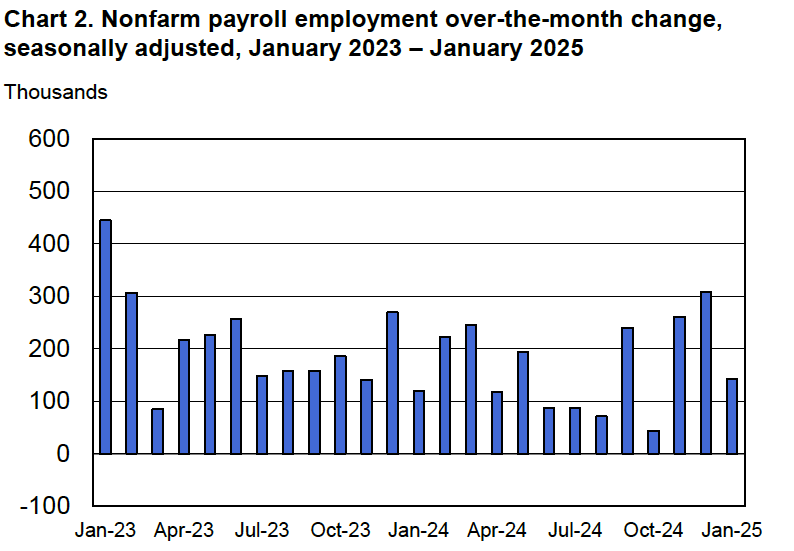
Fed Chair Jerome Powell speaking at a press conference following a meeting of the FOMC (photo from federalreserve.gov)
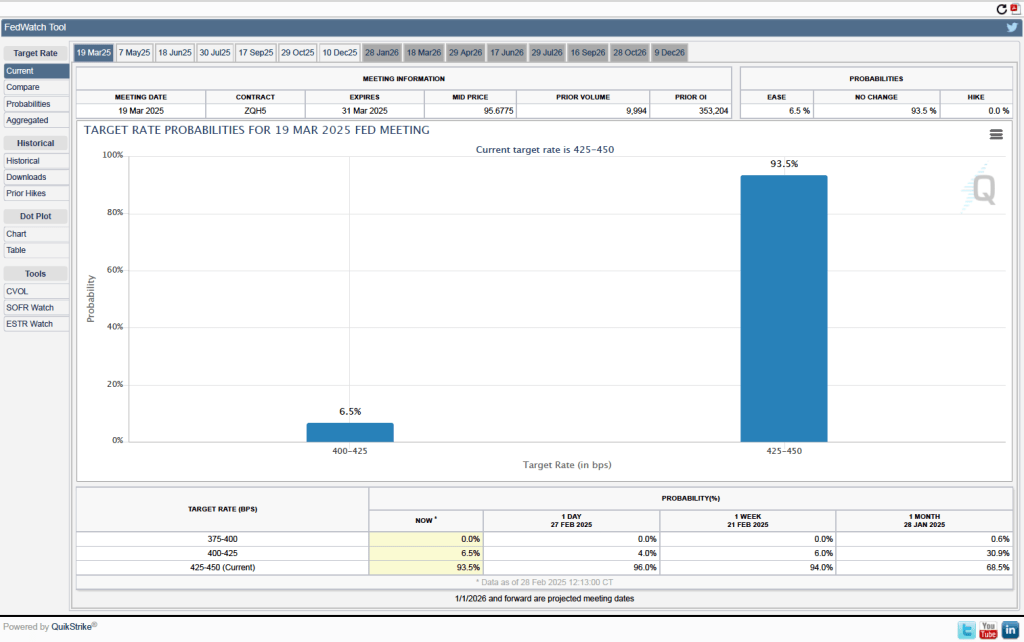
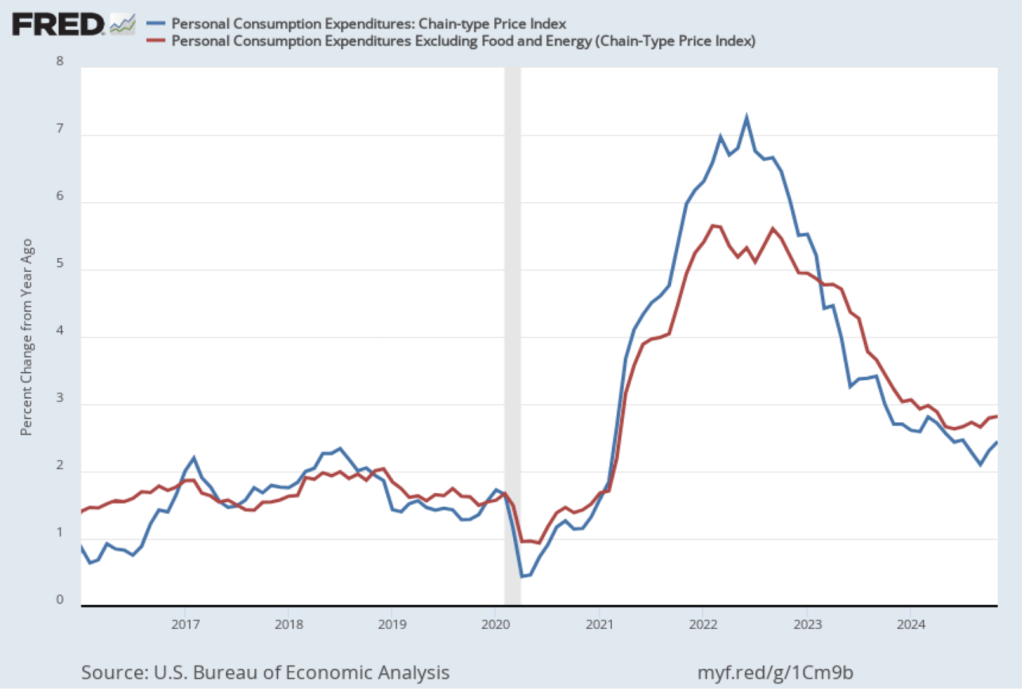
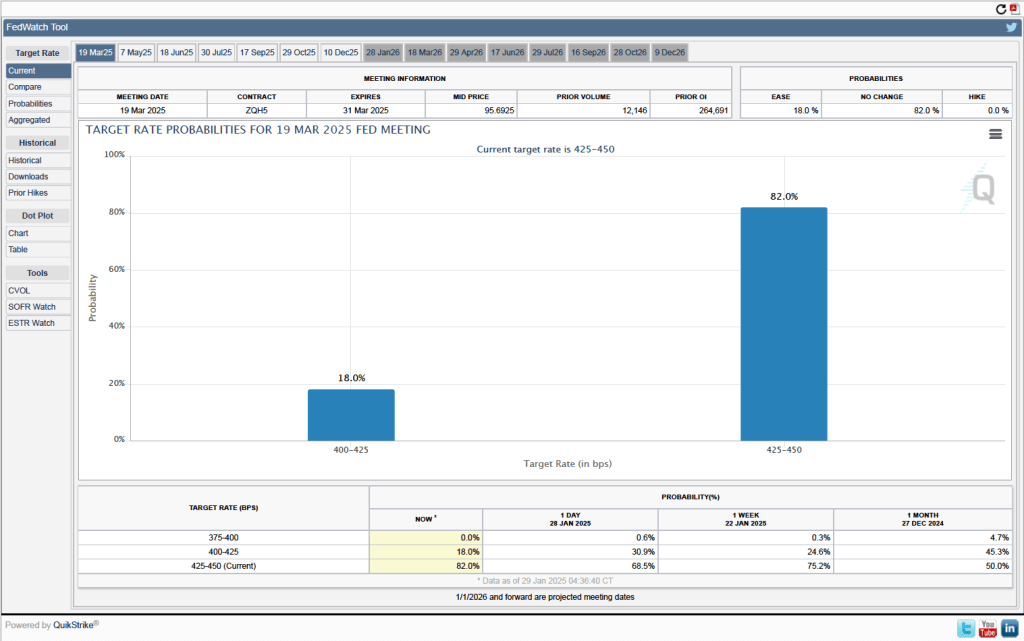
As they had before their previous meeting, members of the Fed’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) had signaled that the committee was likely to leave its target range for the federal funds rate unchanged at 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent at its meeting today (March 19). In a press conference following the meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell noted that the FOMC was facing significant policy uncertainty:
“Looking ahead, the new Administration is in the process of implementing significant policy changes in four distinct areas: trade, immigration, fiscal policy, and regulation…. While there have been recent developments in some of these areas, especially trade policy, uncertainty around the changes and their effects on the economic outlook is high…. We do not need to be in a hurry to adjust our policy stance, and we are well positioned to wait for greater clarity.”
