Image created by ChatGPT
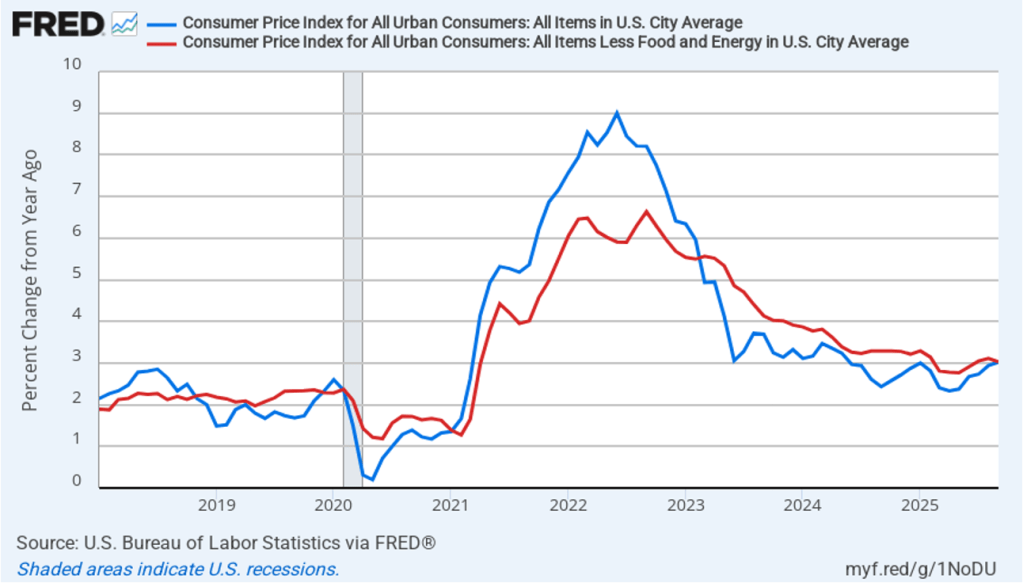
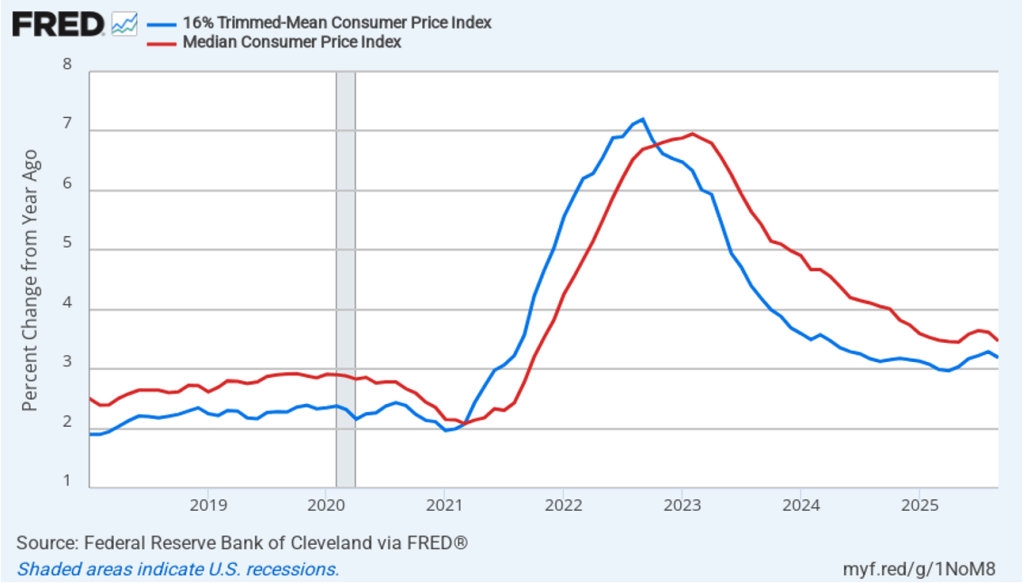
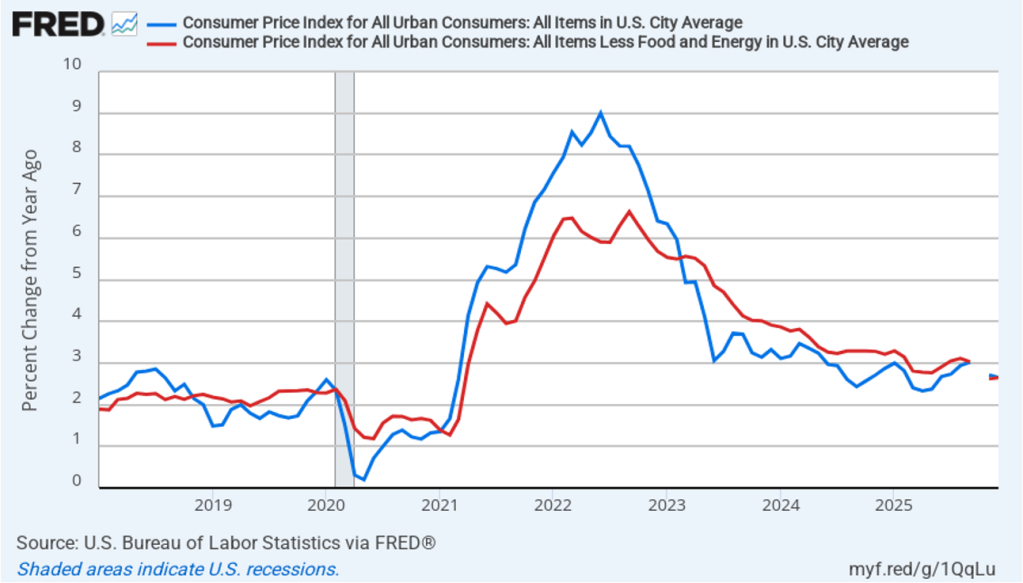
This morning (January 13), the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its report on the consumer price index (CPI) for December. The following figure compares headline CPI inflation (the blue line) and core CPI inflation (the red line). Because of the effects of the federal government shutdown, the BLS didn’t report inflation rates for October or November, so both lines show gaps for those months.
