Photo courtesy of Lena Buonanno
Today (August 14), the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its monthly report on the consumer price index (CPI), which showed inflation falling below 3 percent for the first time since March 2021.
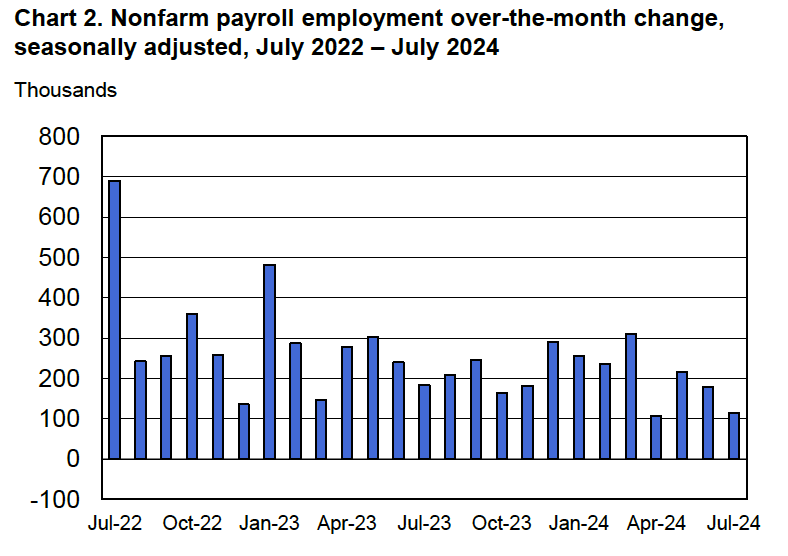
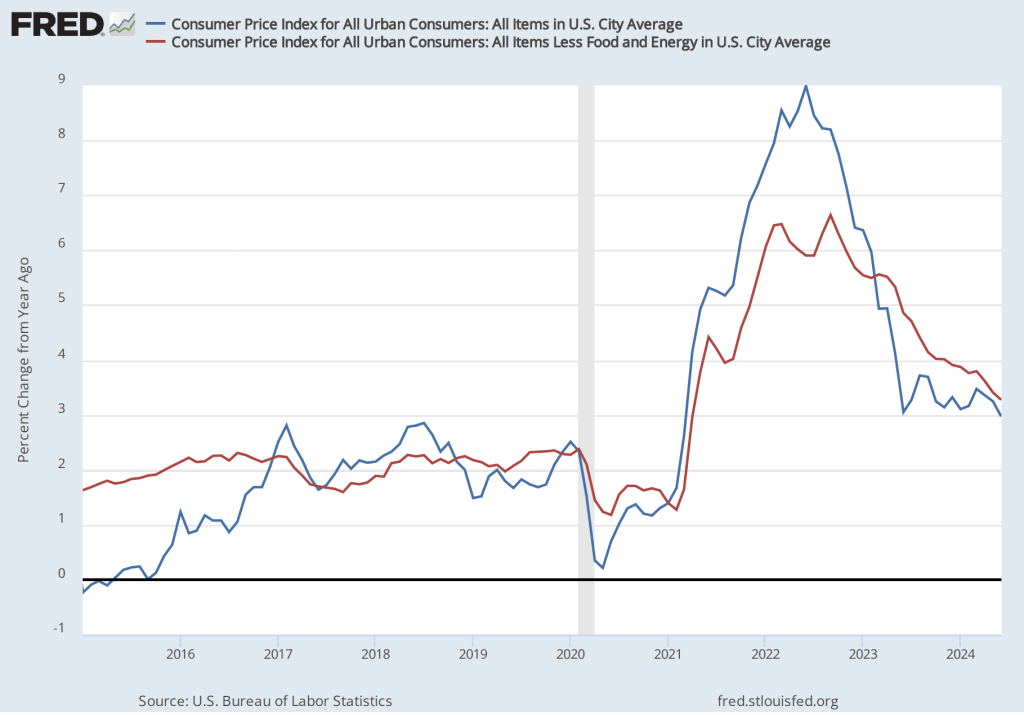
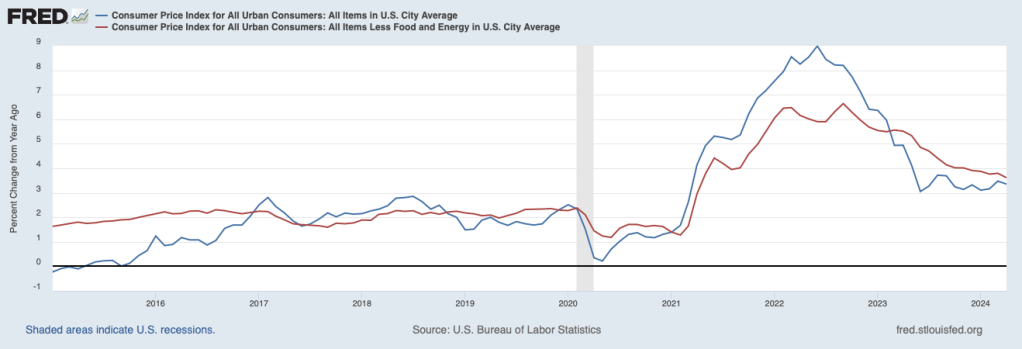
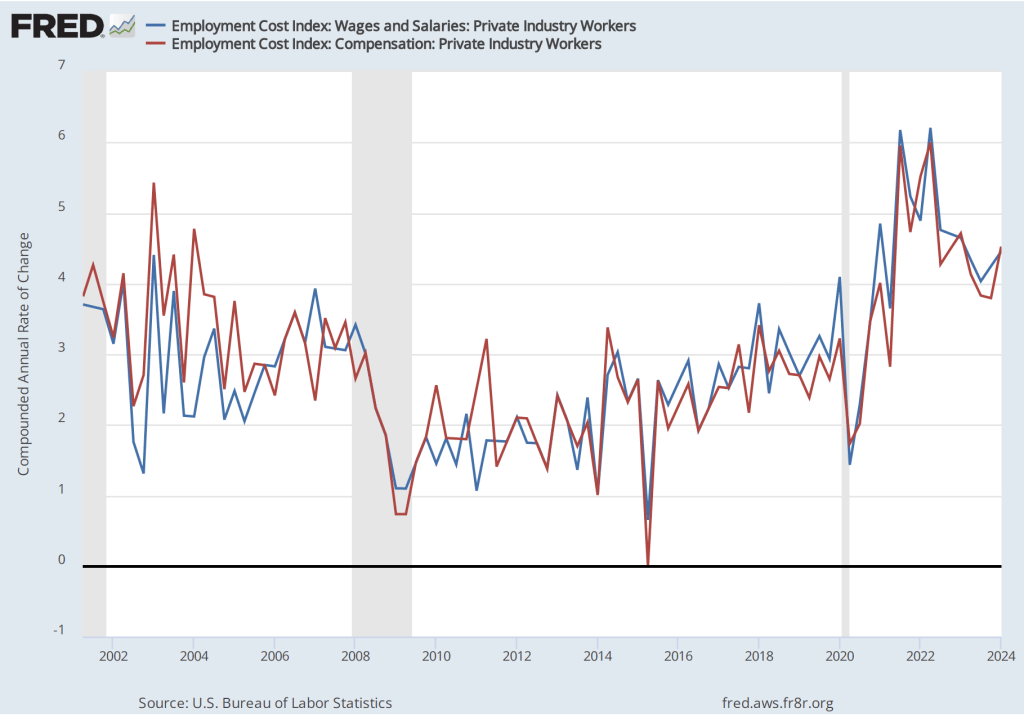
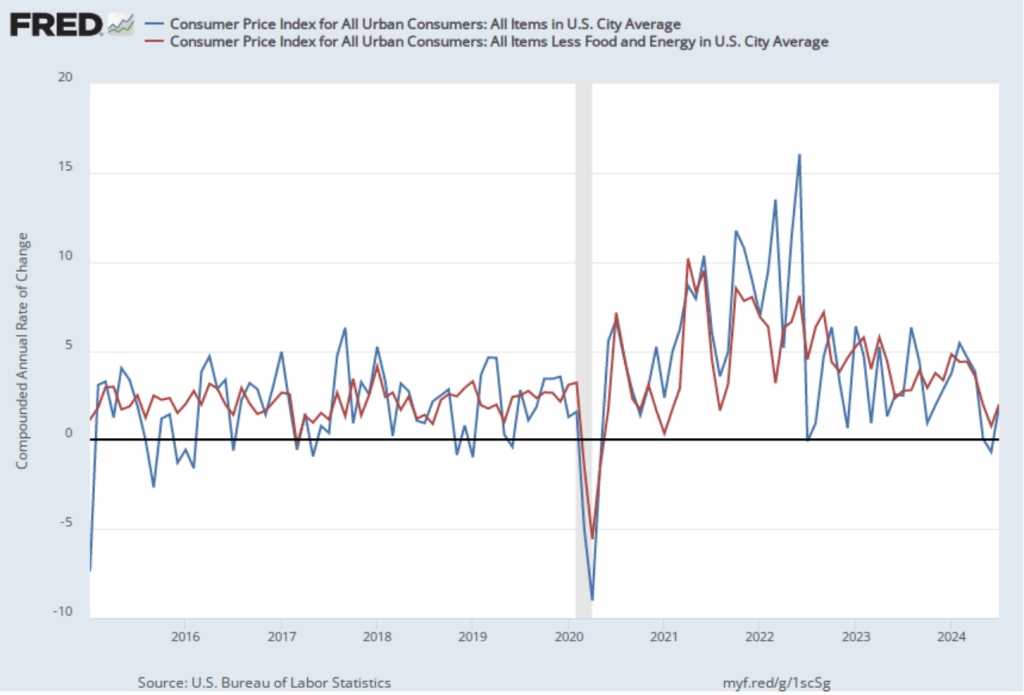
