Image generated by ChatGPT
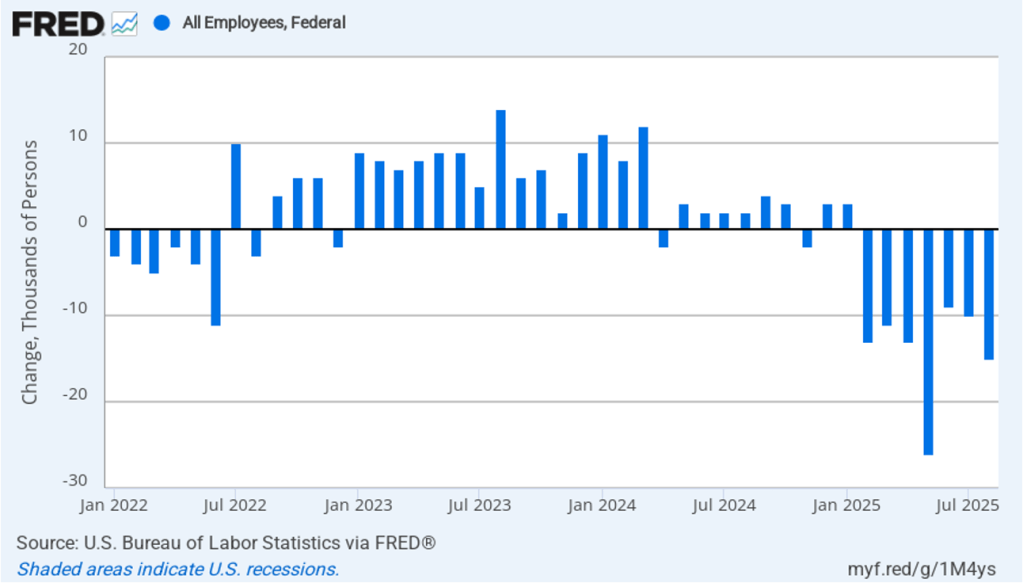
Today (September 26), the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) released monthly data on the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index as part of its “Personal Income and Outlays” report. Yesterday, the BEA released its revised estimate of real GDP growth in the second quarter. Taken together, the two reports show that economic growth remains realtively strong and that inflation continues to run above the Fed’s 2 percent annual target.
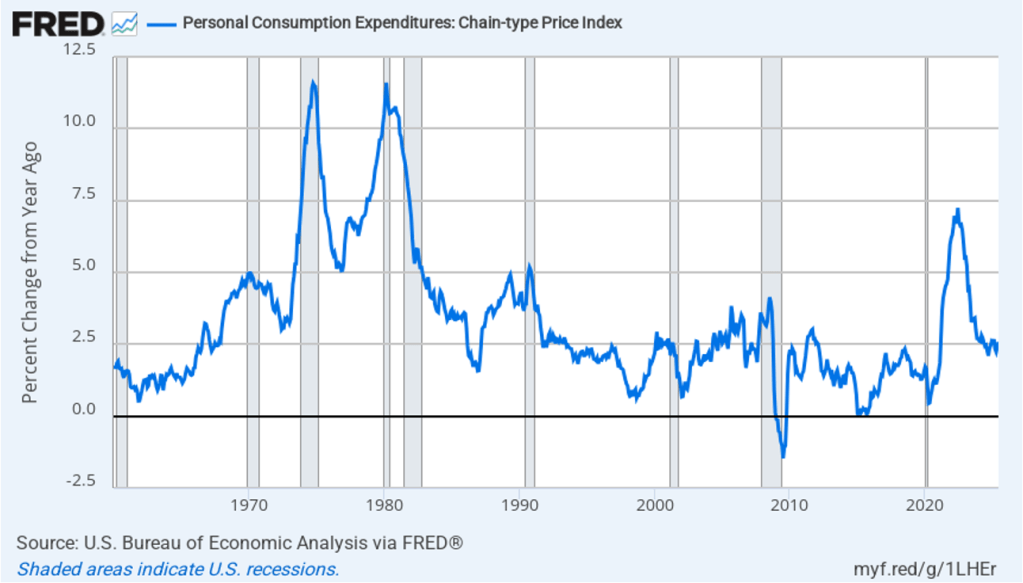
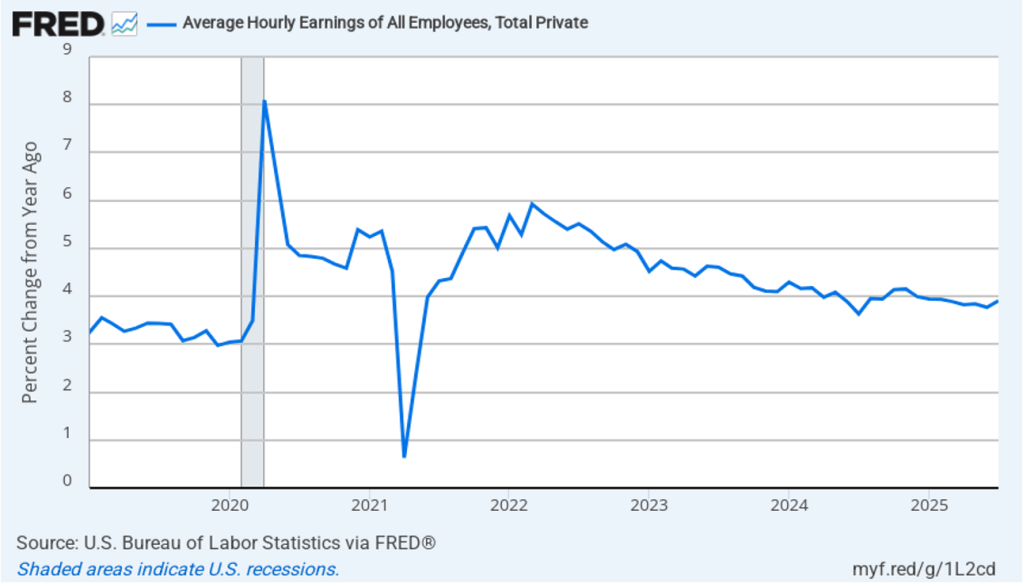
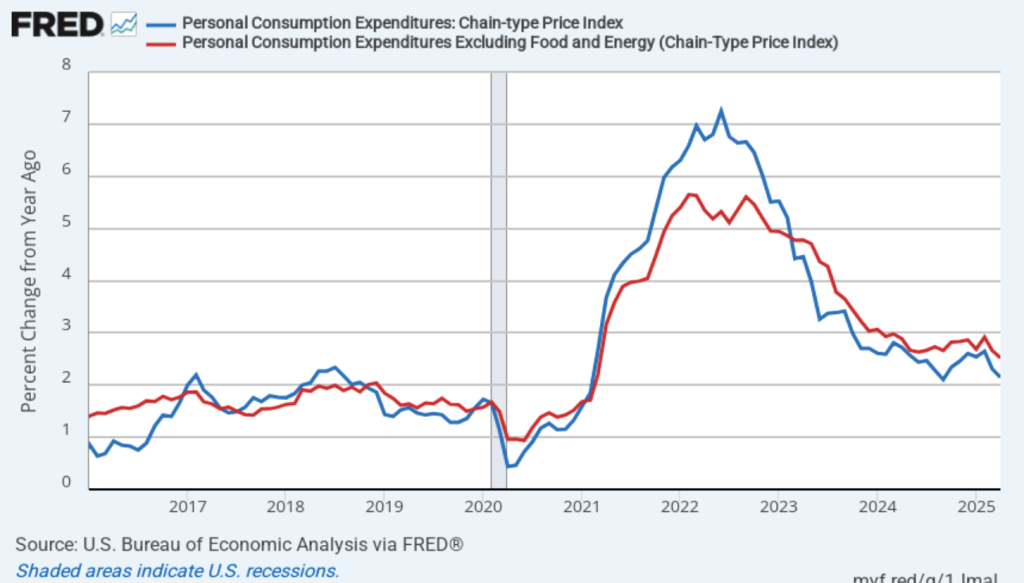
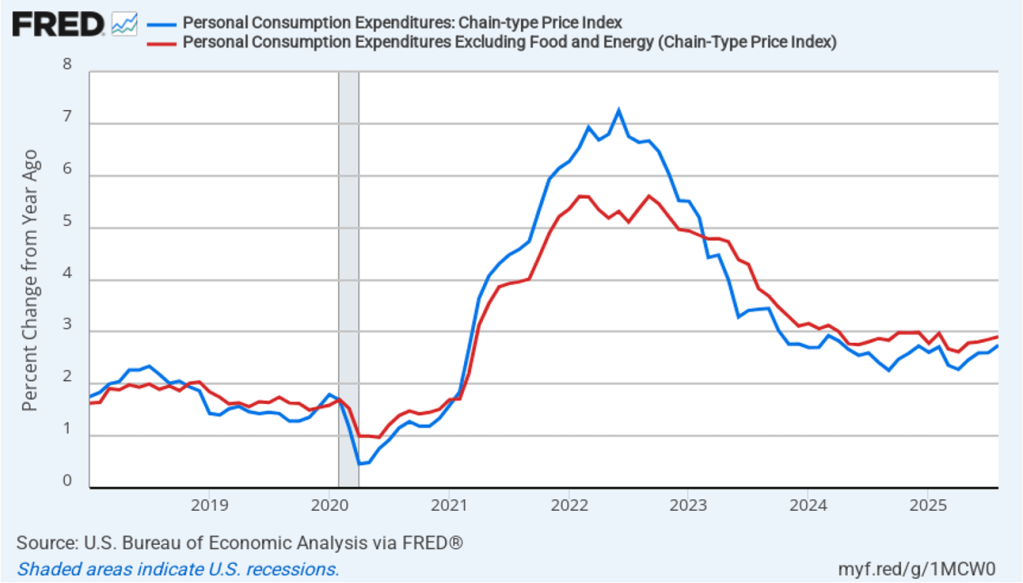
Taking the inflation report first, the following figure shows headline PCE inflation (the blue line) and core PCE inflation (the red line)—which excludes energy and food prices—for the period since January 2018, with inflation measured as the