- The headline inflation rate, which is measured by the percentage change in the CPI from the same month in the previous year, was 2.7 percent in December..
- The core inflation rate, which excludes the prices of food and energy, was 2.6 percent in December.
Headline inflation was the same as economists surveyed by FactSet had forecast, while core inflation was slightly lower.
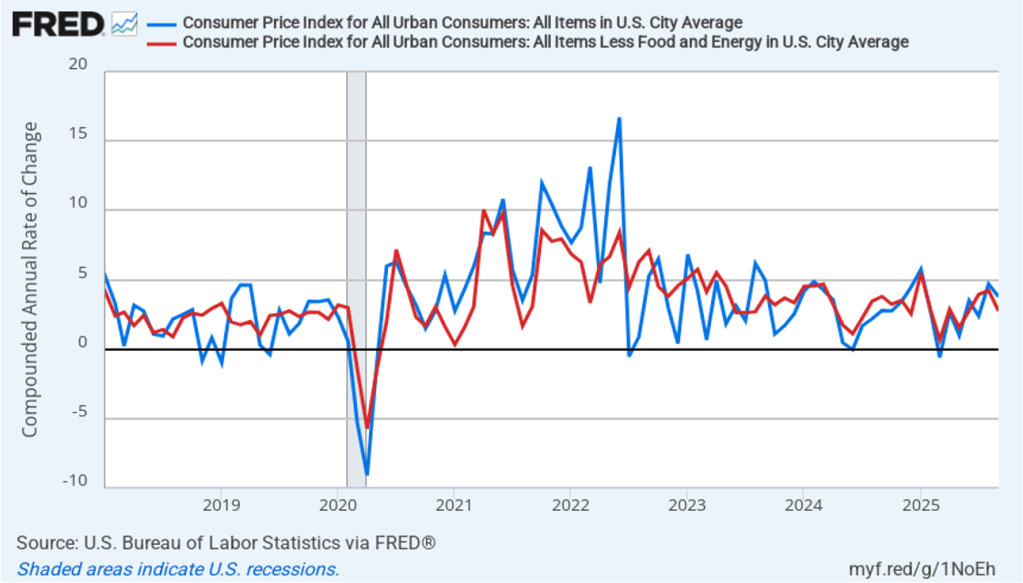
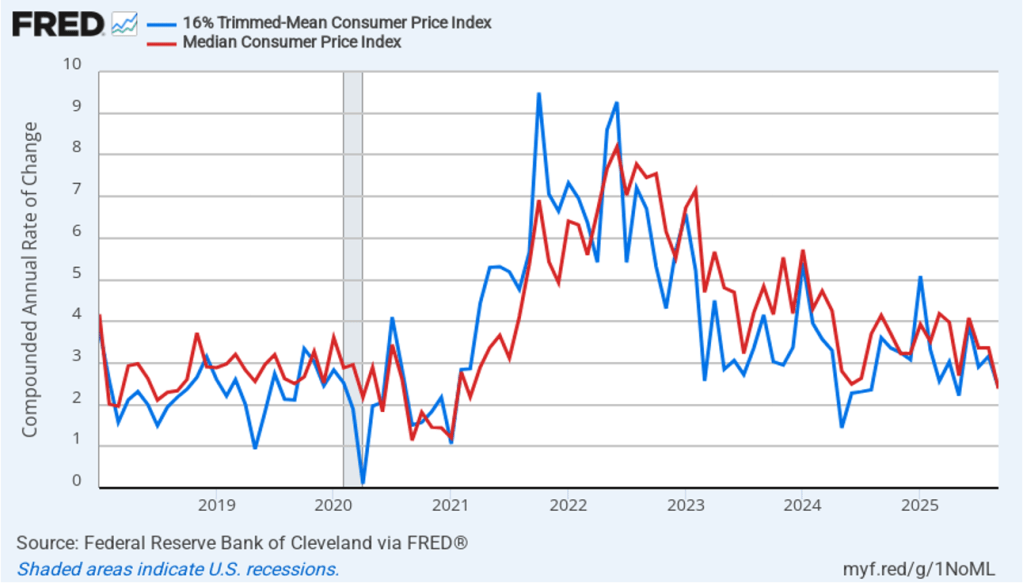
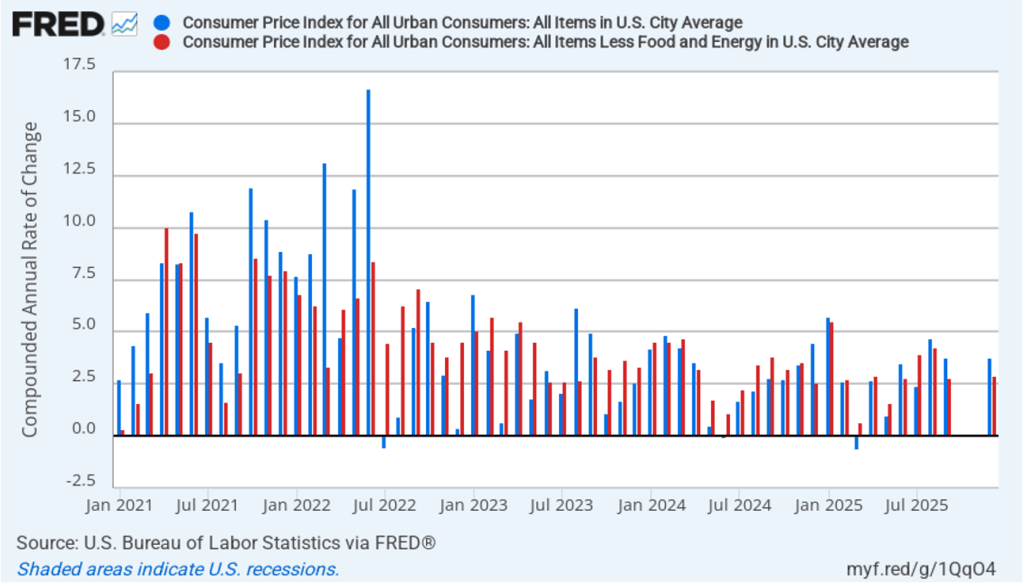
In the following figure, we look at the 1-month inflation rate for headline and core inflation—that is the annual inflation rate calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. We switch from lines to bars to make the December inflation rates easier to see.
Calculated as the 1-month inflation rate, headline inflation (the blue line) was 3.8 percent in December, the same as in September which is the most recent month with data. Core inflation (the red line) was up slightly to 2.9 percent in December from 2.8 percent in September.
The 1-month and 12-month inflation rates are telling similar stories, with both measures indicating that the rate of price increase is running moderately above the Fed’s 2 percent inflation target.
