Fed Chair Jerome Powell speaking at a press conference following a meeting of the FOMC (photo from federalreserve.gov)
Members of the Fed’s policymaking Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) had signaled clearly before today’s (May 7) meeting that the committee would leave its target range for the federal funds rate unchanged at 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent. In the statement released after its meeting, the committee made one significant change to the wording in its statement following its last meeting on March 19. The committee added the words in bold to the following sentence:
“The Committee is attentive to the risks to both sides of its dual mandate and judges that the risks of higher unemployment and higher inflation have risen.”
The key event since the last FOMC meeting was President Trump’s announcement on April 2 that he would implement tariff increases that were much higher than had previously been expected.
As we noted in an earlier blog post, an unexpected increase in tariff rates will result in an aggregate supply shock to the economy. As we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 13,Section 13.3 (Economics, Chapter 23, Section 23.3), an aggregate supply shock puts upward pressure on the price level at the same time as it causes a decline in real GDP and employment. The result, as the FOMC statement indicates, can be both rising inflation and rising unemployment. If higher inflation and higher unemployment persist, the U.S. economy would be experiencing stagflation. The United States last experienced stagflation during the 1970s when large increases in oil prices caused an aggregate supply shock.
During his press conference following the meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell indicated that the increase in tariffs might the Fed’s dual mandate goals of price stability and maximum employment “in tension” if both inflation and unemployment increase. If the FOMC were to increase its target for the federal funds rate in order to slow the growth of demand and bring down the inflation rate, the result might be to further increase unemployment. But if the FOMC were to cut its target for the federal funds rate to increase the growth of demand and reduce the unemployment rate, the result might be to further increase the inflation rate.
Powell emphasized during his press conference that tariffs had not yet had an effect on either inflation or unemployment that was large enough to be reflected in macroeconomic data—as we’ve noted in blog posts discussing recent macroeconomic data releases. As a result, the consensus among committee members is that it would be better to wait to future meetings before deciding what changes in the federal funds rate might be needed: “We’re in a good position to wait and see. We don’t have to be in a hurry.”
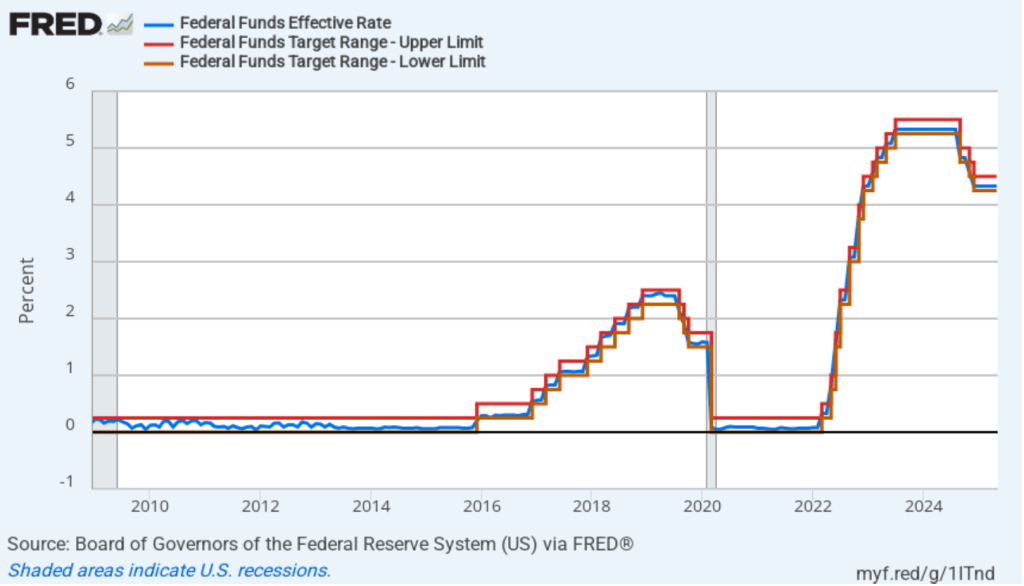
The following figure shows, for the period since January 2010, the upper bound (the blue line) and lower bound (the green line) for the FOMC’s target range for the federal funds rate and the actual values of the federal funds rate (the red line) during that time. Note that the Fed is successful in keeping the value of the federal funds rate in its target range. (We discuss the monetary policy tools the FOMC uses to maintain the federal funds rate in its target range in Macroeconomics, Chapter 15, Section 15.2 (Economics, Chapter 25, Section 25.2).)
In his press conference, Powell indicated that when the committee would change its target for the federal funds rate was dependent on the trends in macroeconomic data on inflation, unemployment, and output during the coming months. He noted that if both unemployment and inflation significantly increased, the committee would focus on which variable had moved furthest from the Fed’s target. He also noted that it was possible that neither inflation nor unemployment might end up significantly increasing either because tariff negotiations lead to lower tariff rates or because the economy proves to be better able to deal with the effects of tariff increases than many economist now expect.