percentage change in the PCE from the same month in the previous year. In August, headline PCE inflation was 2.7 percent, up from 2.6 percent in July. Core PCE inflation in August was 2.9 percent, unchanged from July. Headline PCE inflation was equal to the forecast of economists surveyed, while core PCE inflation was slightly lower than forecast.
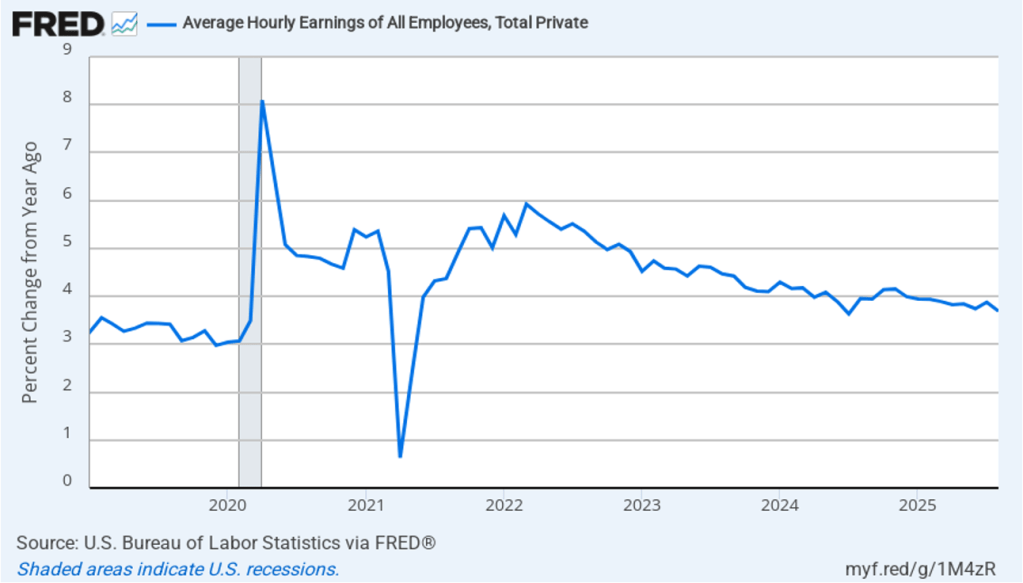
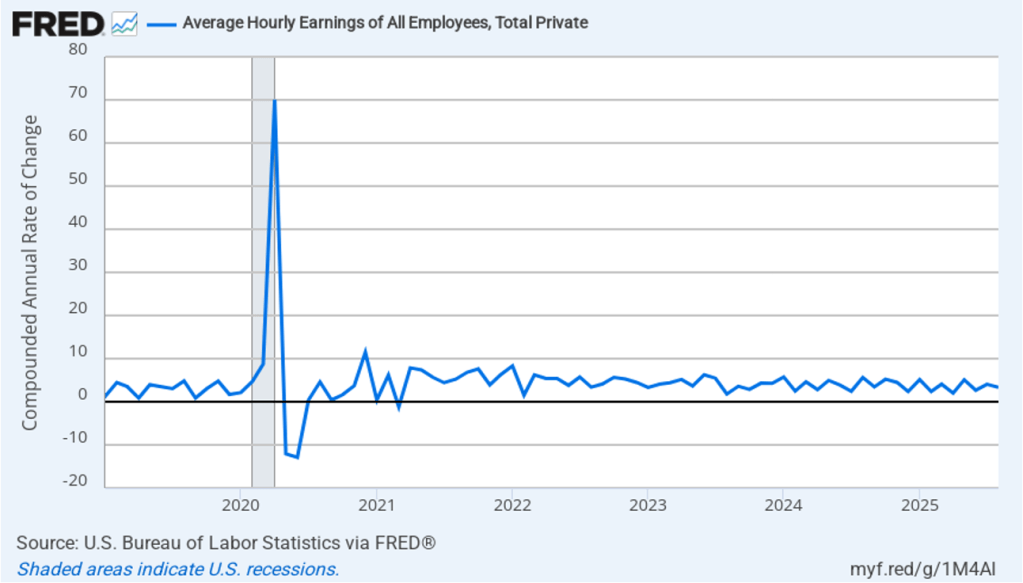
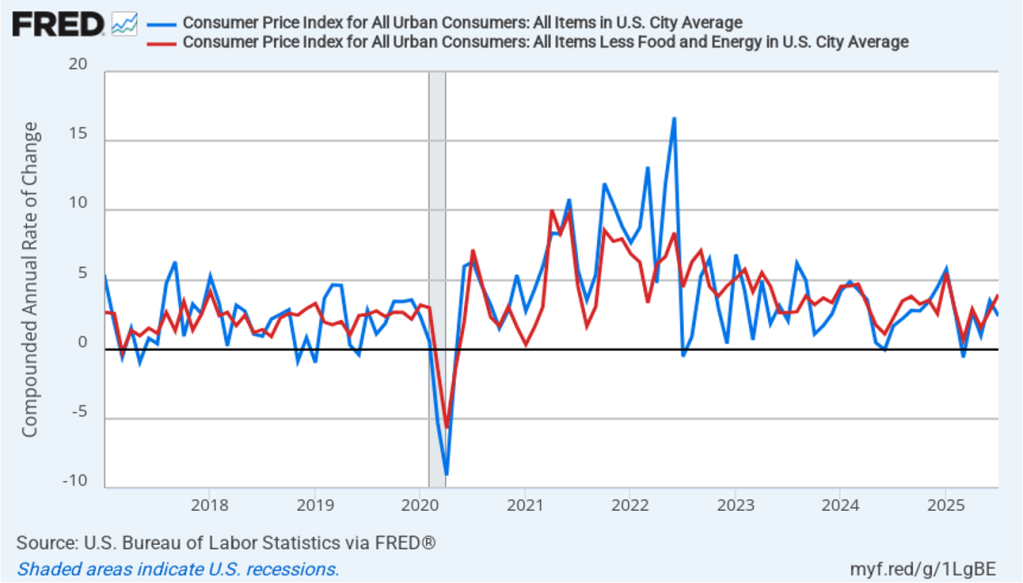
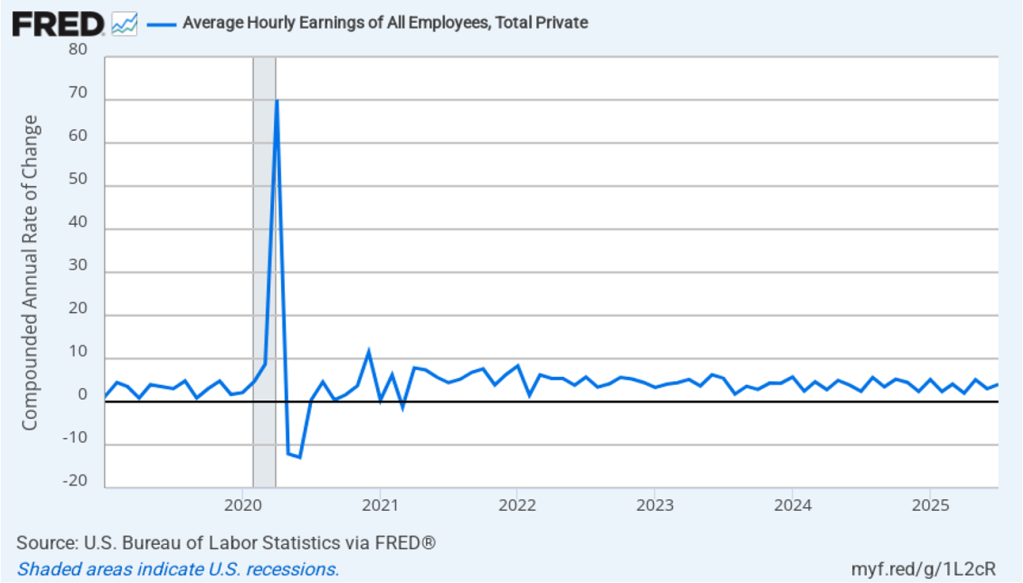
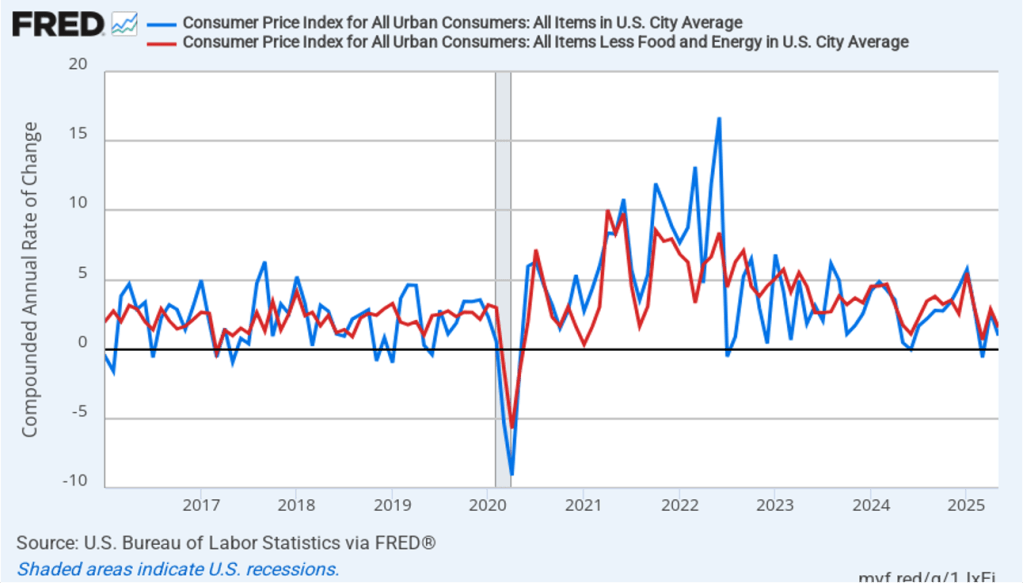
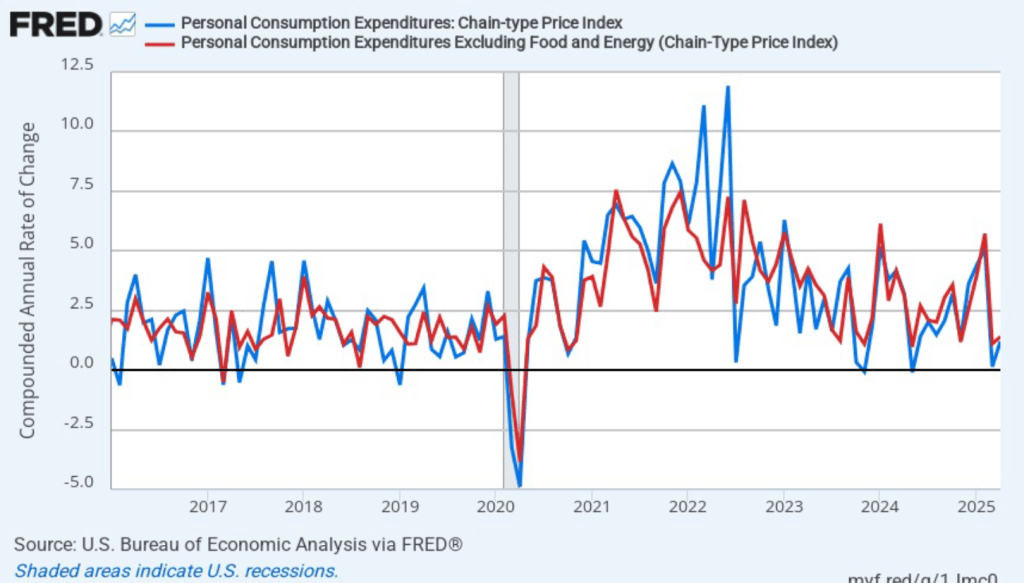
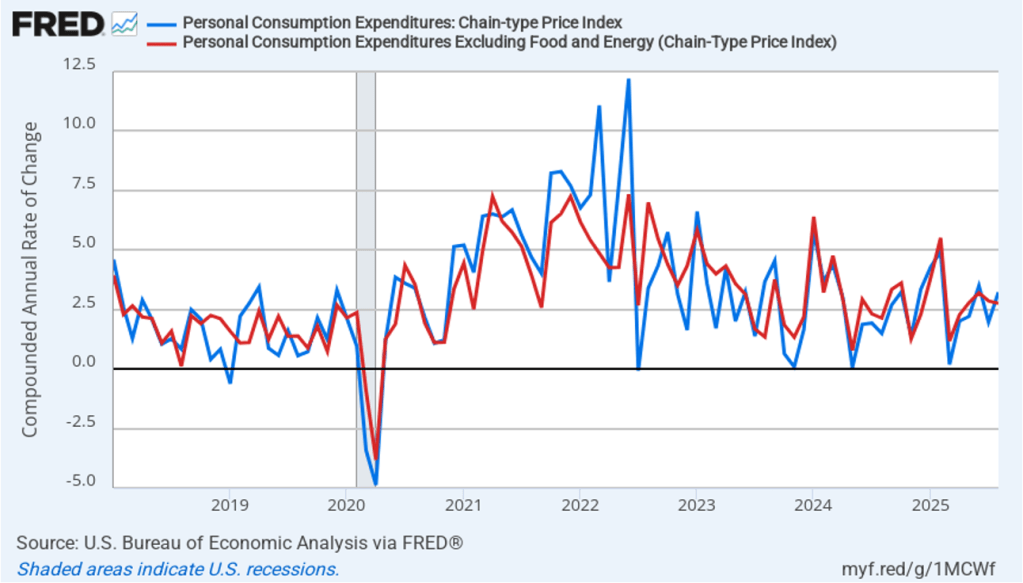
The following figure shows headline PCE inflation and core PCE inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month inflation, while this figure shows 1-month inflation.) Measured this way, headline PCE inflation increased from 2.0 percent in July to 3.2 percent in August. Core PCE inflation declined