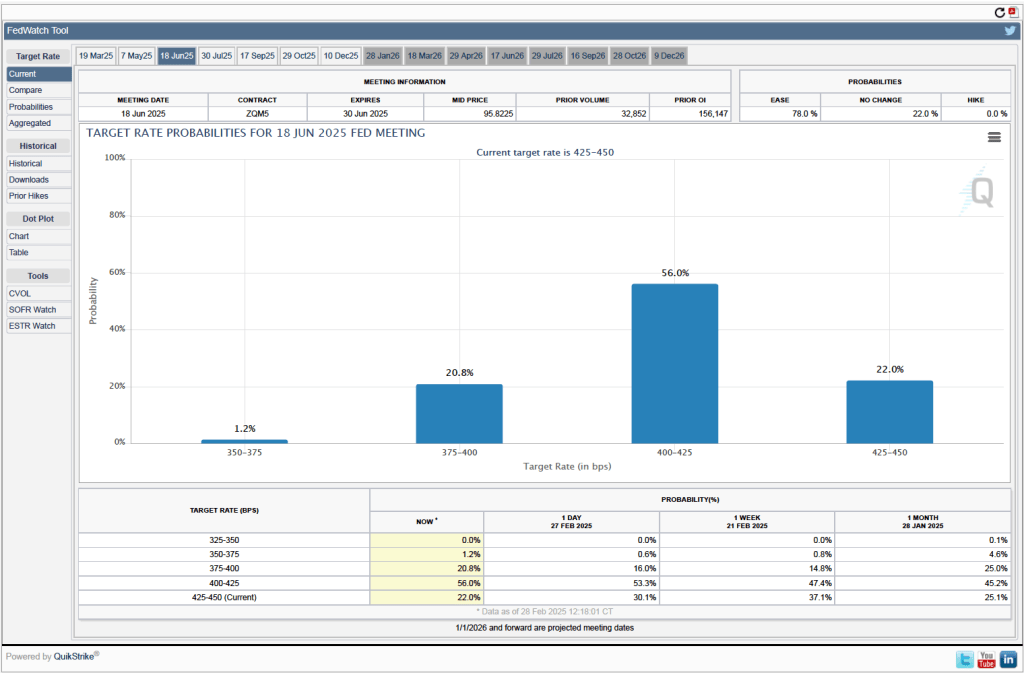
The next scheduled meeting of the FOMC is May 6–7. It seems likely that the committee will also keep its target rate constant at that meeting. Although at his press conference, Powell noted that “Policy is not on a preset course. As the economy evolves, we will adjust our policy stance in a manner that best promotes our maximum employment and price stability goals.” The statement the committee released after the meeting showed that the decision to leave the target rate unchanged was unanimous.
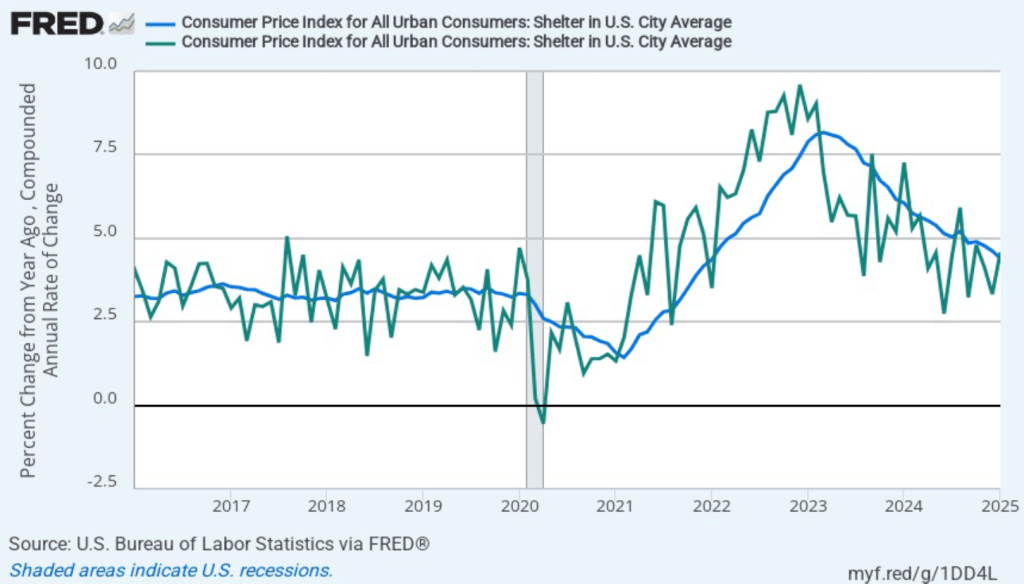
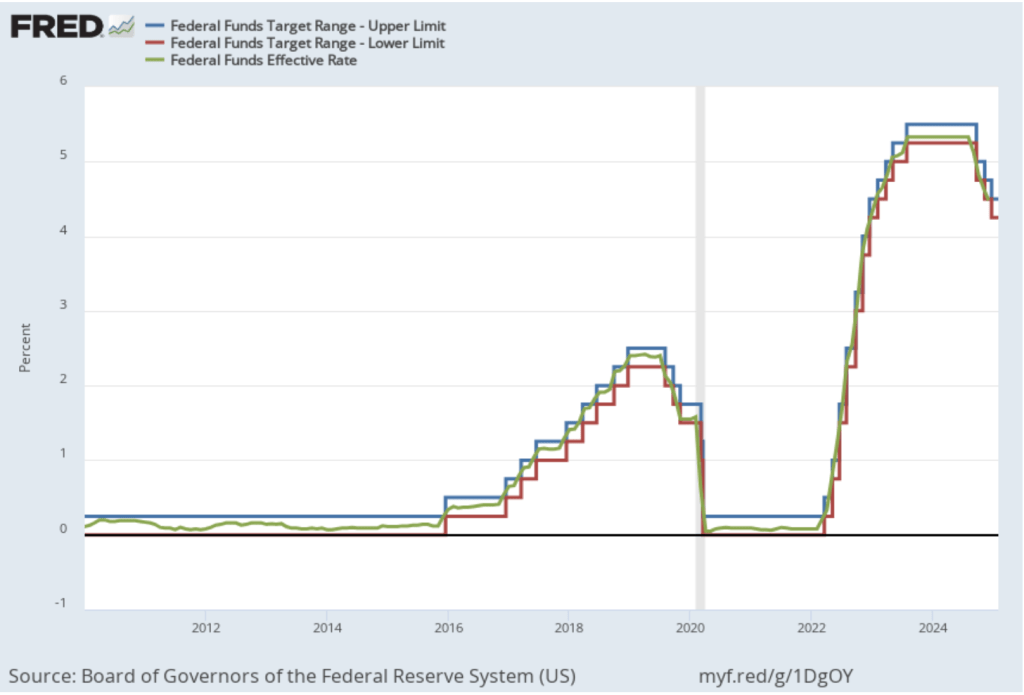
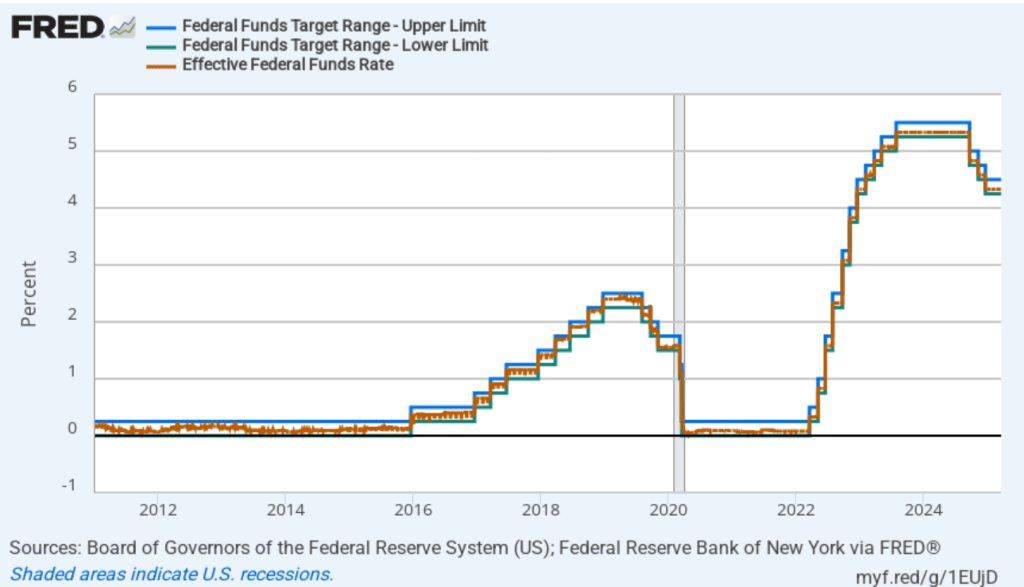