As the following figure shows, the inflation rate for July measured by the percentage change in the CPI from the same month in the previous month—headline inflation (the blue line)—was 2.9 percent down from 3.0 percent in June. Core inflation (the red line)—which excludes the prices of food and energy—was 3.2 percent in July, down from 3.3 percent in June.
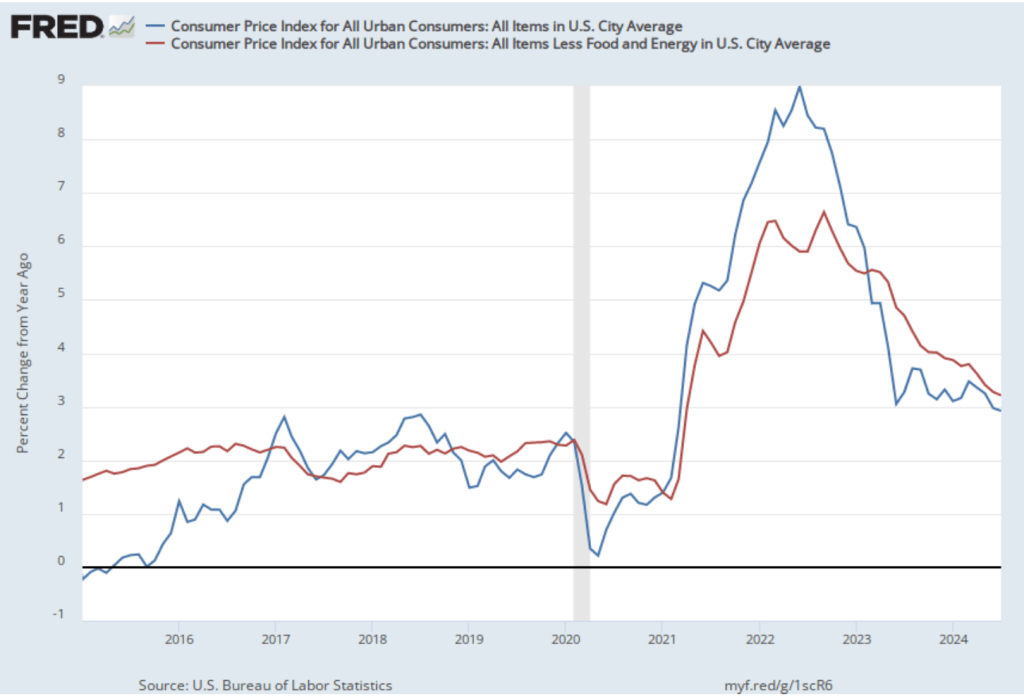
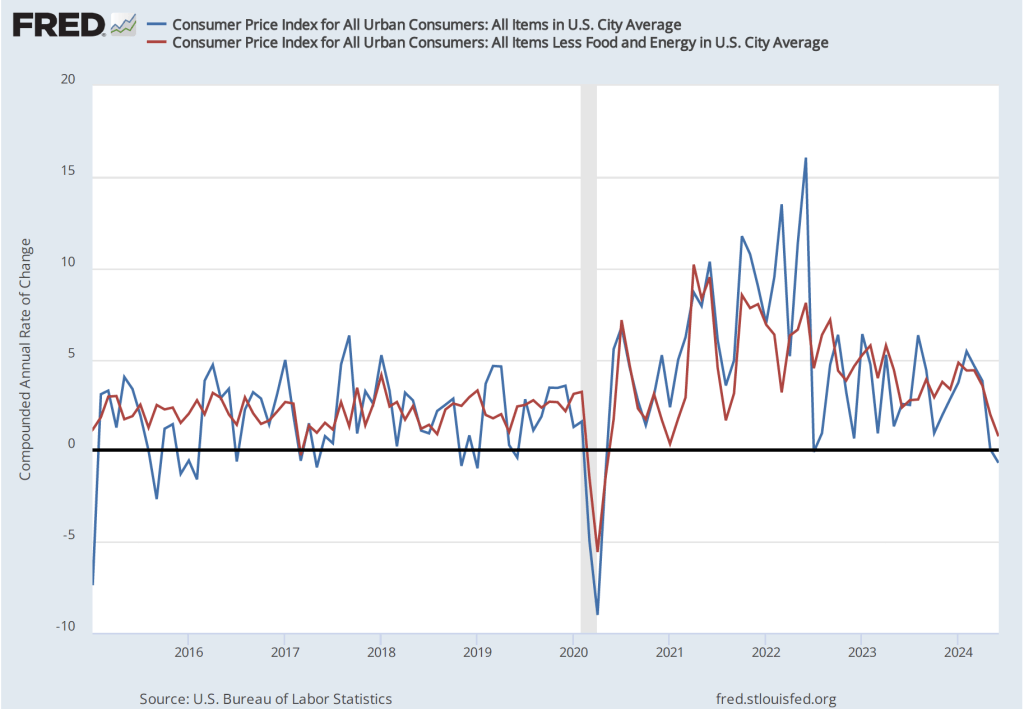
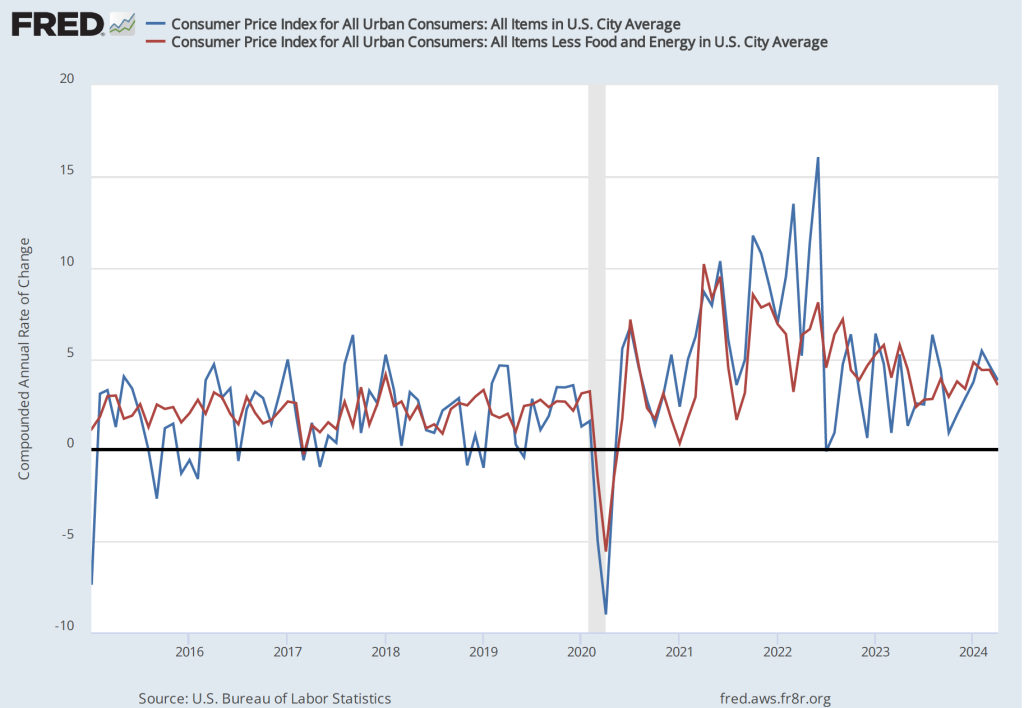
As the following figure shows, if we look at the 1-month inflation rate for headline and core inflation—that is the annual inflation rate calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year—we see an increase in the inflation rate in July, but the increase is from the very low levels in June. Headline inflation (the blue line) increased from –0.7 percent in June (which means that consumer price actually fell that month) to 1.9 percent in July. Core inflation (the red line) increased from 0.8 percent in June to 2.o percent in July. Overall, we can say that, taking 1-month and 12 month inflation together, the U.S. economy seems on course for a soft landing—with the annual inflation rate returning to the Fed’s 2 percent target without the economy being pushed into a recession. (Note, though, that the Fed uses the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, rather than the CPI in evaluating whether it is hitting its 2 percent inflation target.)