slightly from 2.9 percent in July to 2.8 percent in August. So, both 1-month and 12-month PCE inflation are telling the same story of inflation being well above the Fed’s target. The usual caution applies that 1-month inflation figures are volatile (as can be seen in the figure). In addition, these data likely reflect higher prices resulting from the tariff increases the Trump administration has implemented. Once the one-time price increases from tariffs have worked through the economy, inflation may decline. It’s not clear, however, how long that may take and President Trump indicated yesterday that he may impose new tariffs on pharmaceuticals, large trucks, and furniture.
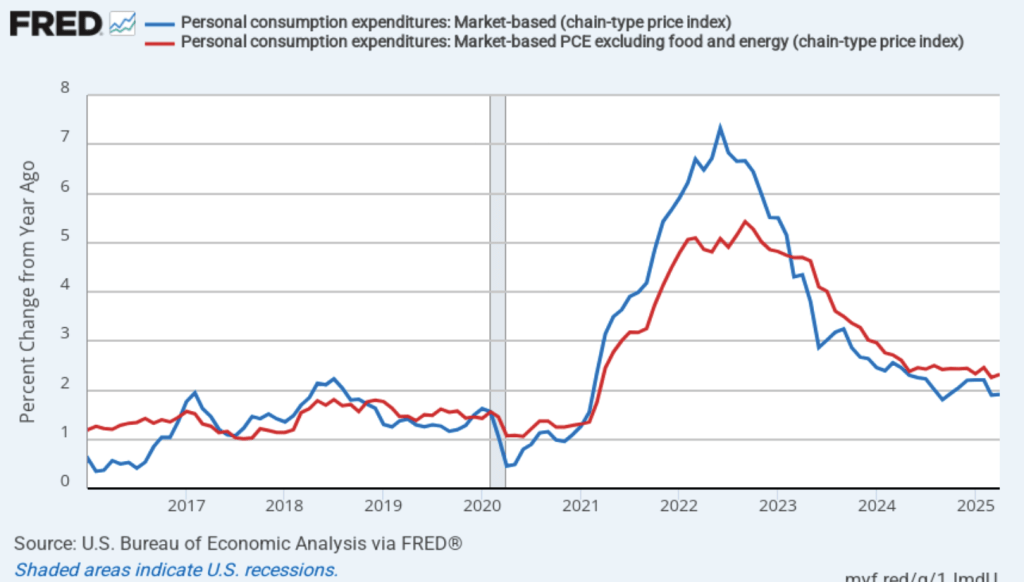
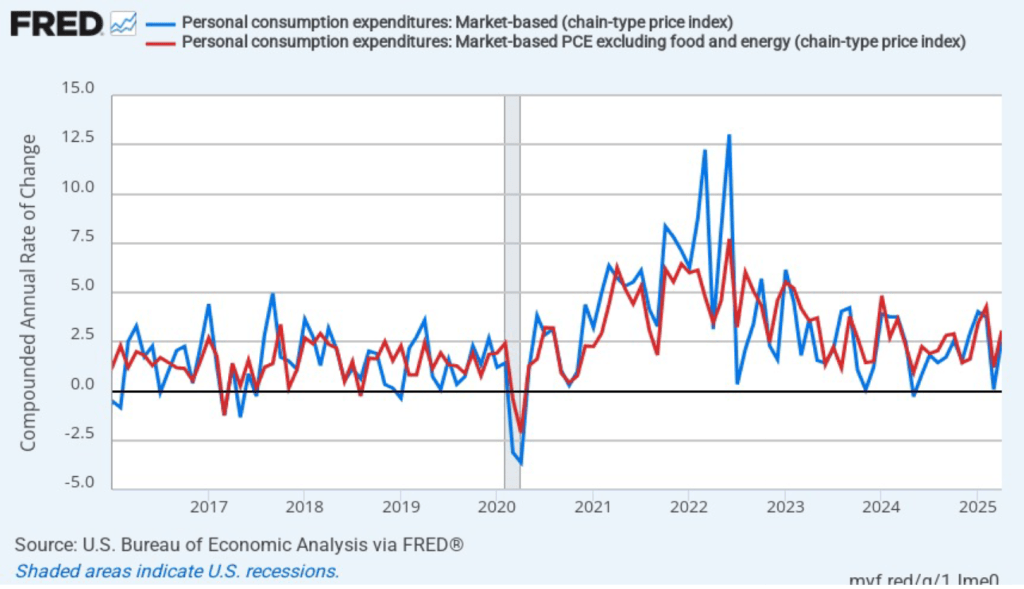
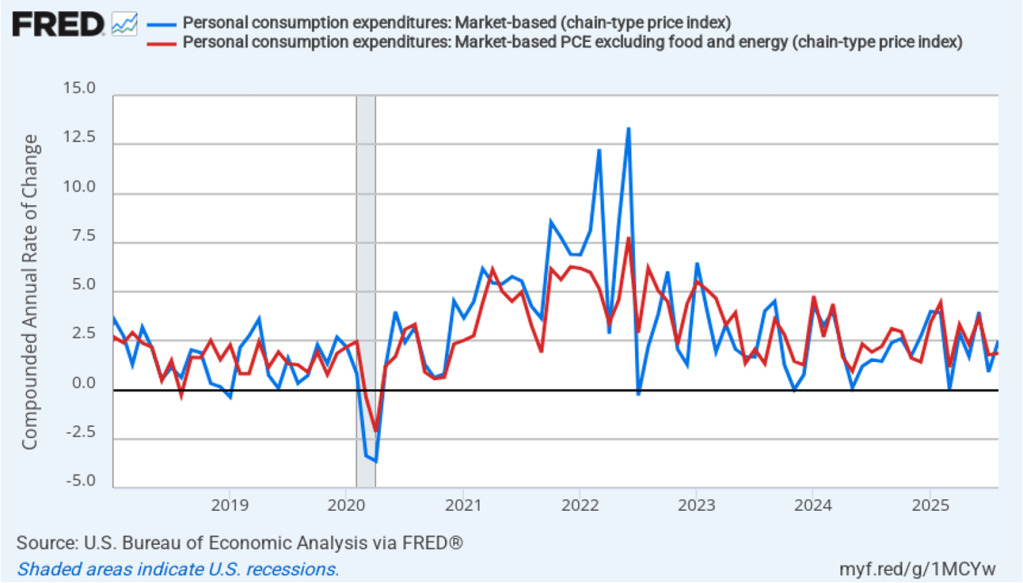
Fed Chair Jerome Powell has frequently mentioned that inflation in non-market services can skew PCE inflation. Non-market services are services