The following figure shows, for the period since January 2010, the upper bound (the blue line) and lower bound (the green line) for the FOMC’s target range for the federal funds rate and the actual values of the federal funds rate (the red line) during that time. Note that the Fed is successful in keeping the value of the federal funds rate in its target range. (We discuss the monetary policy tools the FOMC uses to maintain the federal funds rate in its target range in Macroeconomics, Chapter 15, Section 15.2 (Economics, Chapter 25, Section 25.2).)
After the meeting, the committee also released a “Summary of Economic Projections” (SEP)—as it typically does after its March, June, September, and December meetings. The SEP presents median values of the 18 committee members’ forecasts of key economic variables. The values are summarized in the following table, reproduced from the release.
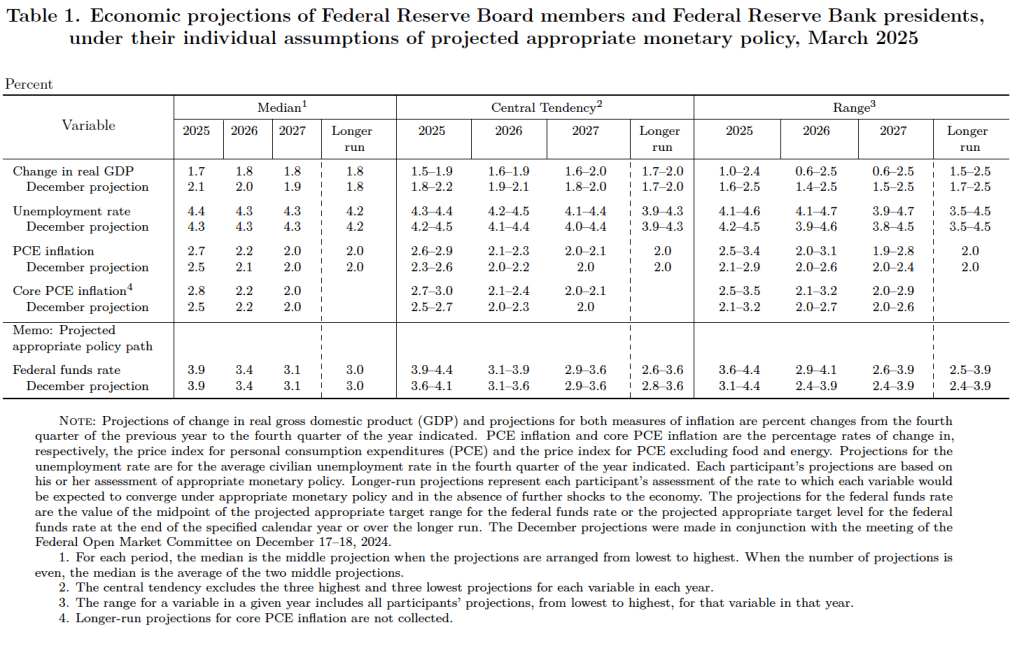
There are several aspects of these forecasts worth noting:
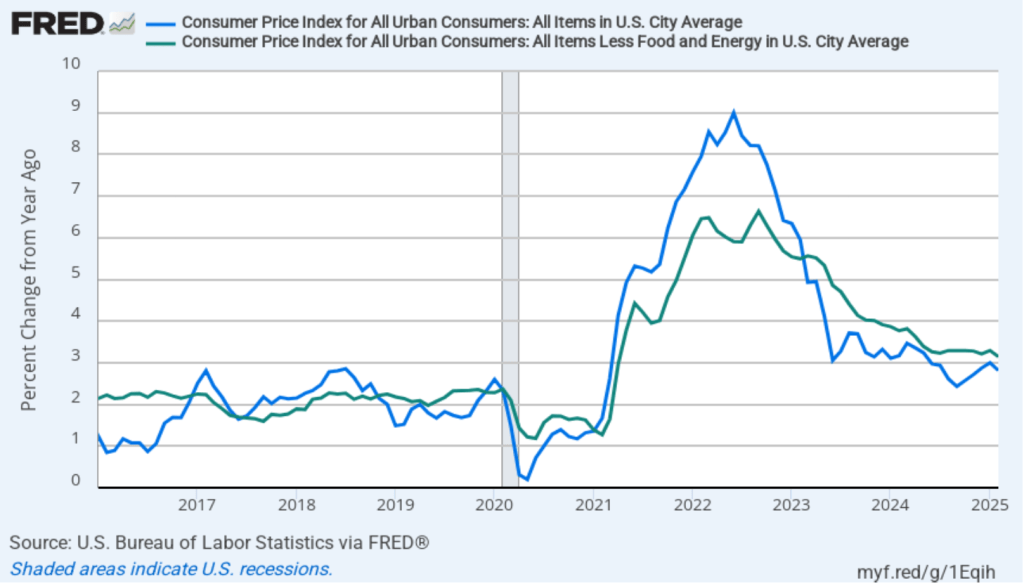
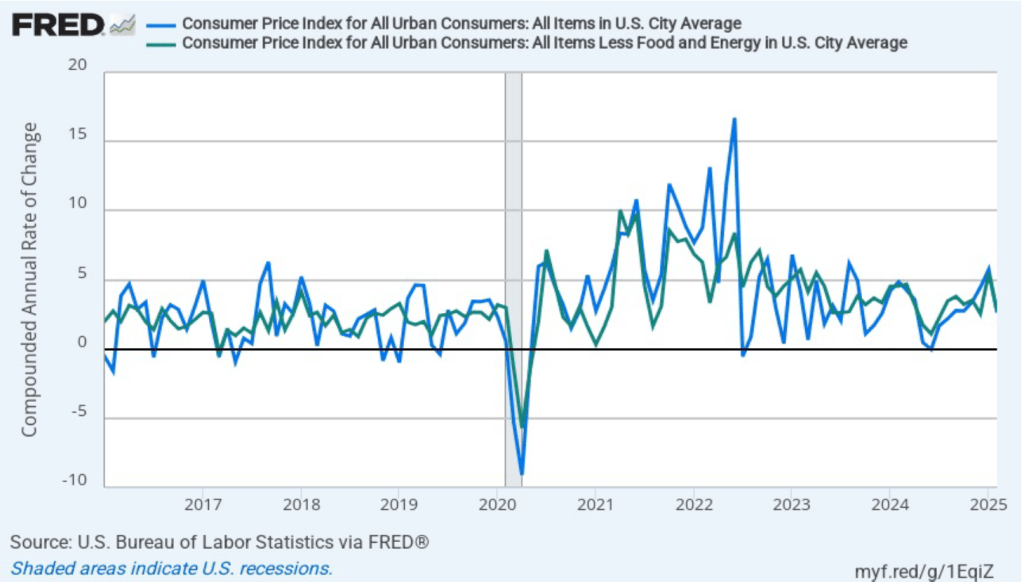
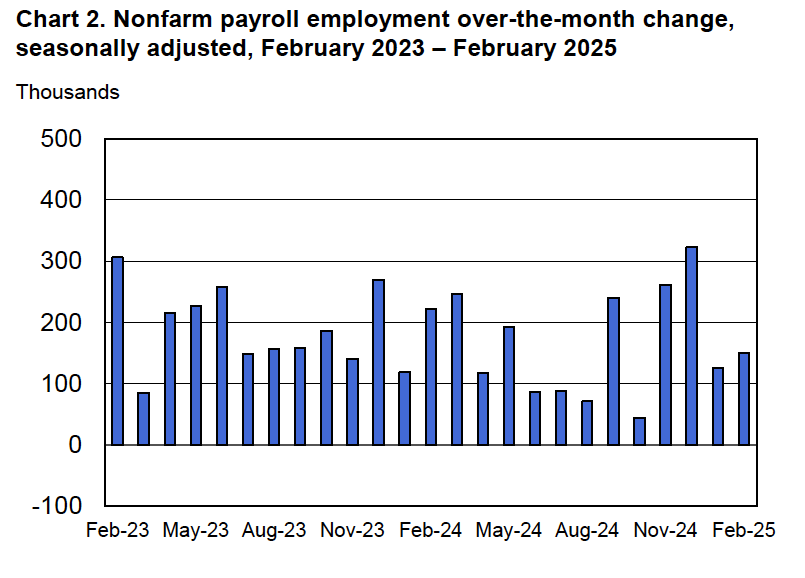
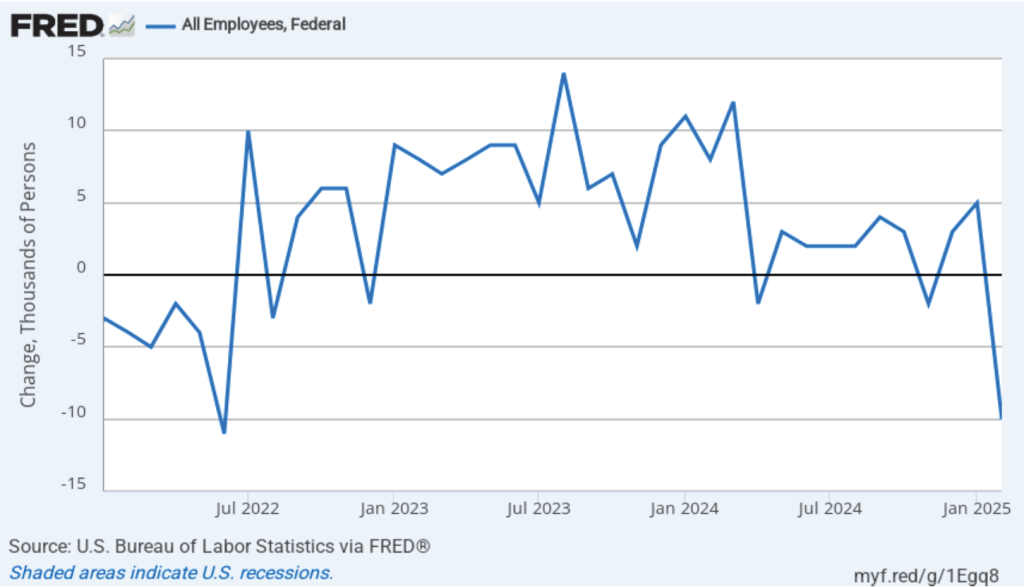
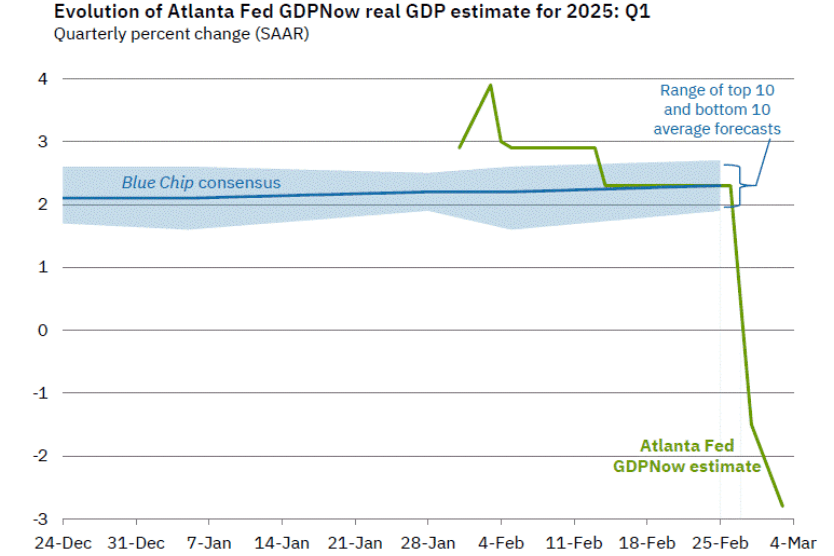
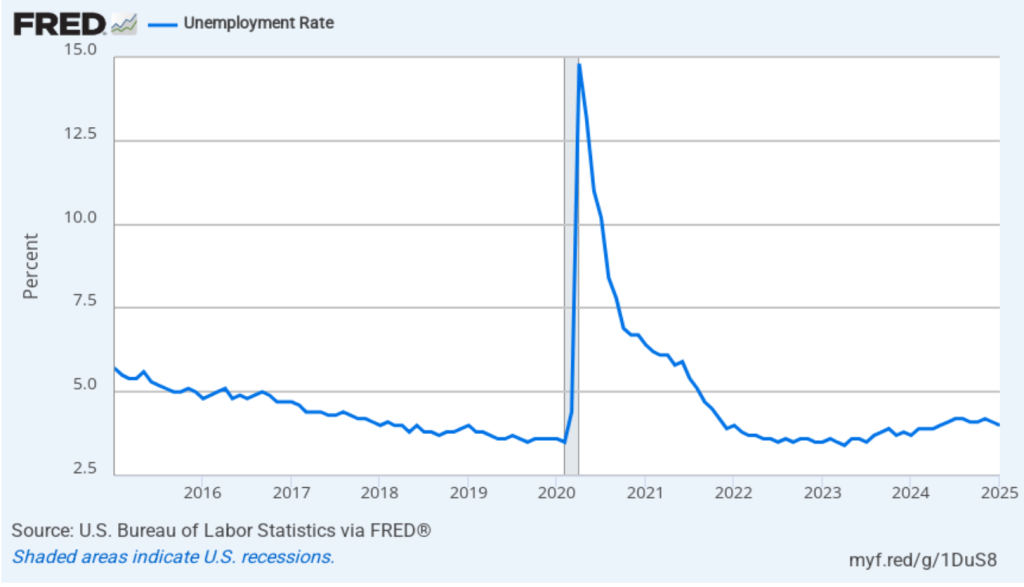
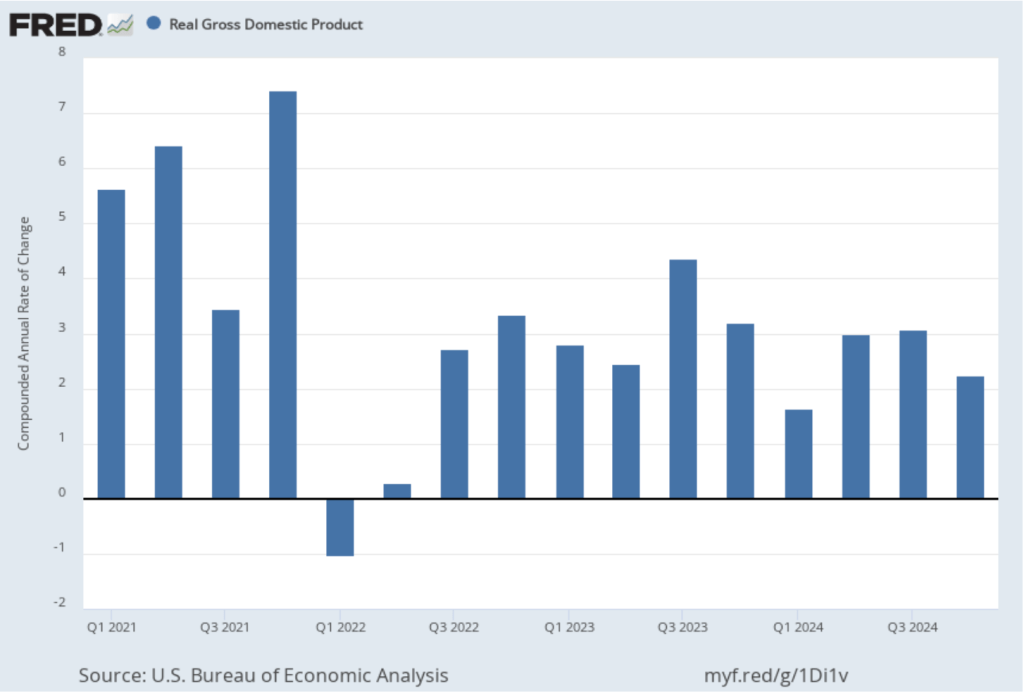