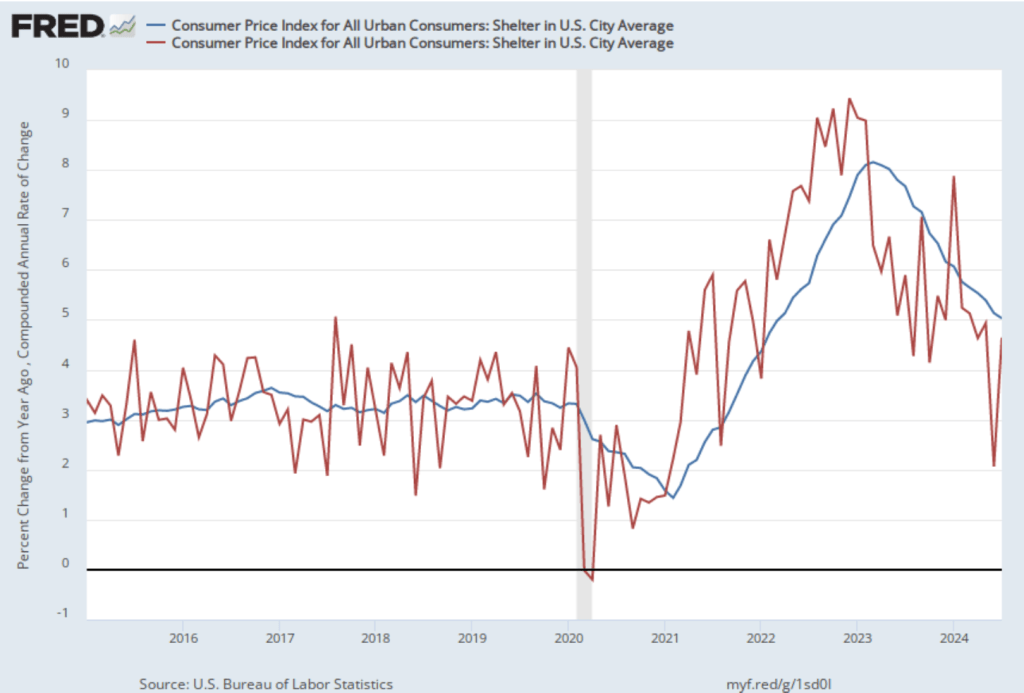
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell and his colleagues on the policy-making Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) have been closely following inflation in the price of shelter. The price of “shelter” in the CPI, as explained here, includes both rent paid for an apartment or house and “owners’ equivalent rent of residences (OER),” which is an estimate of what a house (or apartment) would rent for if the owner were renting it out. OER is included to account for the value of the services an owner receives from living in an apartment or house.
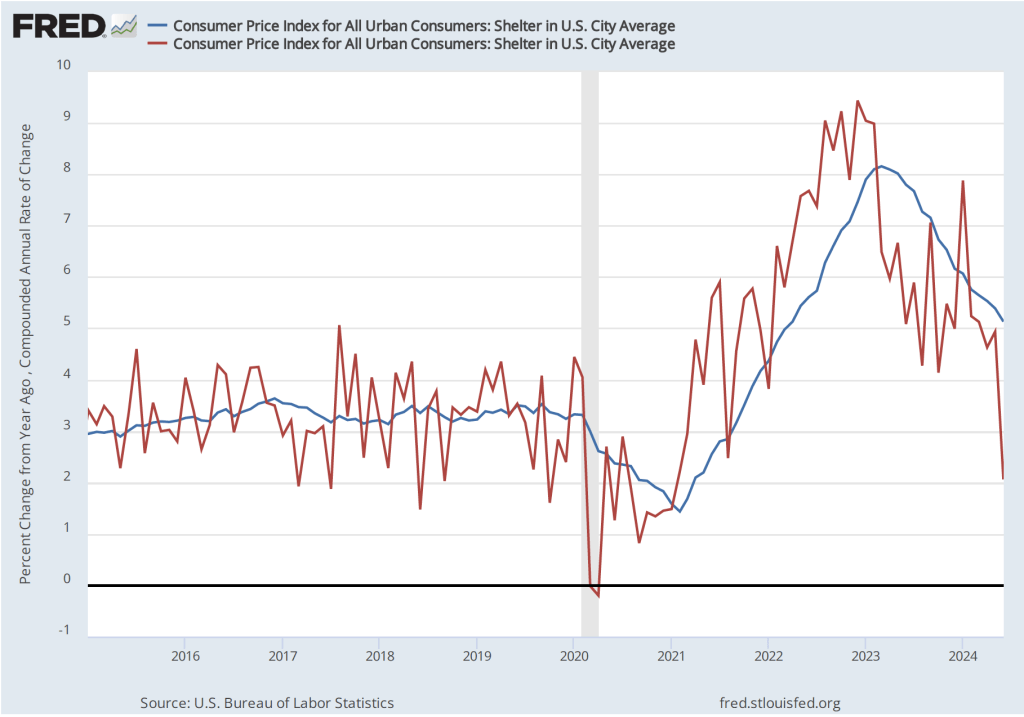
As the following figure shows, inflation in the price of shelter has been a significant contributor to headline inflation. The blue line shows 12-month inflation in shelter and the red line shows 1-month inflation in shelter. Twelve-month inflation in shelter continued its decline that began in the spring of 2023, falling from 5.1 percent in June to 5.0 percent July. One-month inflation in shelter—which is much more volatile than 12-month