whose prices the BEA imputes rather than measures directly. For instance, the BEA assumes that prices of financial services—such as brokerage fees—vary with the prices of financial assets. So that if stock prices fall, the prices of financial services included in the PCE price index also fall. Powell has argued that these imputed prices “don’t really tell us much about … tightness in the economy. They don’t really reflect that.” The following figure shows 12-month headline inflation (the blue line) and 12-month core inflation (the red line) for market-based PCE. (The BEA explains the market-based PCE measure here.)
Headline market-based PCE inflation was 2.4 percent in August, unchanged from July. Core market-based PCE inflation was 2.6 percent in August, also unchanged from July. So, both market-based measures show inflation as stable but above the Fed’s 2 percent target.
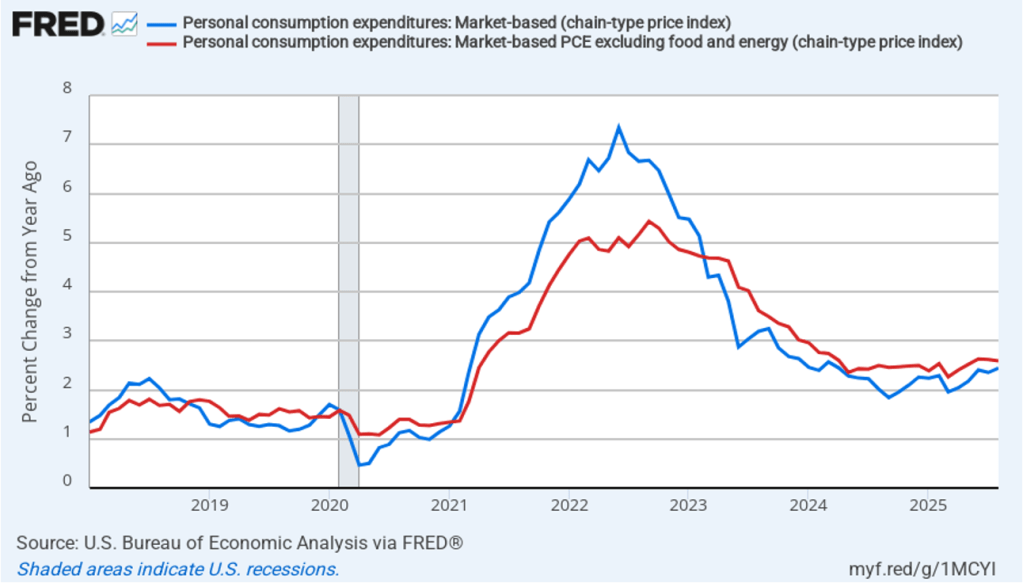