- Committee members reduced their forecast of real GDP growth for 2025 from 2.1 percent in December to 1.7 percent today. Committee members also slightly increased their forecast of the unemployment rate at the end of 2025 from 4.3 percent to 4.4 percent. (The unemployment rate in February was 4.1 percent.)
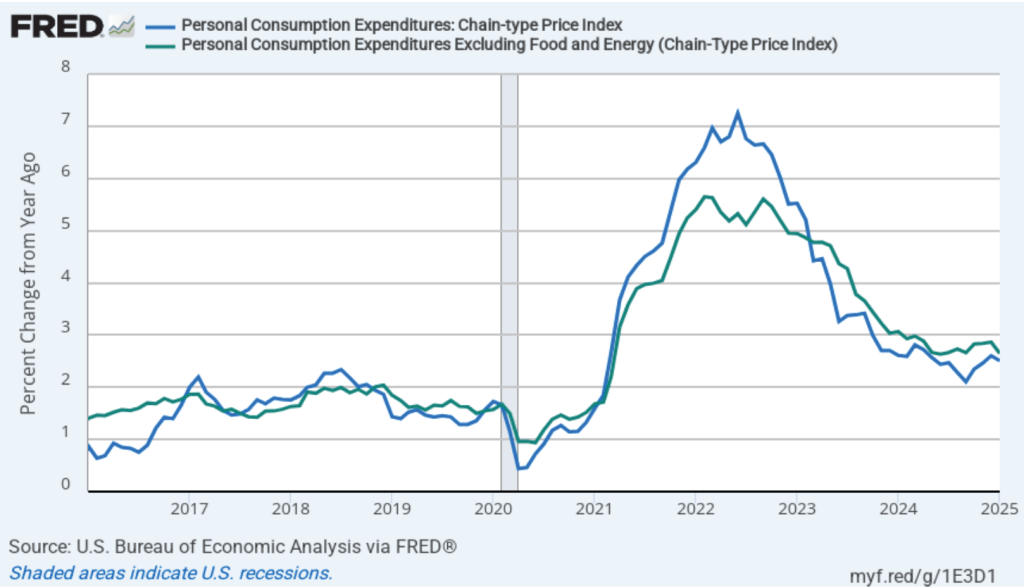
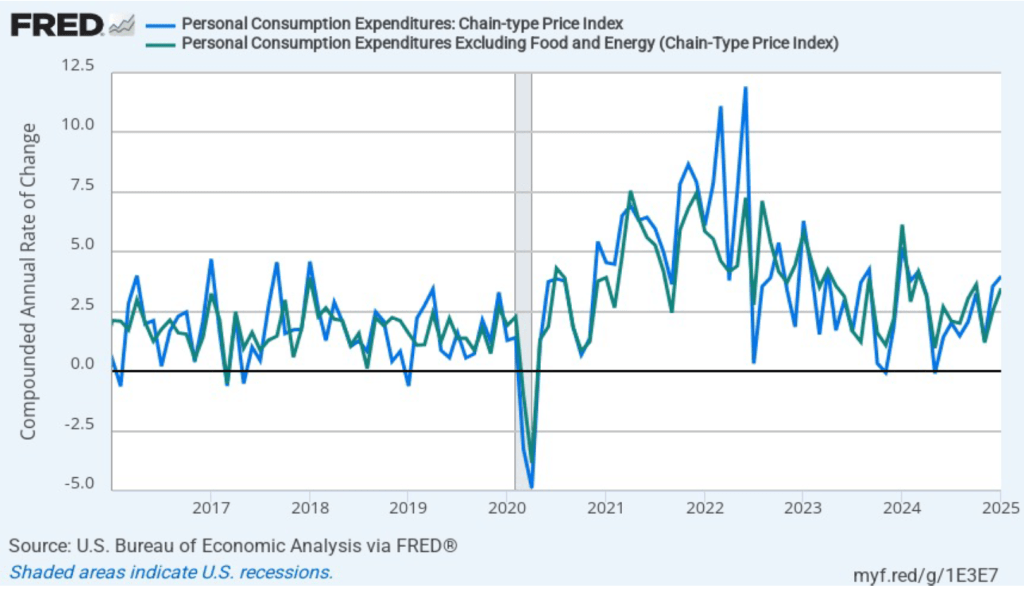
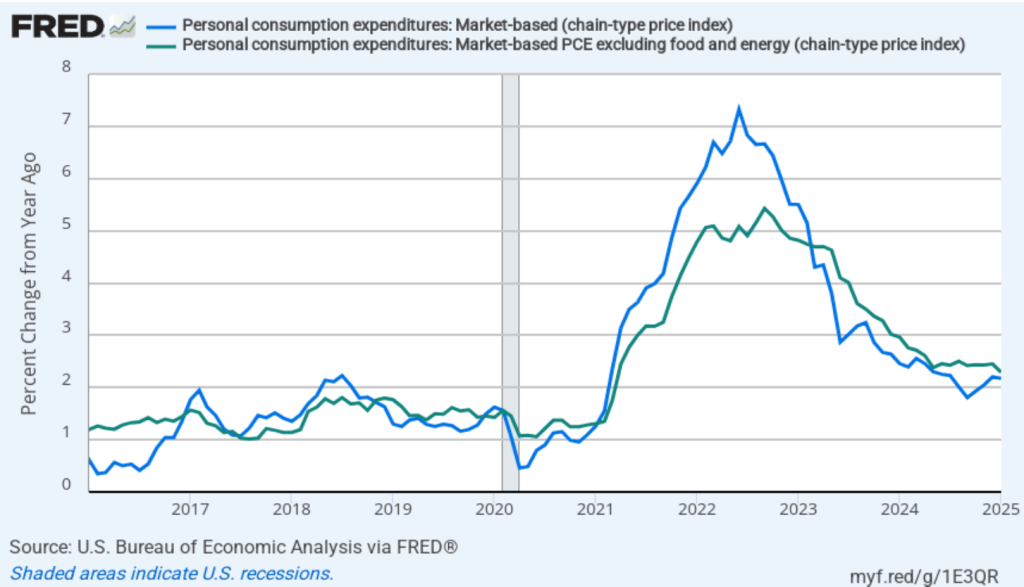
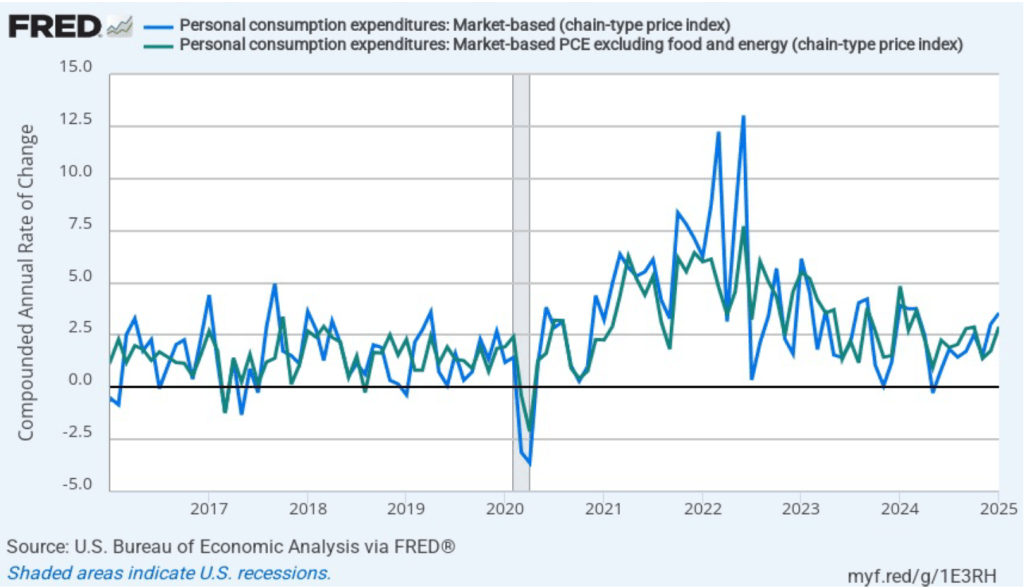
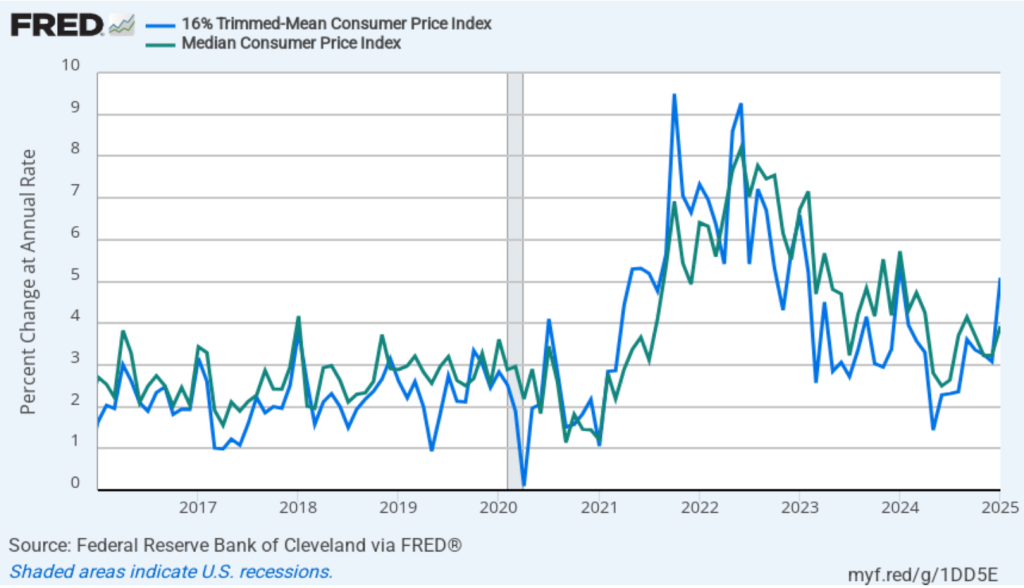
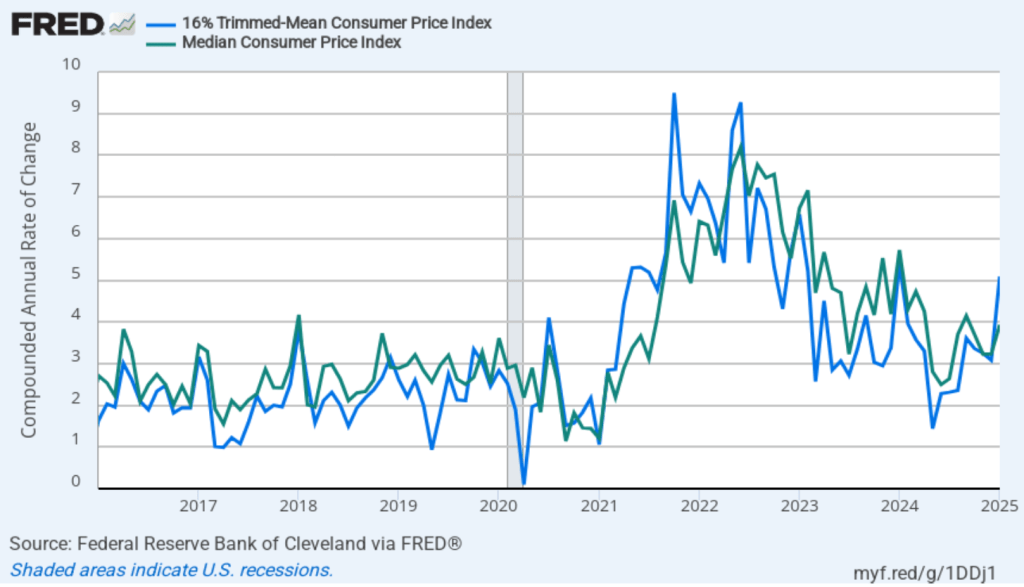
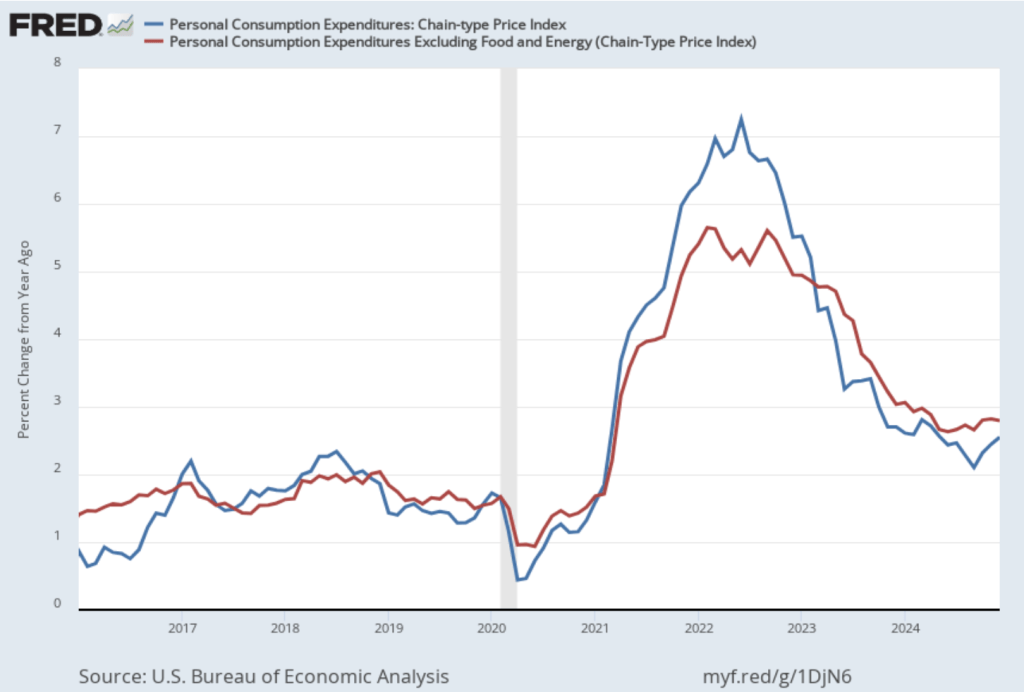
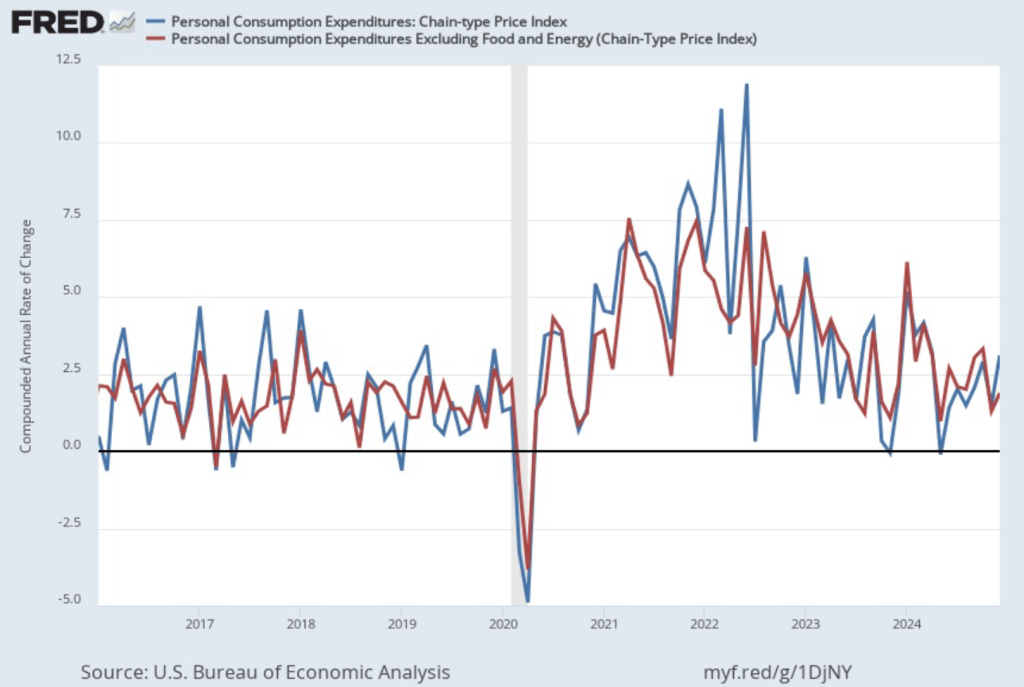
- Committee members now forecast that personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price inflation will be 2.7 