Of course, it’s important not to overinterpret the data from a single month. The figure shows that the 1-month inflation rate is particularly volatile. Also note that the Fed uses the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, rather than the CPI, to evaluate whether it is hitting its 2 percent annual inflation target.
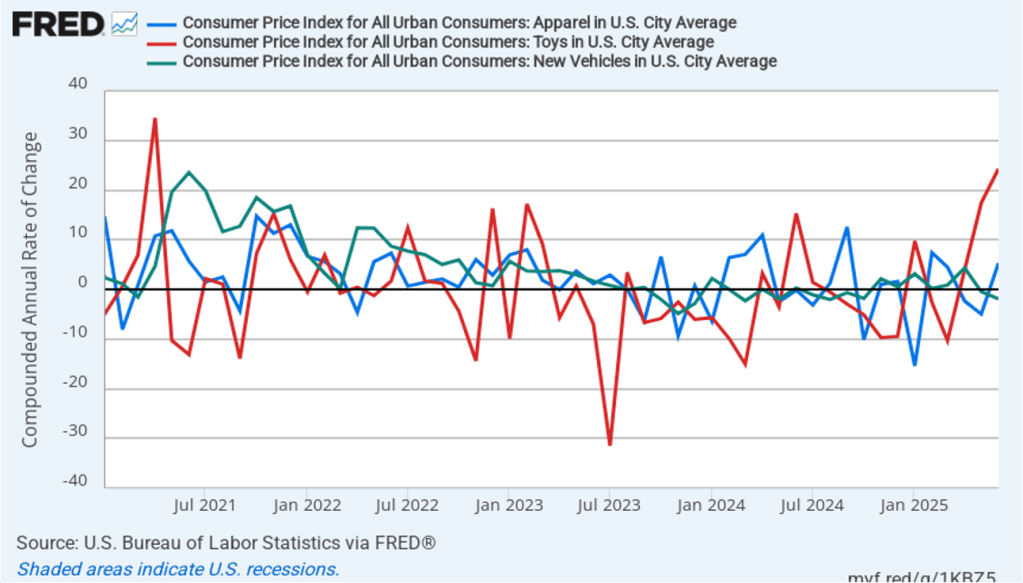
In recent months, there have been many media reports on how consumers are concerned about declining affordability. These concerns are thought to have contributed to Zohran Mamdani’s victory in New York City mayoral race. Affordability has no exact interpretation but typically means concern about inflation in goods and services that consumers buy frequently.
Many consumers seem worried about inflation in food prices. The following figure shows 1-month inflation in the CPI category “food at home” (the blue bar)—primarily food purchased at groceries stores—and the category “food away from home” (the red bar)—primarily food purchased at restaurants. Both measures increased rapidly in December. Food at home increased 9.0 percent in December, up from 4.0 percent in September. Food away from home increased 8.7 percent in December, up from 1.7 percent in September. Again, 1-month inflation rates can be volatile, but these large increases in food prices in December may help explain the recent focus on affordability.

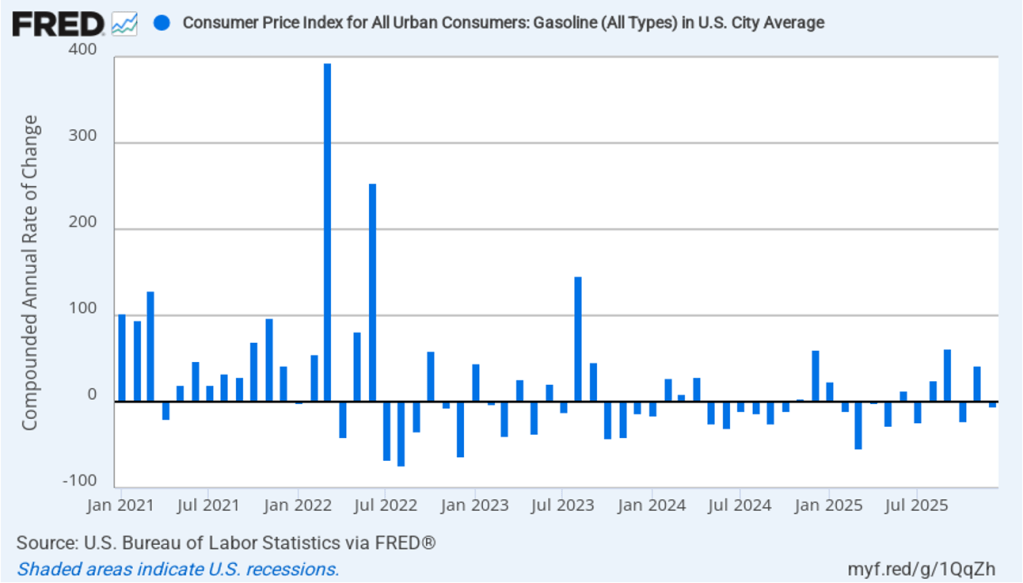
The news on changes in the price of gasoline was better for consumers. The following figure shows 1-month inflation in gasoline prices. In December, the price of gasoline fell by 5.3 percent after a very large 41.9 percent in November. As those values imply, 1-month inflation rates in gasoline are quite volatile.
