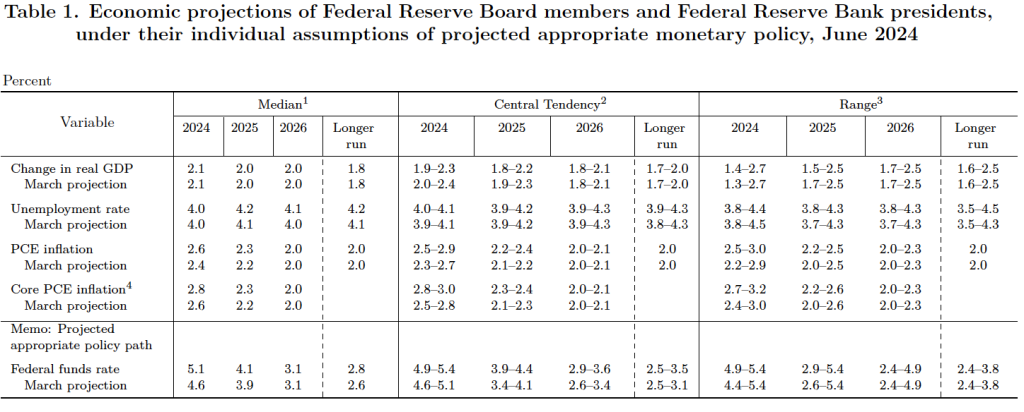
Image of “Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell speaking at a podium” generated by GTP-4o.
At the conclusion of its July 30-31 meeting, the Federal Reserve’s policy-making Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) voted unamiously to leave its target range for the federal funds rate unchanged at 5.25 percent to 5.5 percent. (The statement the FOMC issued following the meeting can be found here.)
In the statement Fed Chair Jerome Powell read at the beginning of his press conference after the meeting, Powell appeared to be repeating a position he has stated in speeches and interviews during the past month:
“We have stated that we do not expect it will be appropriate to reduce the target range for the federal funds rate until we have gained greater confidence that inflation is moving sustainably toward 2 percent. The second-quarter’s