In the following figure, we look at 1-month inflation using these measures. One-month headline market-based inflation increase sharply to 2.5 percent in August from 0.9 percent in July. One-month core market-based inflation increased slightly to 1.9 percent in August from 1.8 percent in July. As the figure shows, the 1-month inflation rates are more volatile than the 12-month rates, which is why the Fed relies on the 12-month rates when gauging how close it is coming to hitting its target inflation rate.
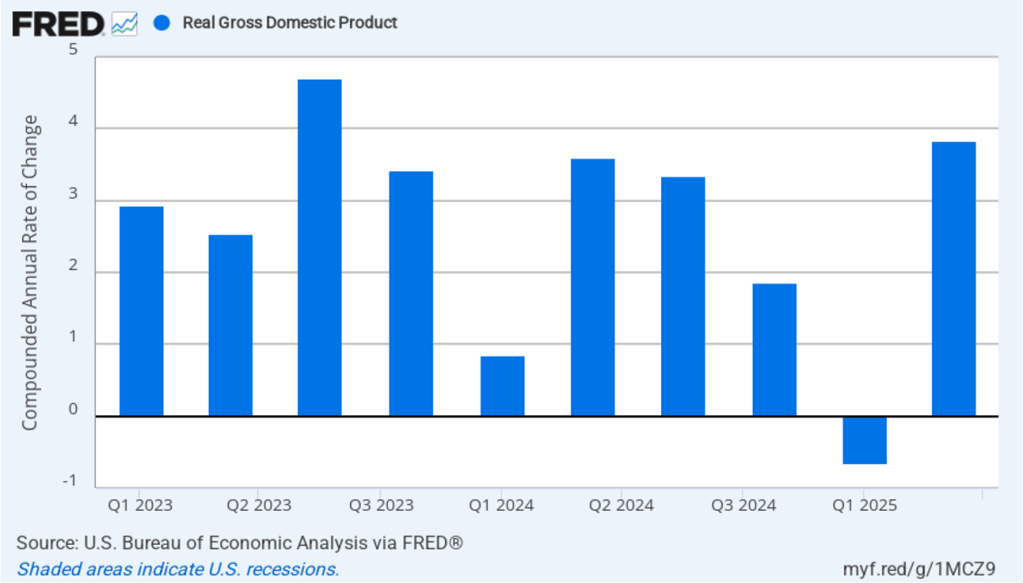
Inflation running above the Fed’s 2 percent target is consistent with relatively strong growth in real GDP. The following figure shows compound annual rates of growth of real GDP, for each quarter since the first quarter of 2023. The value for the second quarter of 2025 is the BEA’s third estimate. This revised estimate increased the growth rate of real GDP to 3.8 percent from the second estimate of 3.3 percent.