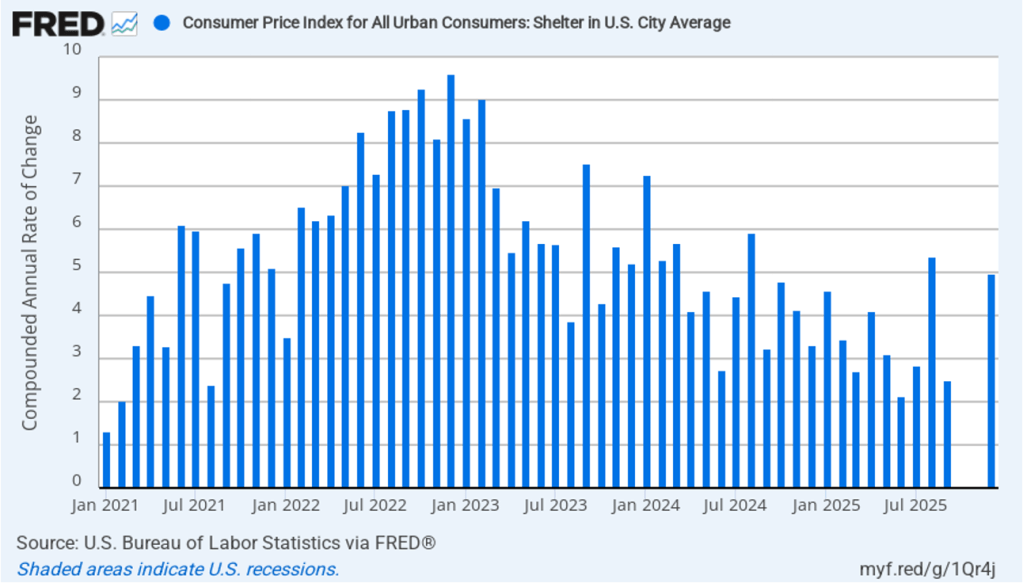
The affordability discussion has also focused on the cost of housing. The price of shelter in the CPI, as explained here, includes both rent paid for an apartment or a house and “owners’ equivalent rent of residences (OER),” which is an estimate of what a house (or apartment) would rent for if the owner were renting it out. OER is included in the CPI to account for the value of the services an owner receives from living in an apartment or house. The following figure shows 1-month inflation in shelter.
One-month inflation in shelter jumped in December to 5.0 percent from 2.5 percent in September, although it was down from 5.4 percent in August.
Overall, then, inflation in food and shelter was high in December, although gasoline prices fell in that month.
This CPI report is unlikely to affect the action the Federal Reserve’s policymaking Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) may take at its next meeting on January 27–28. Investors who buy and sell federal funds futures contracts assign a very high probability to the FOMC leaving its target for the federal funds rate unchanged at that meeting as well as at its meeting on March 17–18. Investors don’t expect the committee to cut its target range for the federal funds rate until its June 16–17 meeting. (We discuss the futures market for federal funds in this blog post.)
By the time of the FOMC’s June meeting, the committee will have several additional months’ data on inflation, employment, and output. Jerome Powell’s term as Fed chair will end on May 15, so presumably the FOMC will have a new chair at that meeting. (This blog post from yesterday includes Powell’s response to the news that he is under investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice and a statement by Glenn and other economists who have served in government objecting to the investigation because they believe that it will undermine the independence of the Fed. We discuss the issue of Fed independence in Macroeconomics, Chapter 17 (Economics, Chapter 27) and Money, Banking, and the Financial System, Chapter 13.)