inflation in shelter—increased from 2.1 percent in June to 4.6 percent in July. The value for 1-month inflation in shelter may concern the members of the FOMC, but the continuing decline in in the less volatile 12-month inflation in shelter provides some reassurance that inflation in shelter is likely continuing to decline.
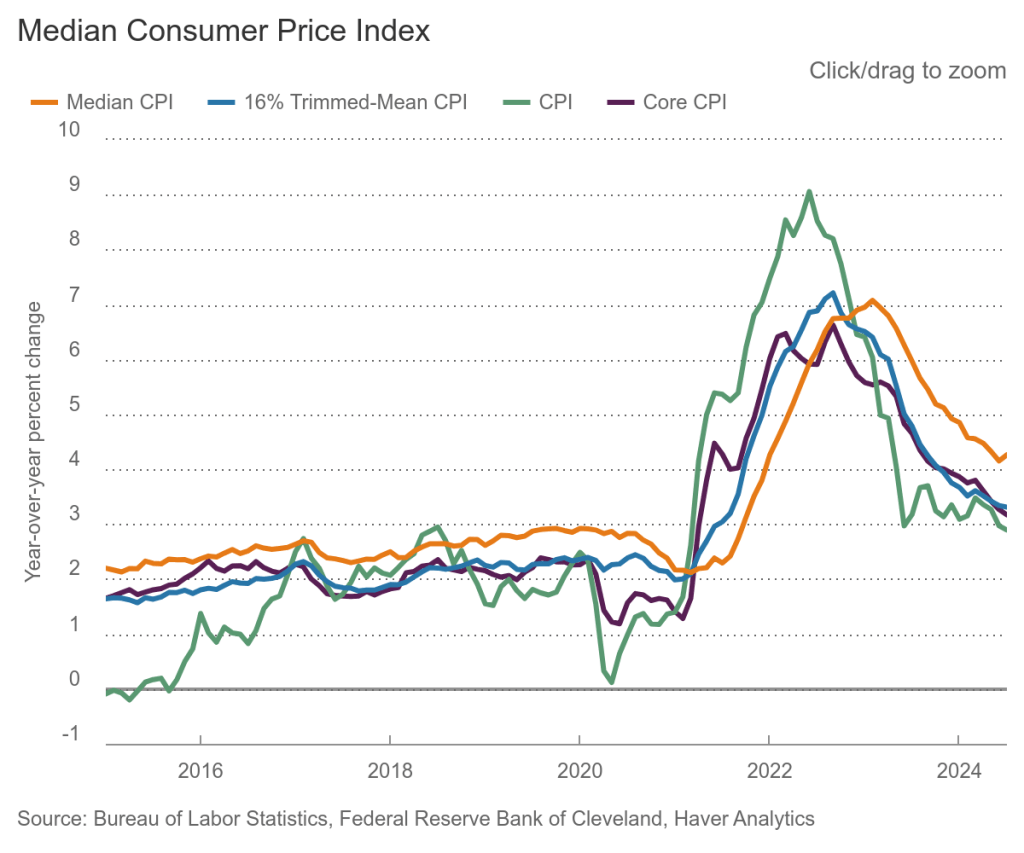
Finally, in order to get a better estimate of the underlying trend in inflation, some economists look at median inflation and trimmed mean inflation. Median inflation is calculated by economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland and Ohio State University. If we listed the inflation rate in each individual good or service in the CPI, median inflation is the inflation rate of the good or service that is in the middle of the list—that is, the inflation rate in the price of the good or service that has an equal number of higher and lower inflation rates. Trimmed mean inflation drops the 8 percent of good and services with the higherst inflation rates and the 8 percent of goods and services with the lowest inflation rates.