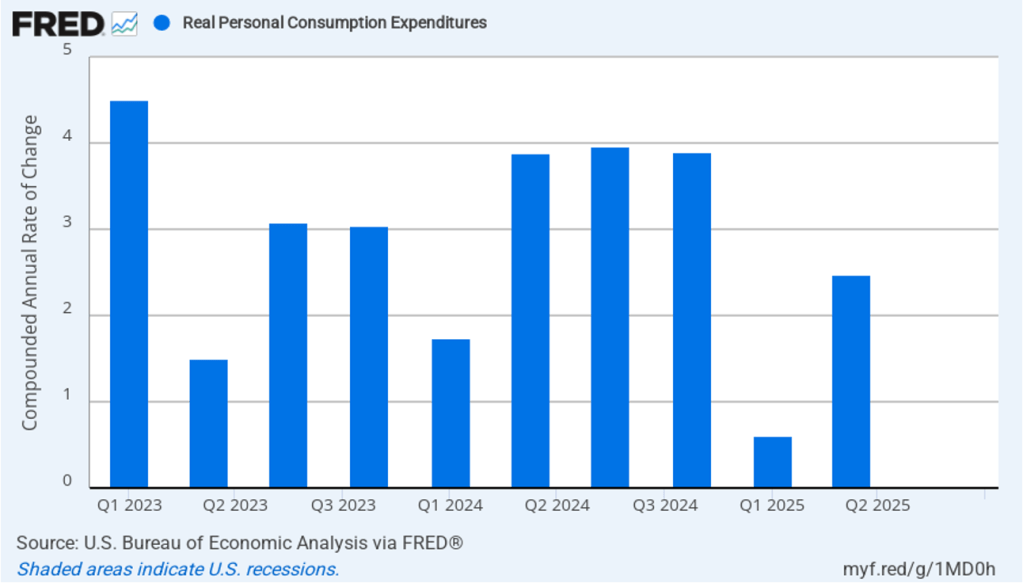
The most important contributor to real GDP growth was growth in real personal consumption expenditures, which, as shown in the following figure, increased aat compound annual rate of 2.5 percent in the second quarter, up from 0.6 percent in the first quarter.
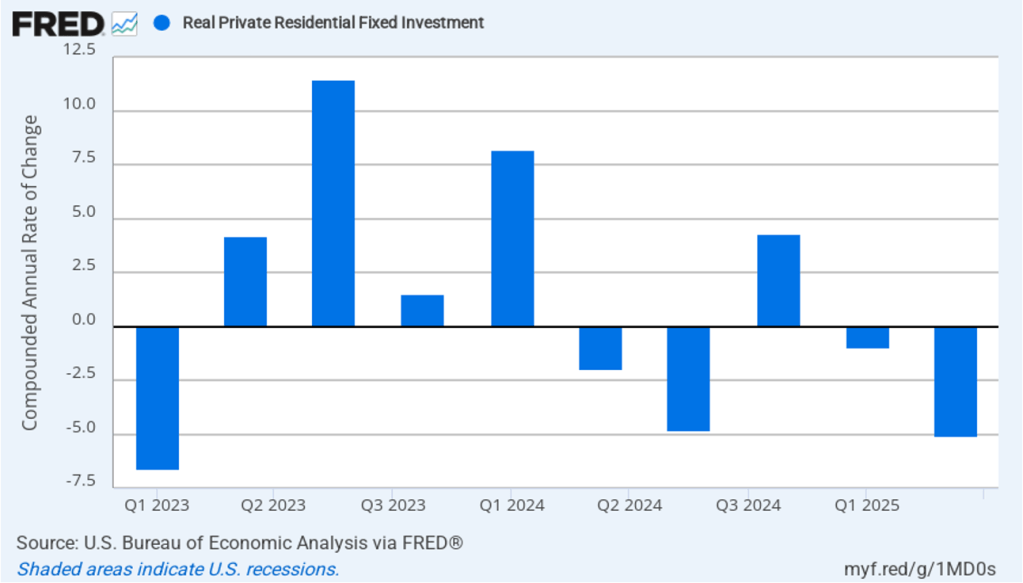
High interest rates continue to hold back residential construction, which declined by a compound annual rate of 5.1 percent in the second quarter after declining 1.0 percent in the first quarter.
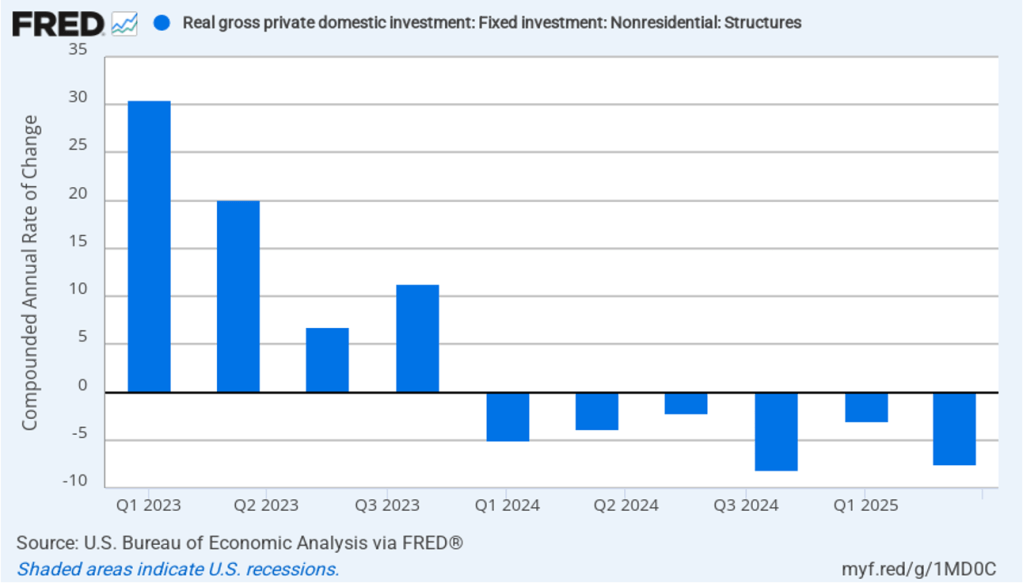
Business investment in structures, such as factories and office buildings, continued a decline that began in the first quarter of 2024.