inflation readings have added to our confidence, and more good data would further strengthen that confidence. We will continue to make our decisions meeting by meeting.”
But in answering questions from reporters, he made it clear that—as many economists and Wall Street investors had already concluded—the FOMC was likely to reduce its target for the federal funds rate at its next meeting on September 17-18. Powell noted that recent data were consistent with the inflation rate continuing to decline toward the Fed’s 2 percent annual target. Powell summarized the consensus from the discussion among committee members as being that “the time was approaching for cutting rates.”
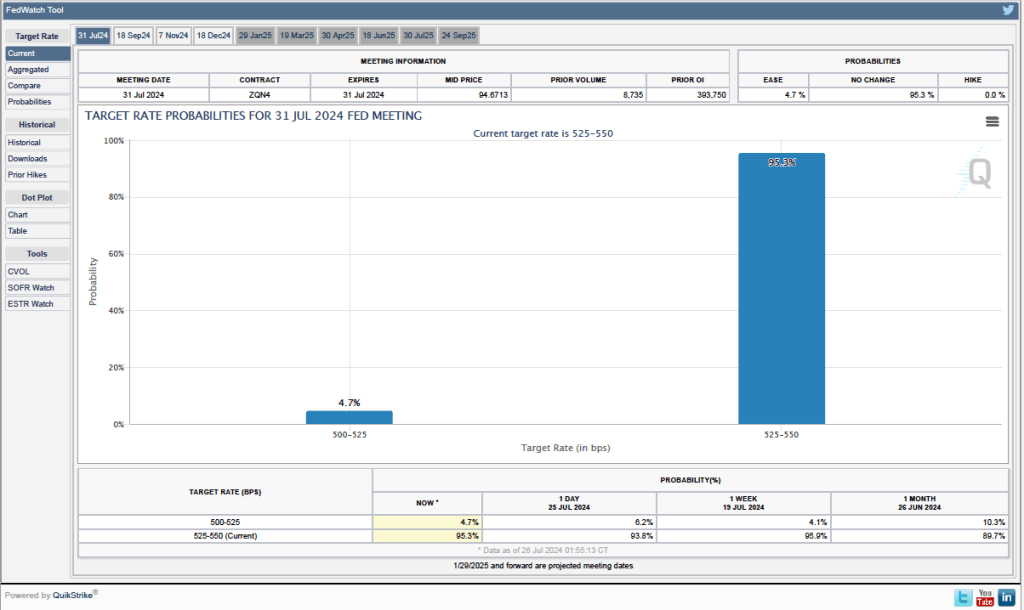
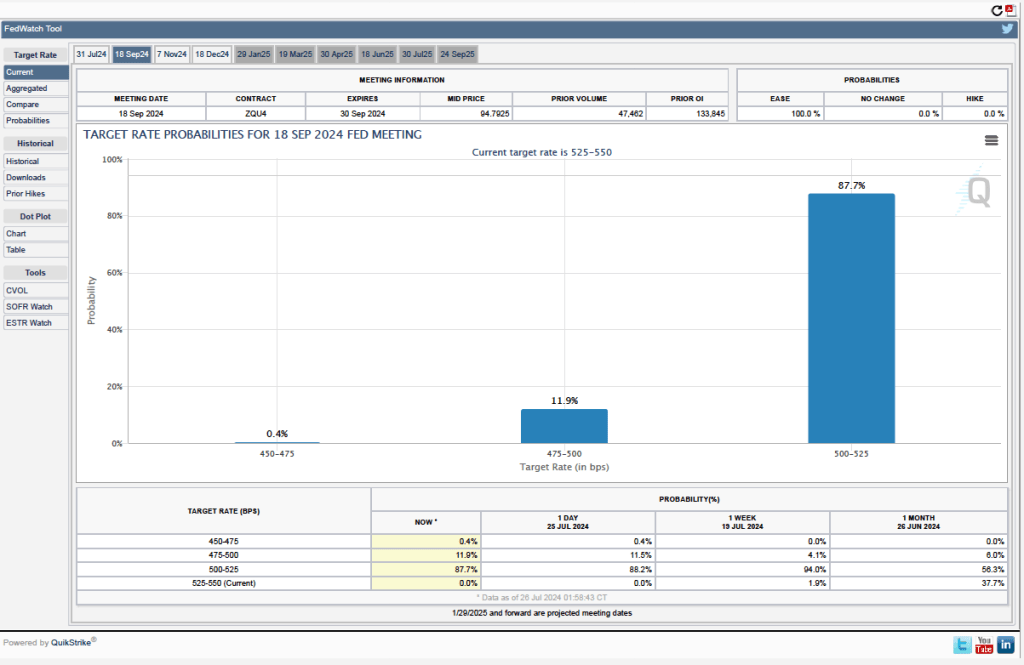
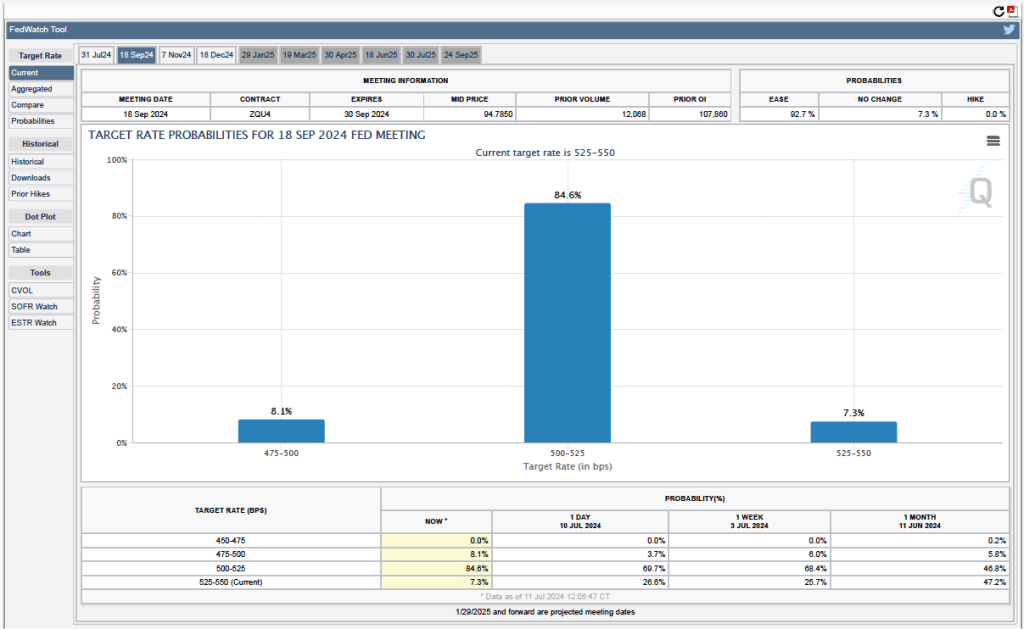
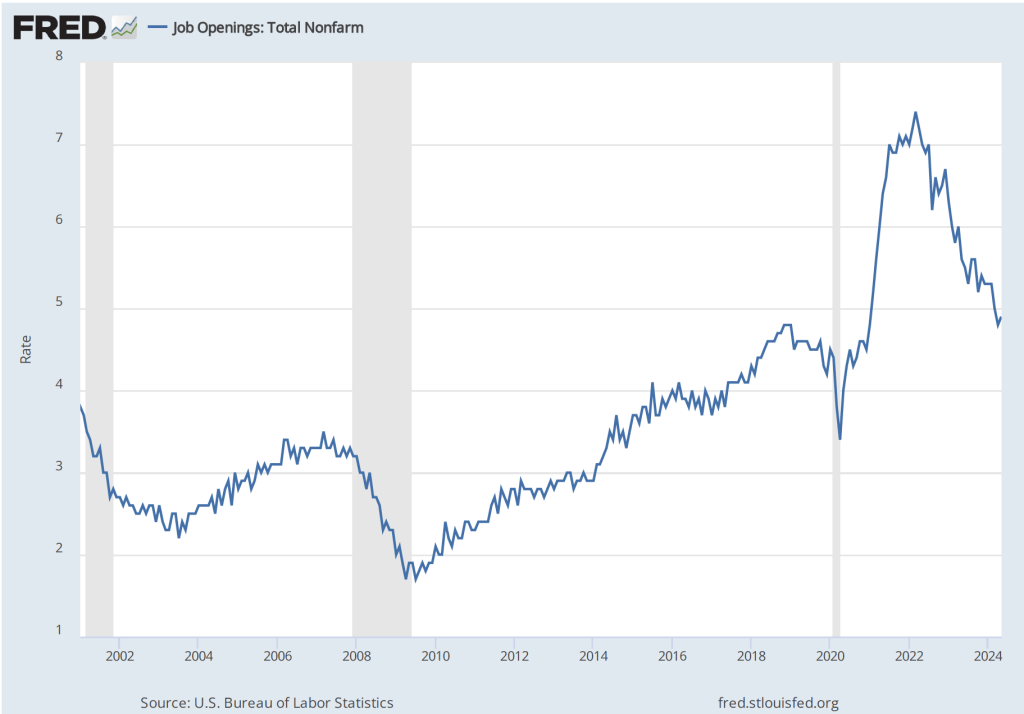
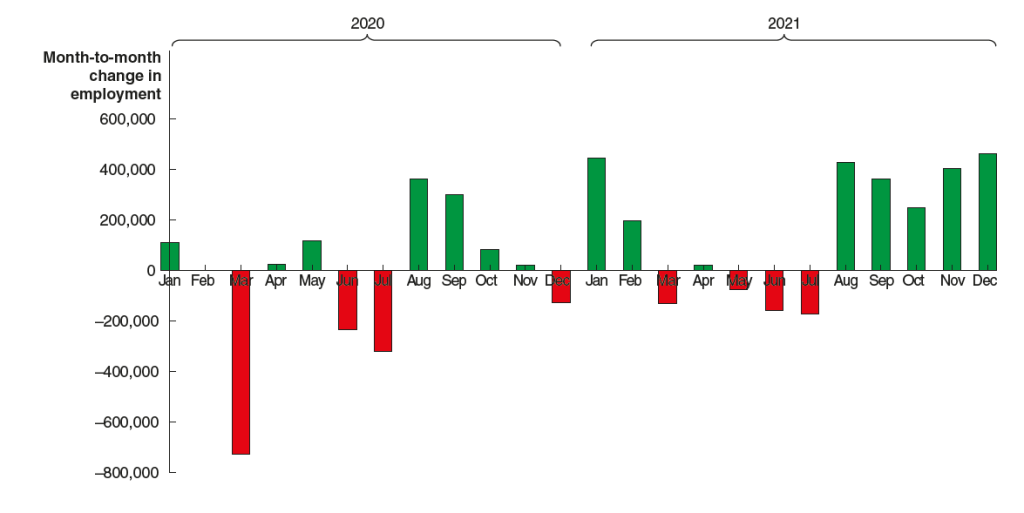
Futures markets allow investors to buy and sell futures contracts on commodities–such as wheat and oil–and on financial assets. Investors can use futures contracts both to hedge against risk—such as a sudden increase in oil prices or in interest rates—and to speculate by, in effect, betting on whether the price of a commodity or financial asset is likely to rise or fall. (We discuss the mechanics of futures markets in Chapter 7, Section 7.3 of Money, Banking, and the Financial System.) The CME Group was formed from several futures markets, including the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, and allows investors to trade federal funds futures contracts. The data that result from trading on the CME indicate what investors in financial markets expect future values of the federal funds rate to be. The following chart from the CME’s FedWatch Tool shows the current values resulting from trading of federal funds futures.