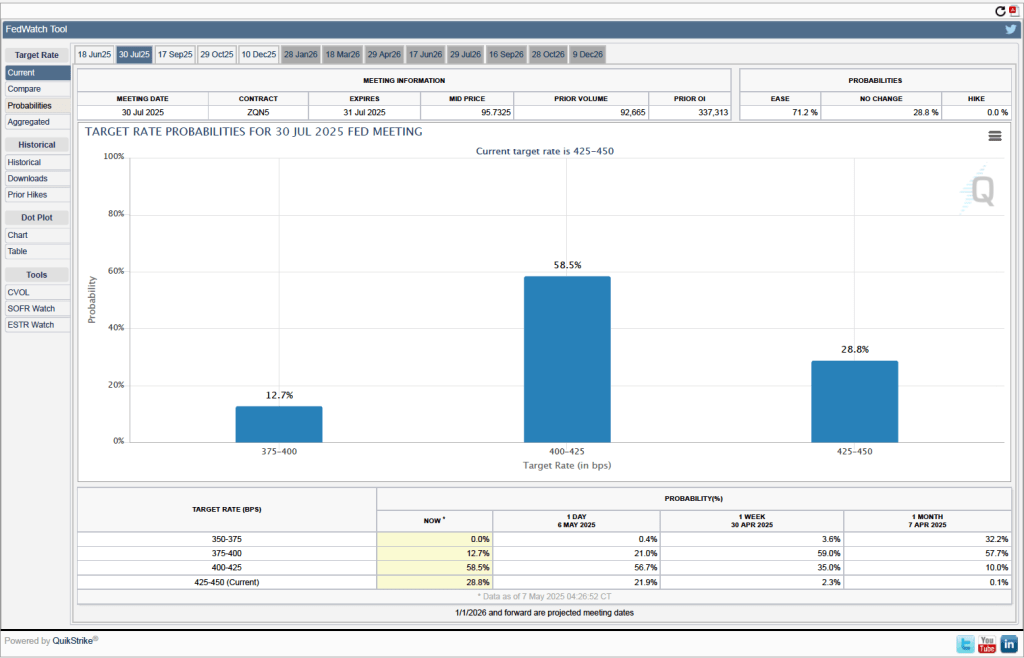
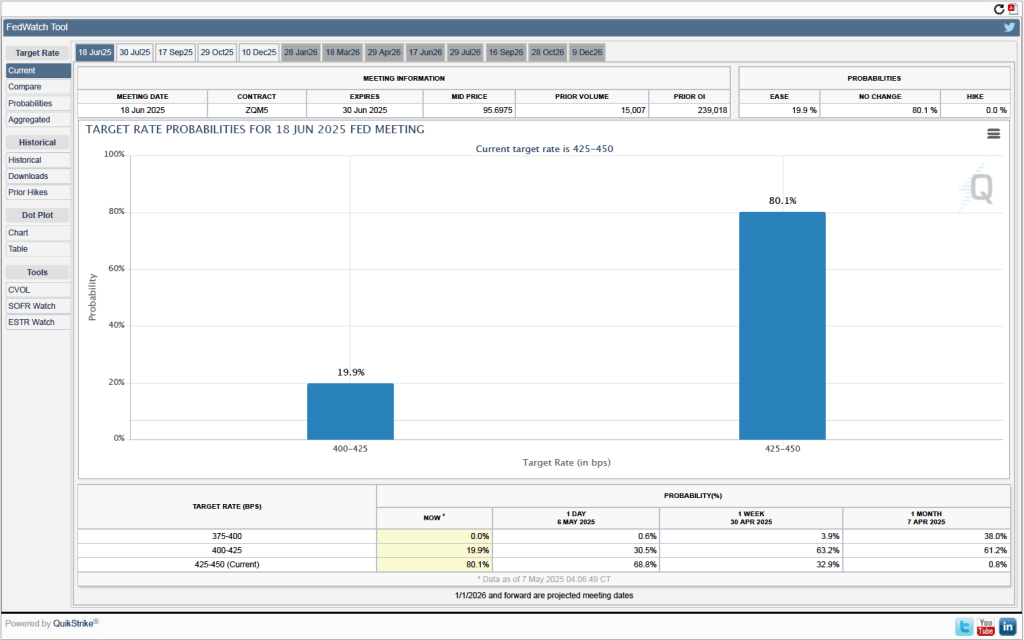
One indication of expectations of future changes in the target for the federal funds rate comes from investors who buy and sell federal funds futures contracts. (We discuss the futures market for federal funds in this blog post.) The data from the futures market indicate that investors don’t expect that the FOMC will cut its target for the federal funds rate at its May 17–18 meeting. As shown in the following figure, investors assign a 80.1 percent probability to the committee keeping its target unchanged at 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent at that meeting.
When will the Fed likely cut its target for the federal funds rate? As the following figure shows, investors expect it to happen at the FOMC’s July 29–30 meeting. Investors assign a probably of 58.5 percent to the committee cutting its target by 0.25 percentage point (25 basis points) at that meeting and a probability of 12.7 percent to the committee cutting its target by 50 basis points. Investors assign a probability of only 28.8 percent to the committee leaving its target unchanged.