As the following figure (from the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland) shows, median inflation (the brown line) ticked up slightly from 4.2 percent in June to 4.3 percent in July. Trimmed mean inflation (the blue line) was unchanged in July at 3.3 percent. One conclusion from these data is that headline and core inflation may be somewhat understating the underlying rate of inflation.
For the past few weeks investores in financial markets have been expecting that recent inflation and employment data will lead the FOMC to cut its target for the federal funds at its next meeting on Septembe 17-18 .
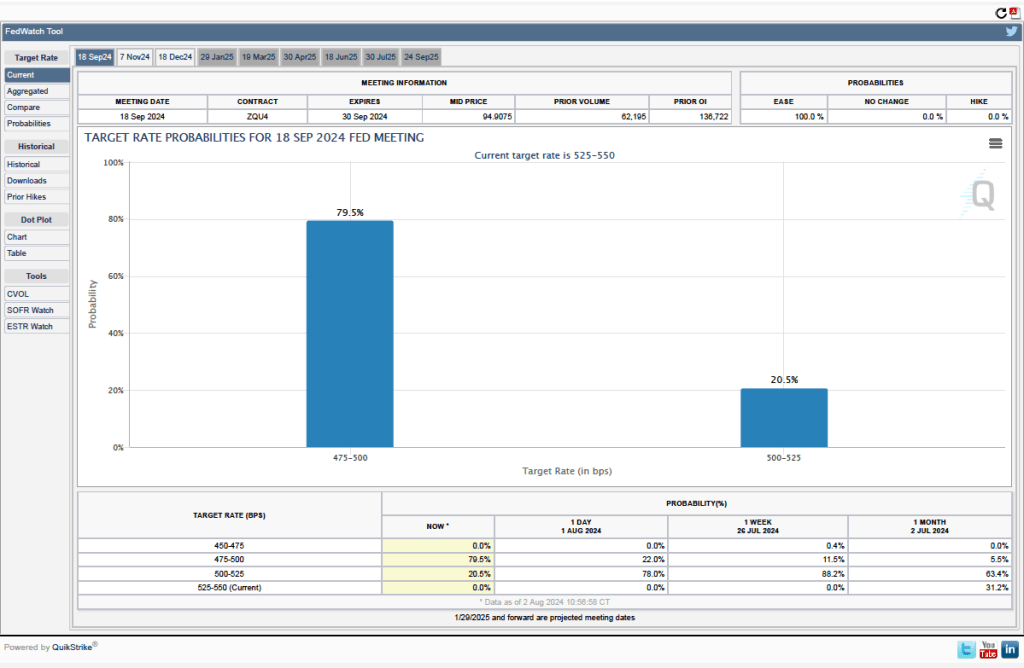
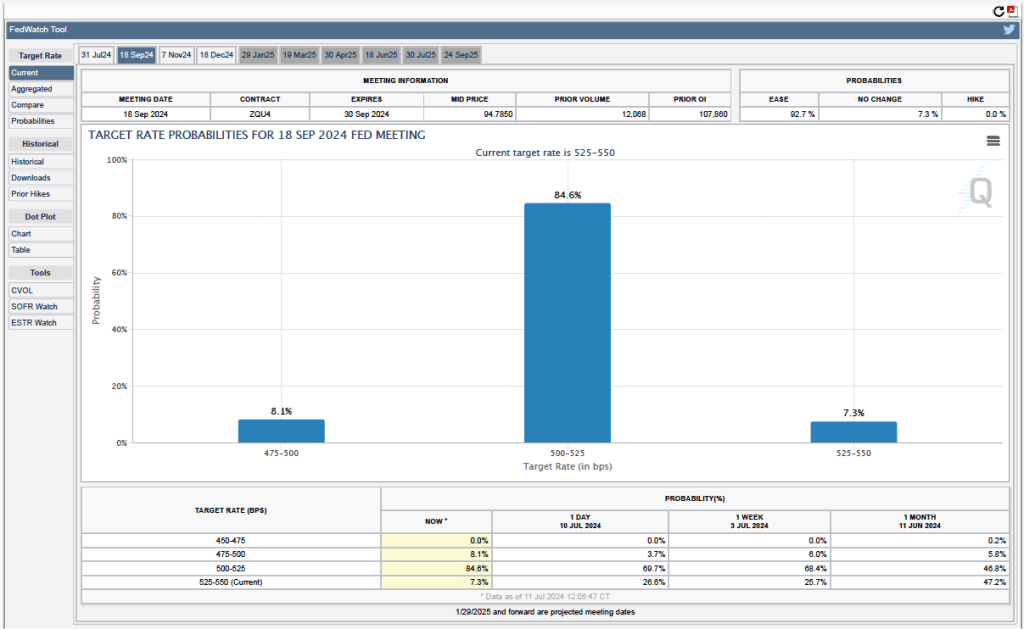
Futures markets allow investors to buy and sell futures contracts on commodities–such as wheat and oil–and on financial assets. Investors can use futures contracts both to hedge against risk—such as a sudden increase in oil prices or in interest rates—and to speculate by, in effect, betting on whether the price of a commodity or financial asset is likely to rise or fall. (We discuss the mechanics of futures markets in Chapter 7, Section 7.3 of Money, Banking, and the Financial System.) The CME Group was formed from several futures