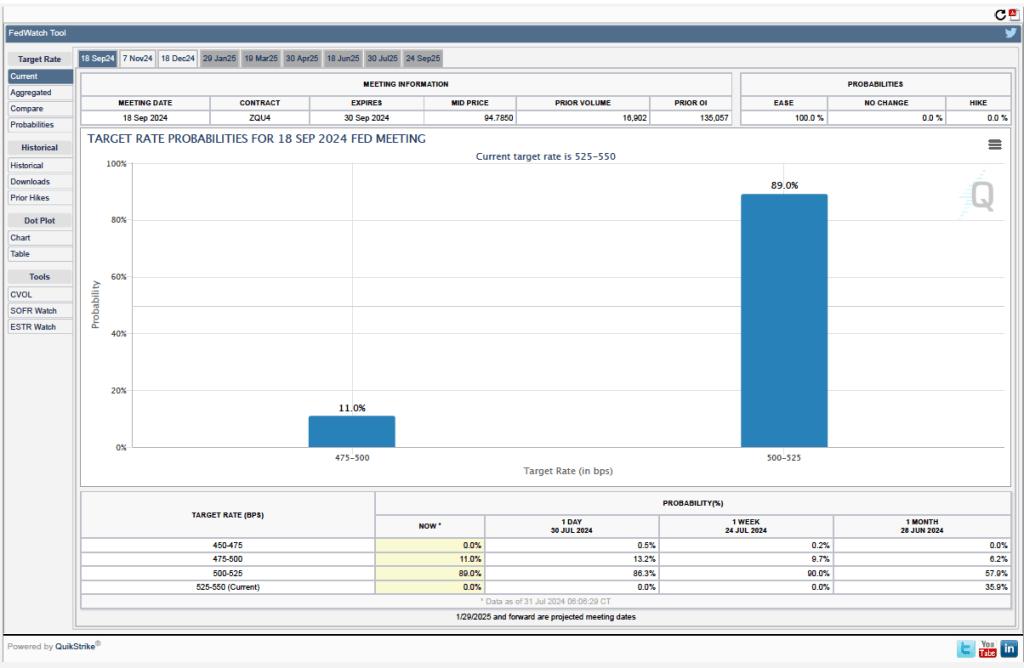
The probabilities in the chart reflect investors’ predictions of what the FOMC’s target for the federal funds rate will be after the committee’s September meeting. The chart indicates that investors assign a probability of 100 percent to the FOMC cutting its federal funds rate target at this meeting. Investors assign a probability of 89.0 percent that the committee will cut its target by 0.25 percentage point and a probability of 11.0 percent that the commitee will cut its target by 0.50 percentage point. When asked at his press conference whether the committee had given any consideration to making a 0.50 percentage point cut in its target, Powell said that it hadn’t.