percent at the end of 2025. In December, they had forecast that it would 2.5 percent. Similarly, their forecast of core PCE inflation increased from 2.5 percent to 2.8 percent. The committee does not expect that PCE inflation will decline to the Fed’s 2 percent annual target until 2027.
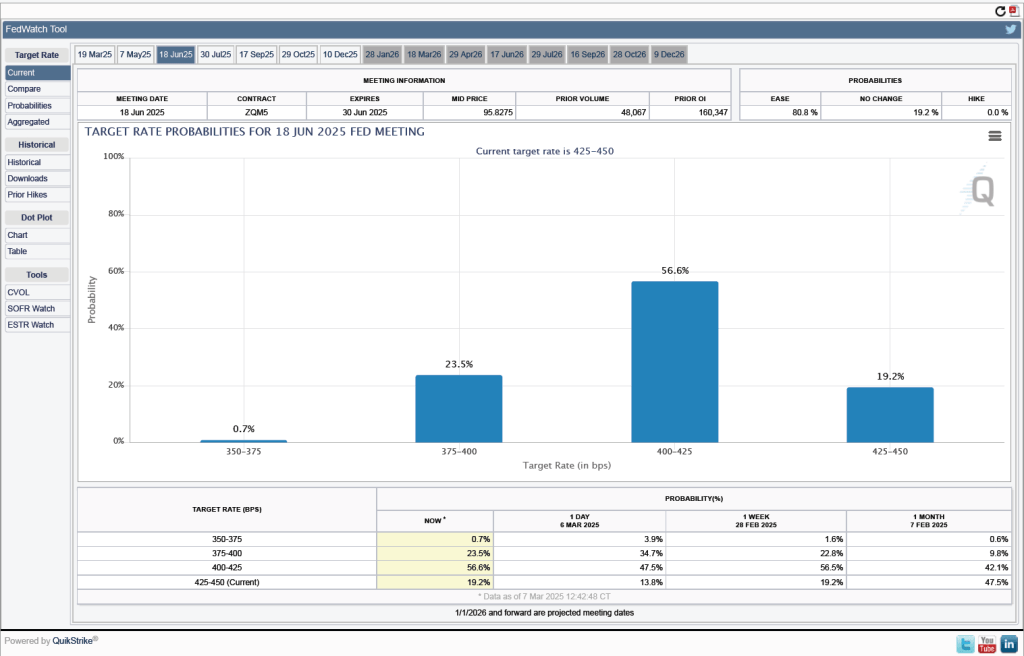
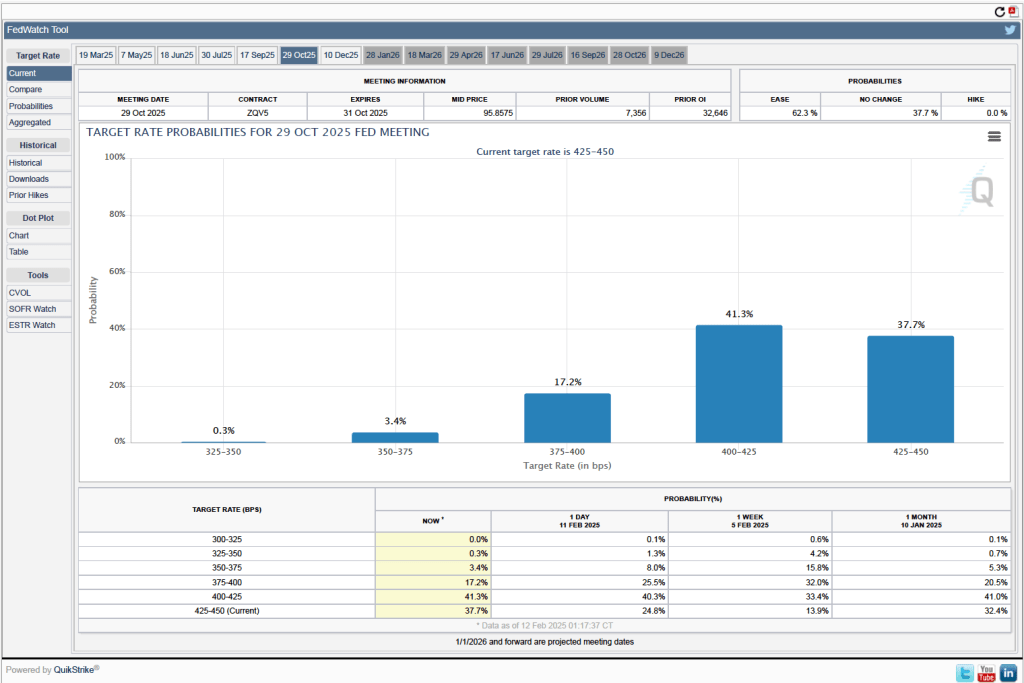
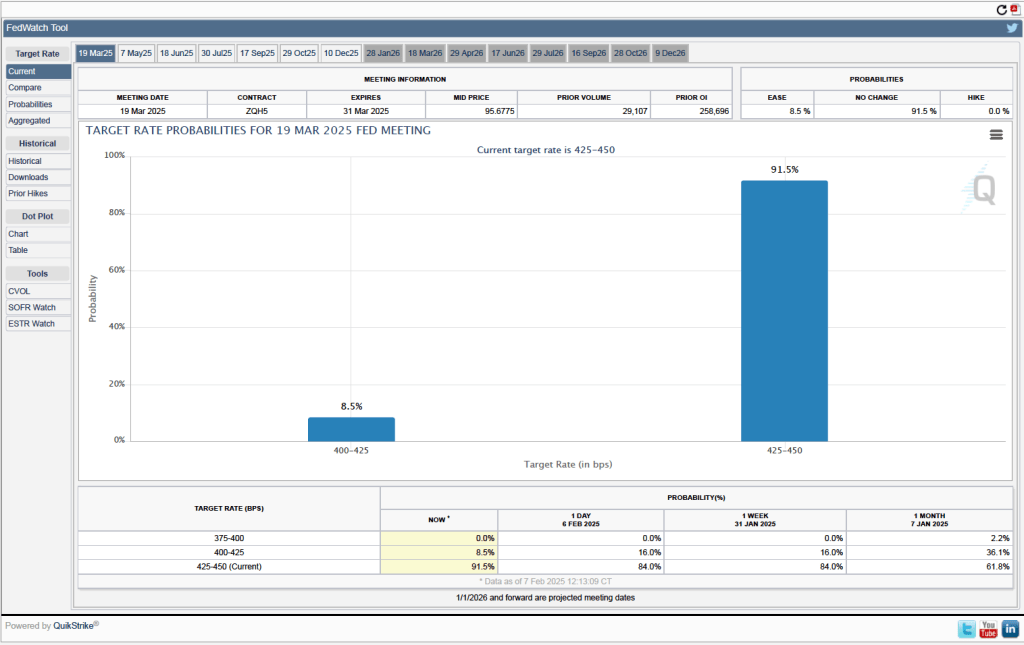
- The committee’s forecast of the federal funds rate at the end of 2025 was unchanged at 3.9 percent. The federal funds rate today is 4.33 percent, which indicates that committee members expect to make two 0.25 percentage point (25 basis points) cuts in their target for the federal funds rate this year. Investors are similarly forecasting two 25 basis point cuts.