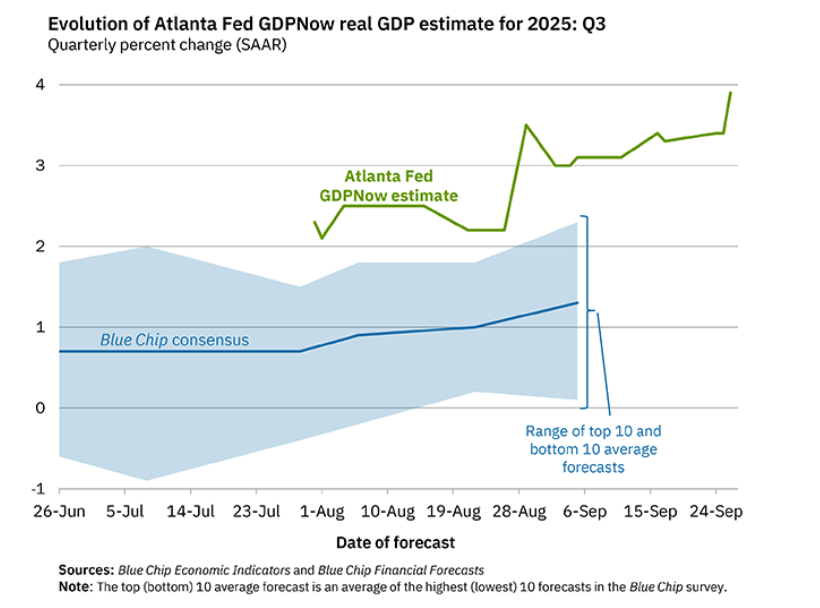
Will the relatively strong growth in real GDP in the second quarter continue in the third quarter? Economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta prepare nowcasts of real GDP. A nowcast is a forecast that incorporates all the information available on a certain date about the components of spending that are included in GDP. The Atlanta Fed calls its nowcast GDPNow. As the following figure from the Atlanta Fed website shows, today the GDPNow forecast is for real GDP to grow at an annual rate of 3.9 percent in the third quarter.
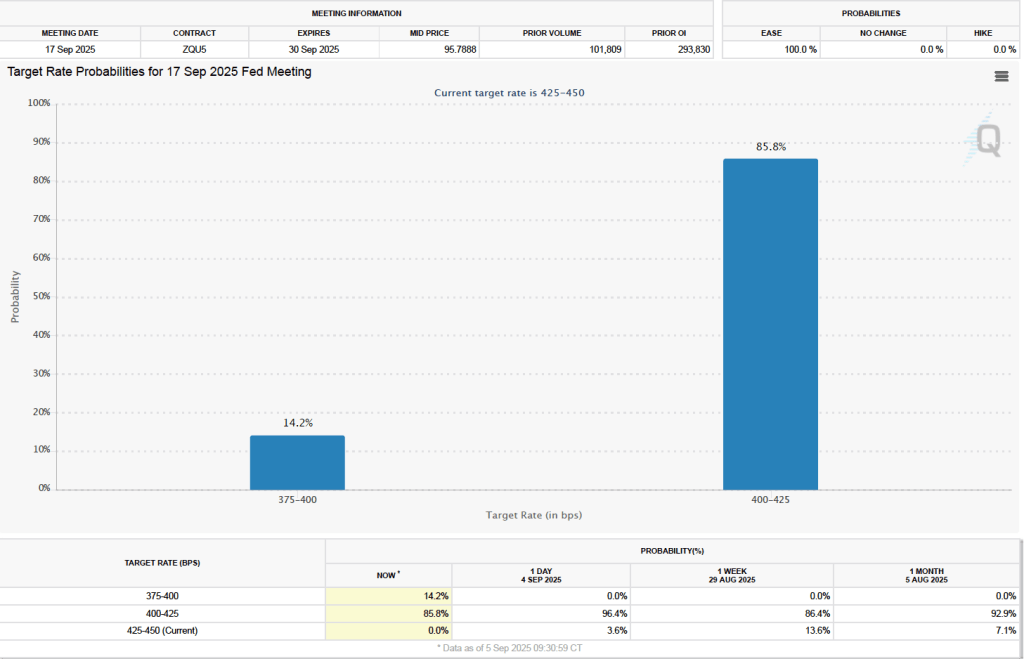
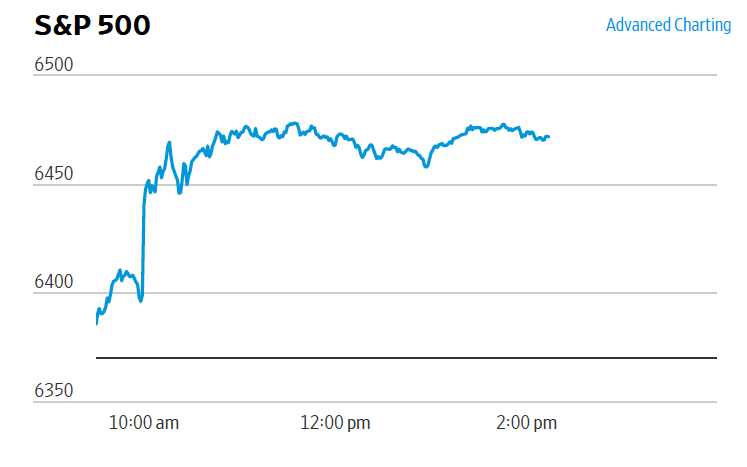
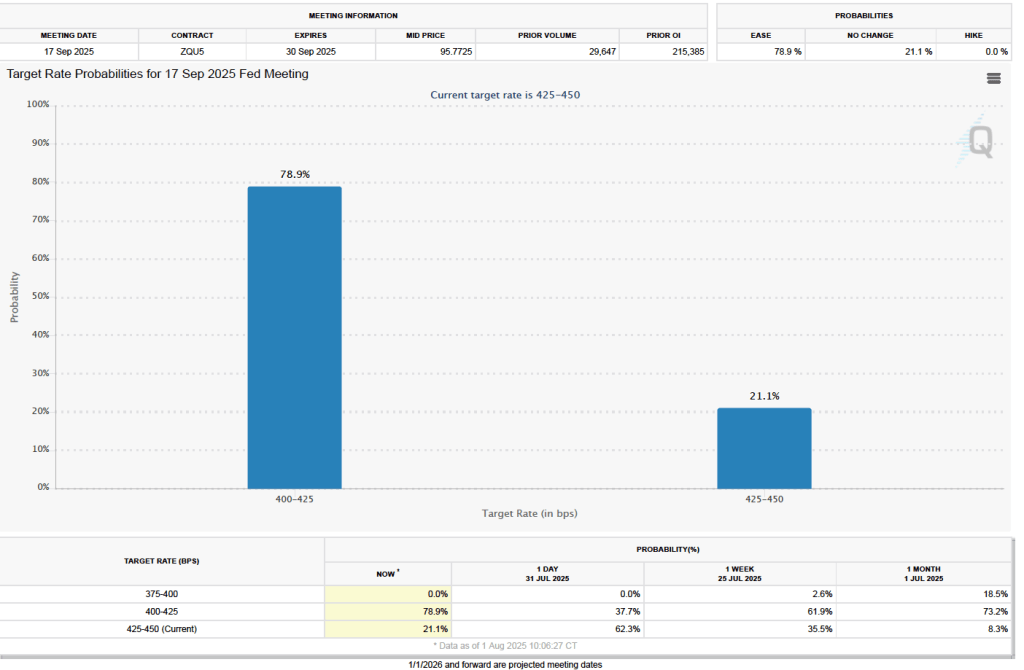
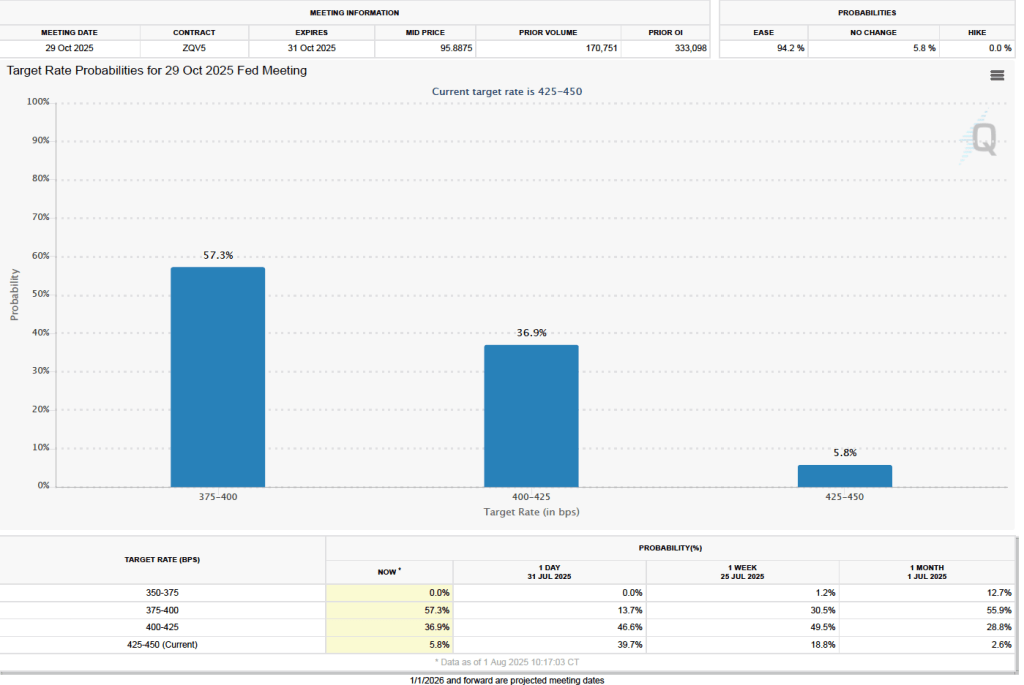
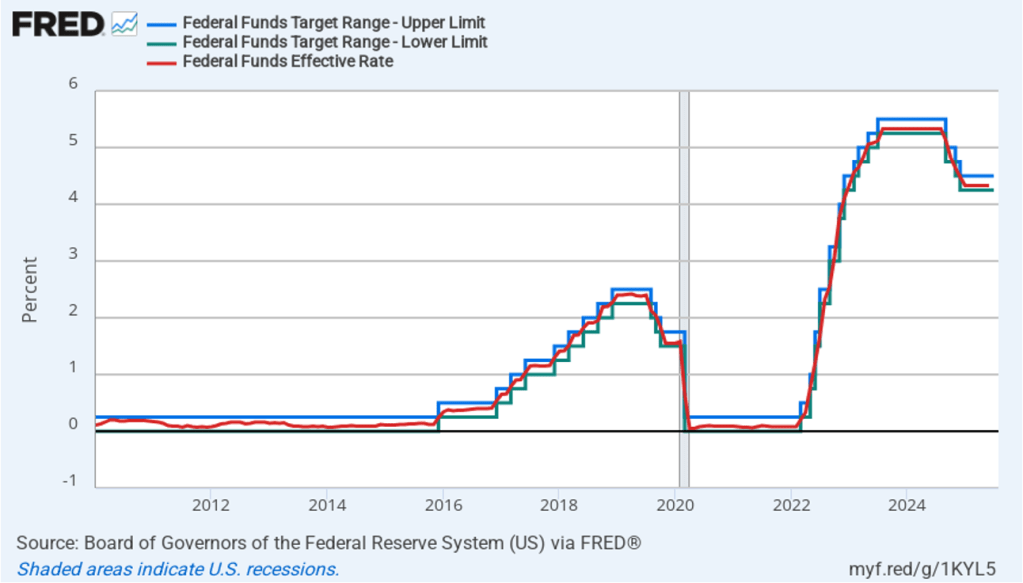