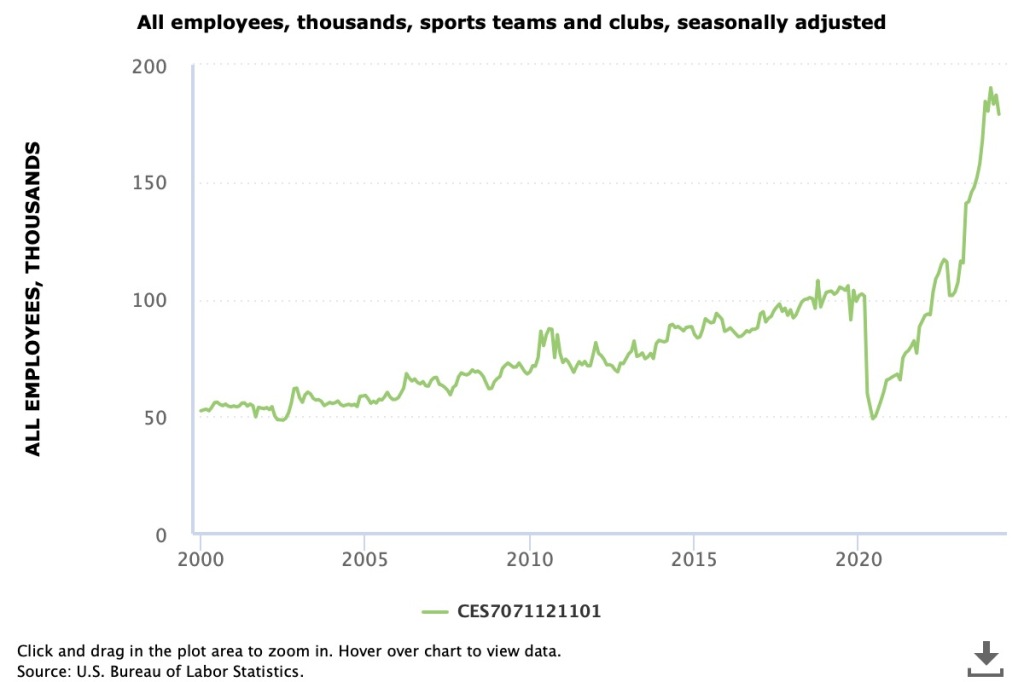
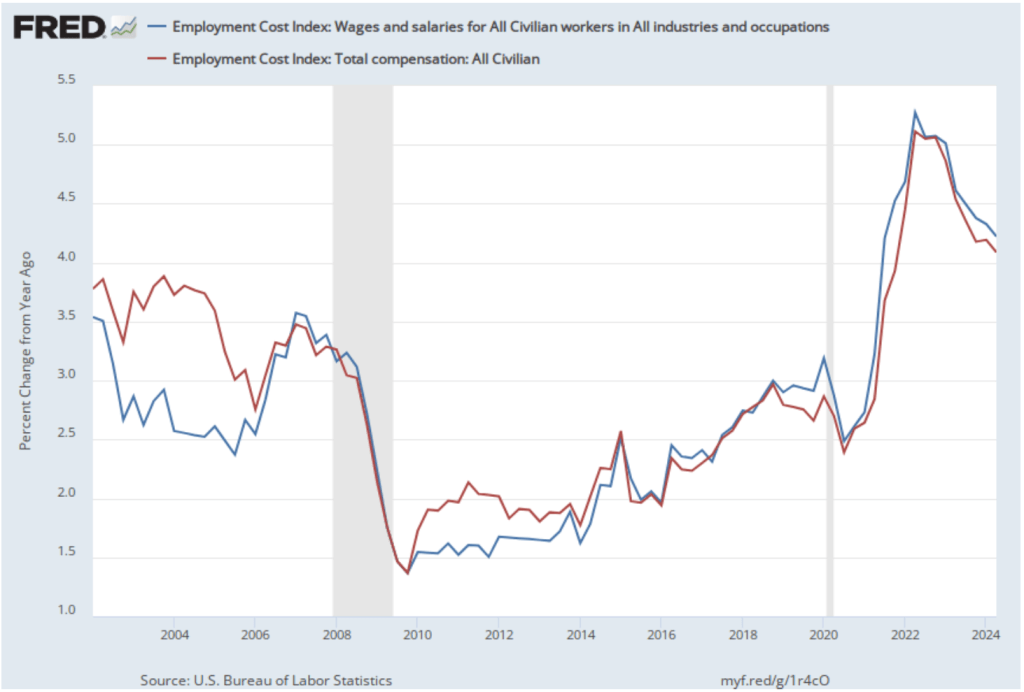
Powell stated that the latest data on wage increases had led the committee to conclude that the labor market was no longer a source of inflationary pressure. The morning of the press conference, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its latest report on the Employment Cost Index (ECI). As we’ve noted in earlier posts, as a measure of the rate of increase in labor costs, the FOMC prefers the ECI to average hourly earnings (AHE).
As a measure of how wages are increasing or decreasing during a particular period, AHE can suffer from composition effects because AHE data aren’t adjusted for changes in the mix of occupations workers are employed in. In contrast, the ECI holds the mix of occupations constant. The ECI does have the drawback that it is only available quarterly whereas the AHE is available monthly.