markets, including the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, and allows investors to trade federal funds futures contracts. The data that result from trading on the CME indicate what investors in financial markets expect future values of the federal funds rate to be. The following chart from the CME’s FedWatch Tool shows the current values from trading of federal funds futures.
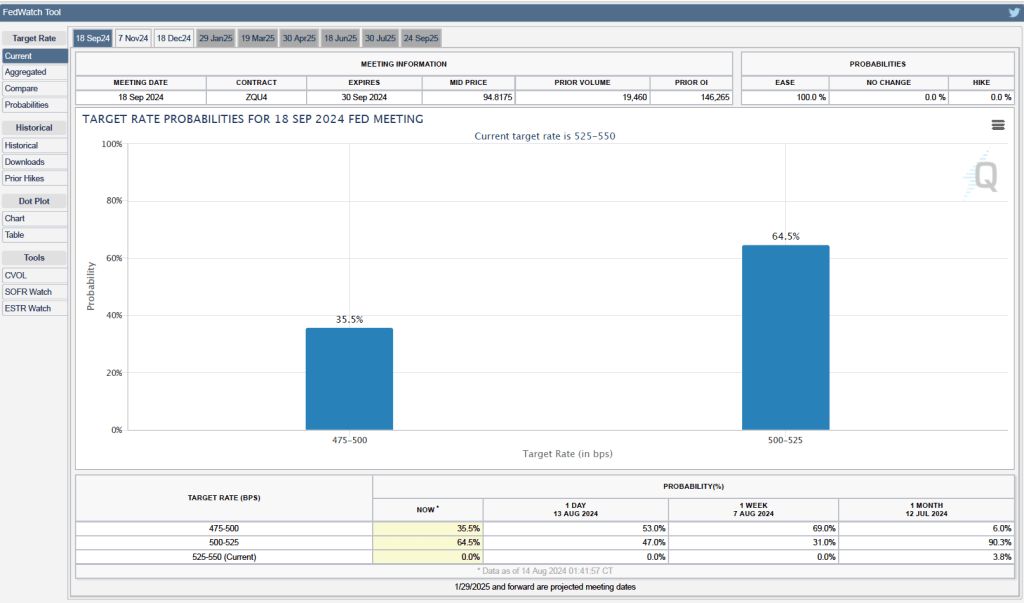
The probabilities in the chart reflect investors’ predictions of what the FOMC’s target for the federal funds rate will be after the committee’s September meeting. The chart indicates that investors assign a probability of 35.5 percent to the FOMC cutting its target range for the federal funds rate by 0.50 percentage point from the current 5.25 prcent to 5.50 percent to 4.75 percent to 5.25 percent. Investors assign a much larger probability—64.5 percent—to the FOMC cutting its target range for the federal funds rate by 0.25 percentage point to 5.00 percent to 5.25 percent.
It would most likely require the next BLS “Employment Situation” report—which is scheduled for release on September 6—to show unexpected weakness for the FOMC to cut its target for the federal funds rate by more than 0.25 percentage point.