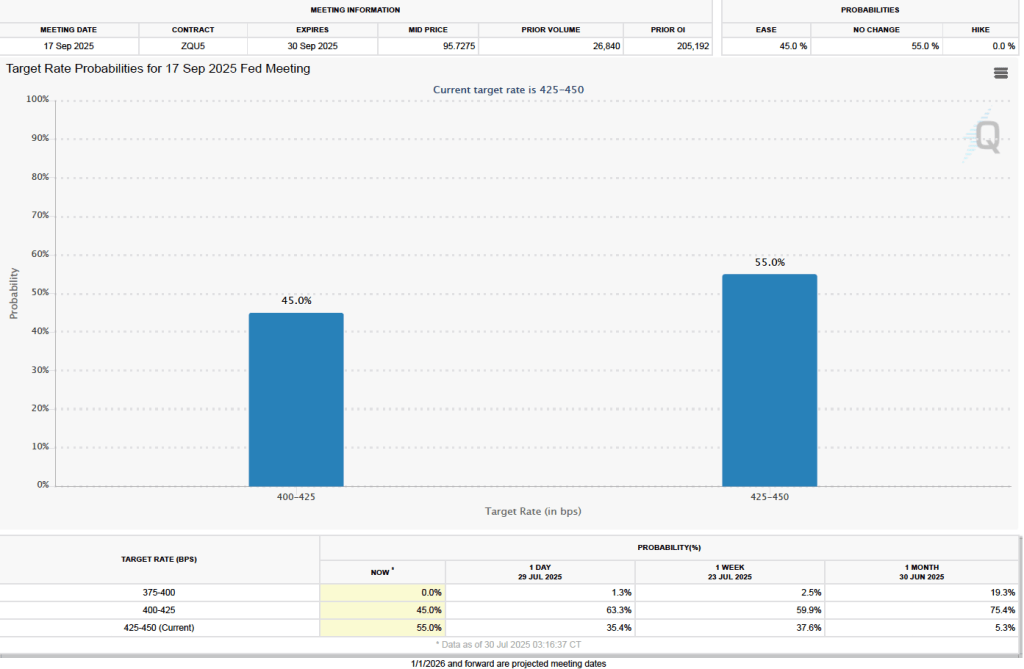
Finally, the macroeconomic data released in the last two days has had realtively little effect on the expectations of investors trading federal funds rate futures. Investors assign an 89.8 percent probability to the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) cutting its target for the federal funds rate at its meeting on October 28–29 by 0.25 percentage point (25 basis points) from its current range of 4.00 percent to 4.25 percent. That probability is only slightly lower than 91.9 percent probaiblity that investors had assigned to a 25 basis point cut a week ago. However, the probability of the committee cutting its target rate by another 25 basis points at its December 9–10 fell to 67.0 percent today from 78.6 percent one week ago.