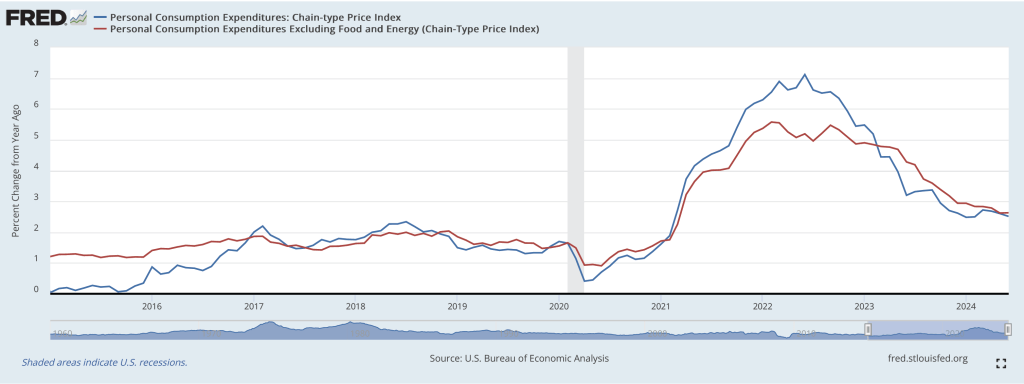
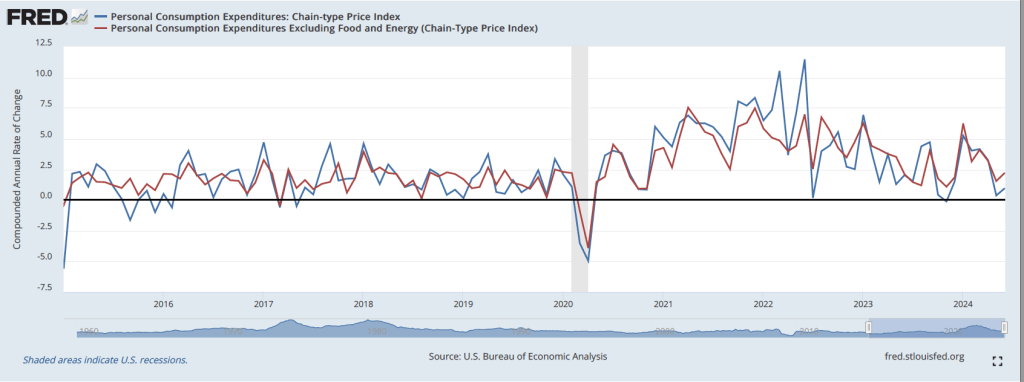
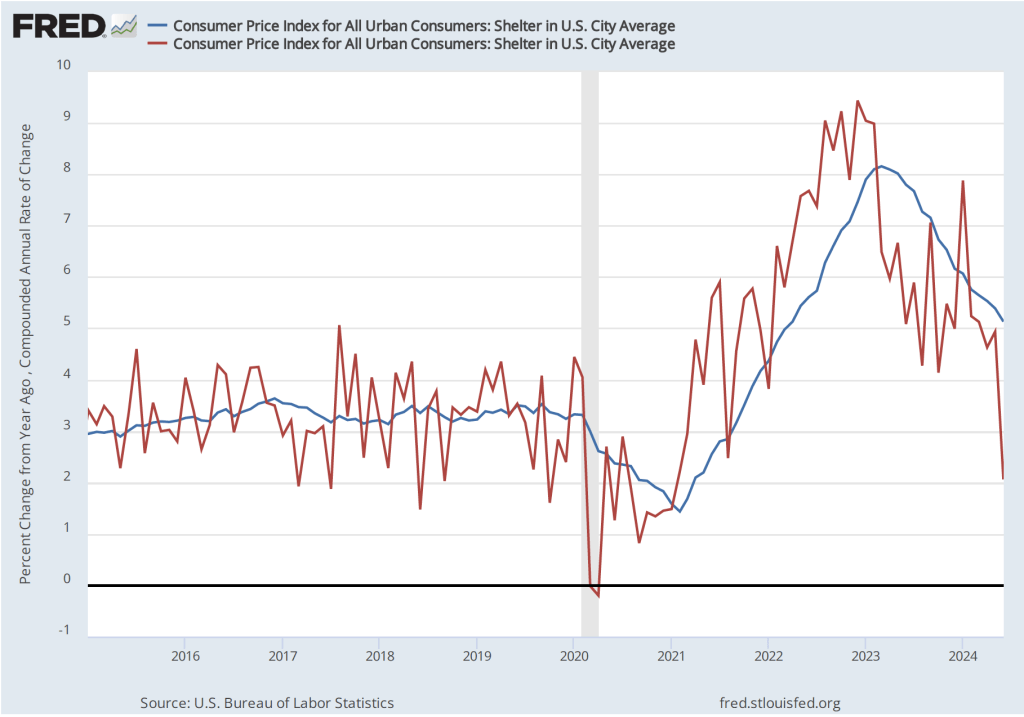
The following figure shows the percentage change in the ECI for all civilian workers from the same quarter in the previous year. The blue line looks only at wages and salaries, while the red line is for total compensation, including non-wage benefits like employer contributions to health insurance. The rate of increase in the wage and salary measure decreased slightly from 4.3 percent in the first quarter of 2024 to 4.2 percent in the second quarter of 2024. The rate of increase in compensation also declined slightly from 4.2 percent to 4.1 percent. As the figure shows, both measures continued their declines from the peak of wage inflation during the second quarter of 2022. In his press conference, Powell said that the this latest ECI report was a little better than the committee had expected.