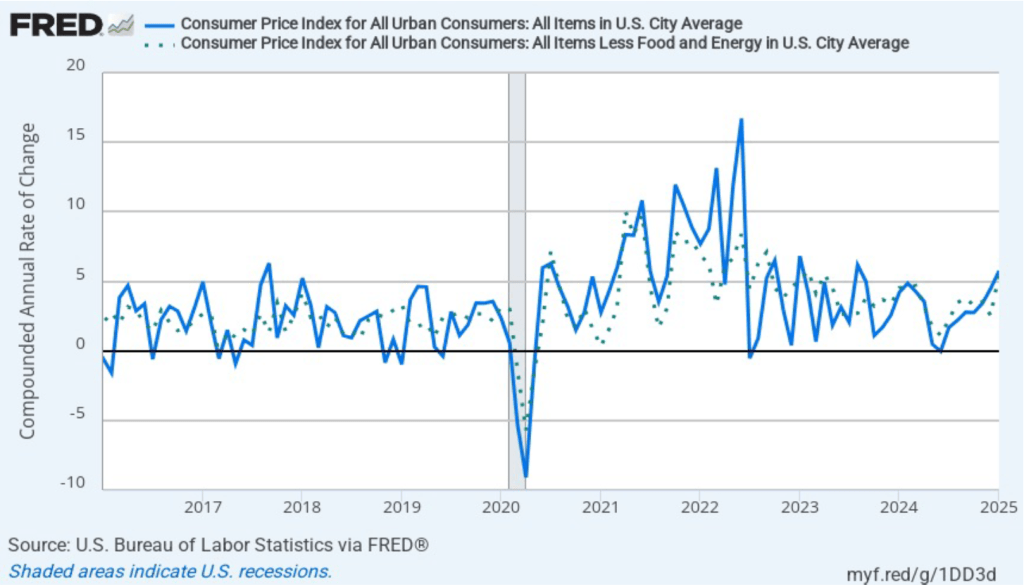
During his press conference, Powell indicated that a significant part of the increase in goods inflation during the first two months of the year was likely due to tariffs, although the Fed’s staff was unable to make a precise estimate of how much. Economists generally believe that tariffs cause one-time increases in the price level, rather than persistent inflation. Powell was asked during the press conference whether the FOMC was likely to “look through”—that is, not respond—to the tariffs. Powell replied that it was too early to make that decision, but that: “If there’s an inflation that’s going to go away on its own, it’s not the correct response to tighten policy.”
Powell noted that although surveys show that businesses and consumers expect an increase in inflation, over the long run, expectations are that the inflation rate will return to the Fed’s 2 percent annual target. In that sense, Powell said that expectations of inflation remain “well anchored.”
Barring a sharp slowdown in the growth of real GDP, a significant rise in the unemployment rate, or a significant rise in the inflation rate, the FOMC seems likely to leave its target for the federal funds rate unchanged over the next few months.