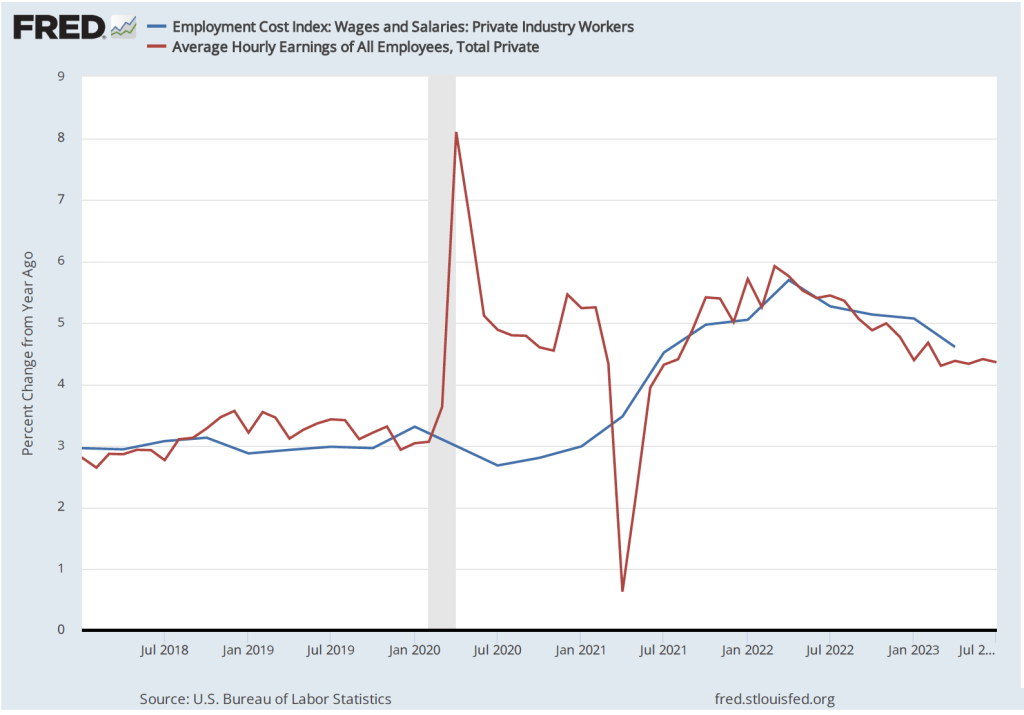
Although the employment data indicate that conditions in the labor market are easing in a way that may be consistent with inflation returning to the Fed’s 2 percent target, the data on wage growth are so far sending a different message. Average hourly earnings—data on which are collected in the establishment survey—increased by 4.1 percent in December compared with the same month in 2022. This rate of increase was slightly higher than the 4.0 percent increase in November. The following figure shows movements in the rate of increase in average hourly earnings since January 2021.
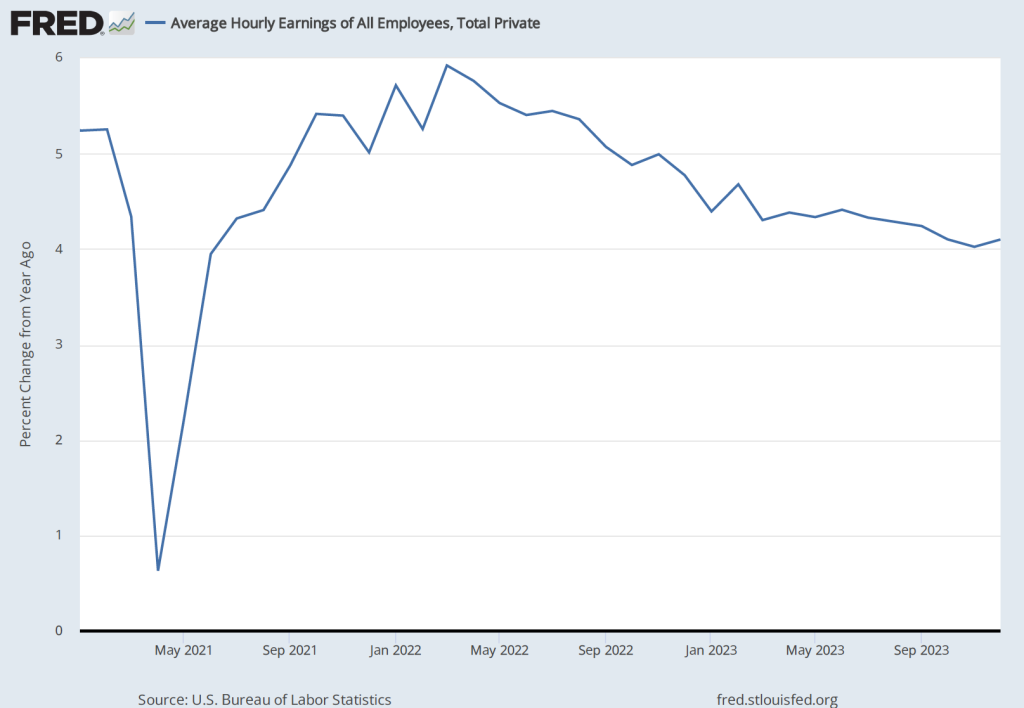
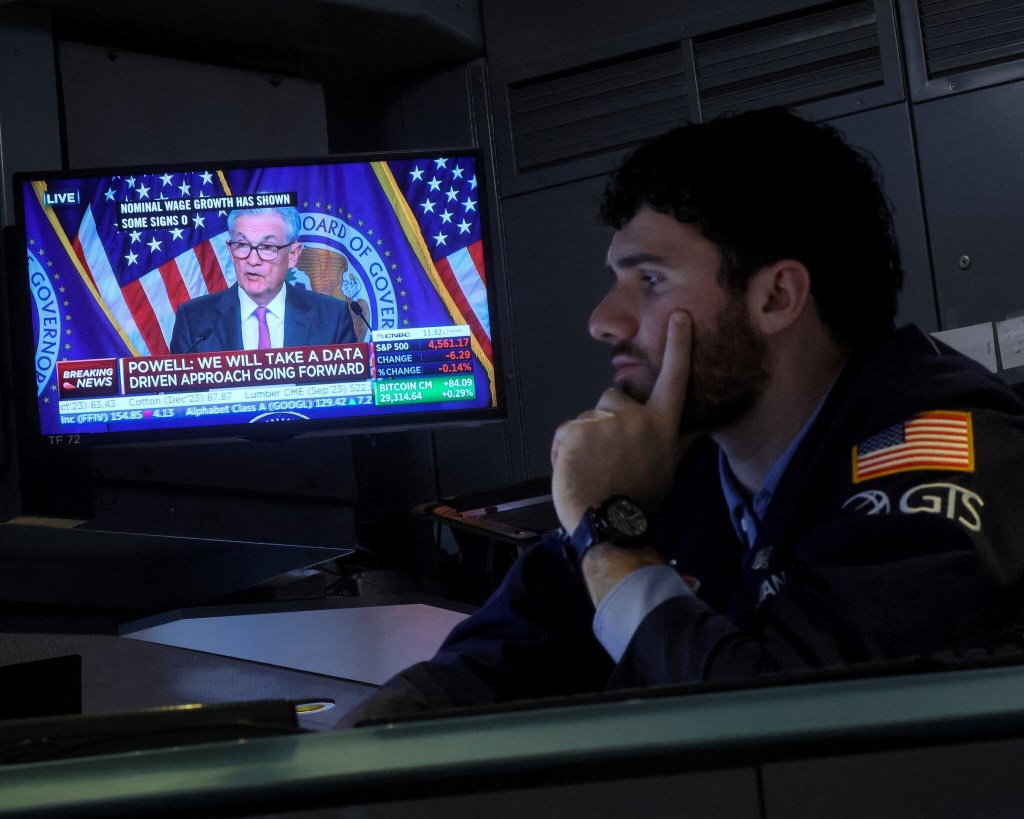
In his press conference following the FOMC’s December 13, 2023 meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell noted that increases in wages at 4 percent or higher were unlikely to result in inflation declining to the Fed’s 2 percent goal:
“So wages are still running a bit above what would be consistent with 2 percent inflation over a long period of time. They’ve been gradually cooling off. But if wages are running around 4 percent, that’s still a bit above, I would say.”
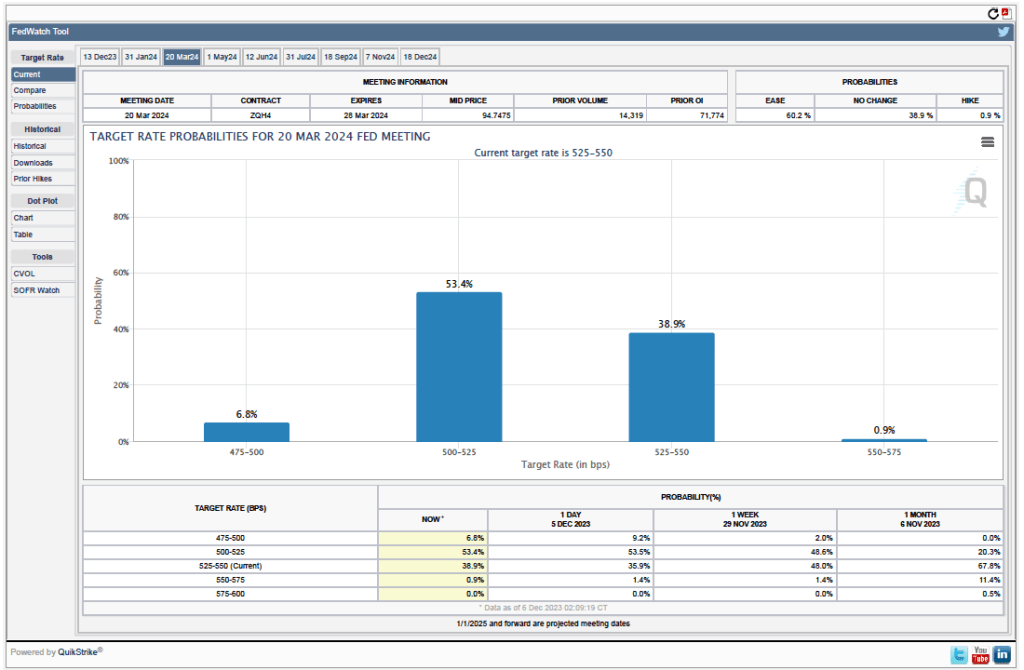
The FOMC’s next meeting is on January 30-31. At this point it seems likely that the committee will maintain its current target for the federal funds. The data in the latest employment report make it somewhat less likely that the committee will begin reducing its target at its meeting on March 19-20, as some economists and some Wall Street analysts had been expecting. (The calendar of the FOMC’s 2024 meetings can be found here.)