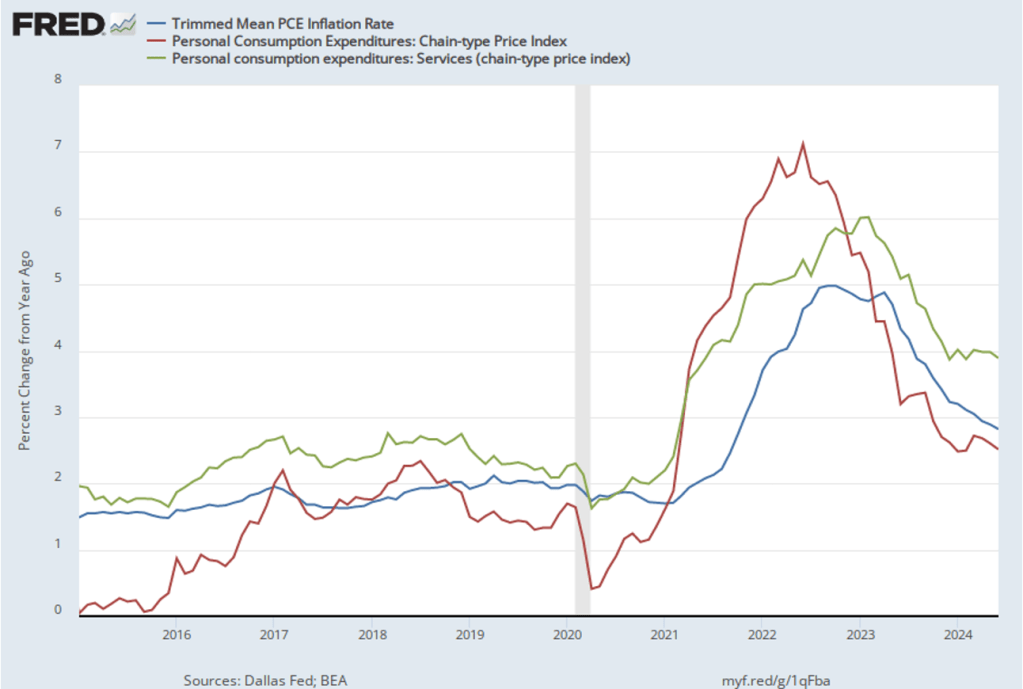
Finally, Powell noted that the committee saw no indication that the U.S. economy was heading for a recession. He observed that: “The labor market has come into better balance and the unemployment rate remains low.” In addition, he said that output continued to grow steadily. In particular, he pointed to growth in real final sales to private domestic purchasers. This macro variable equals the sum of personal consumption expenditures and gross private fixed investment. By excluding exports, government purchases, and changes in inventories, final sales to private domestic purchasers removes the more volatile components of gross domestic product and provides a better measure of the underlying trend in the growth of output.
As the following figure shows, this measure of output has grown at an annual rate of more than 2.5 percent in each of the last three quarters. Output expanding at that rate is indicative of an economy that is neither overheating nor heading toward a recession.

At this point, unless macro data releases are unexpectedly strong or weak during the next six weeks, it seems nearly certain that at its September meeting the FOMC will reduce its target range for the federal funds rate by 0.25 percentage point.