Image created by ChatGPT
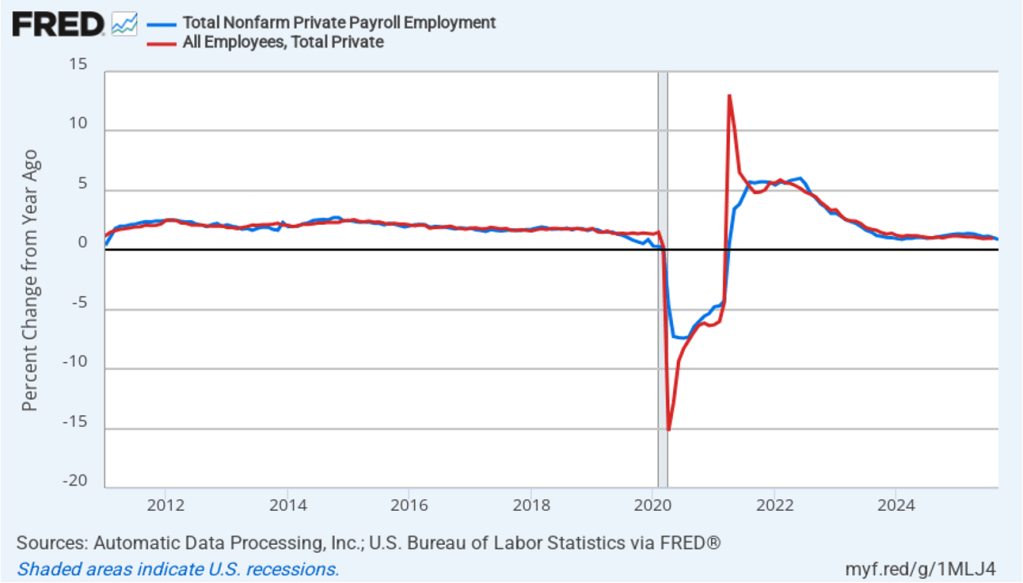
This morning (March 6), the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its “Employment Situation” report (often called the “jobs report”) for February. The jobs report for January showed a much stronger than expected increase in employment. Today’s report was a surprise in the opposite direction with employment unexpectedly declining.
The jobs report has two estimates of the change in employment during the month: one estimate from the establishment survey, often referred to as the payroll survey, and one from the household survey. As we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 9, Section 9.1 (Economics, Chapter 19, Section 19.1), many economists and Federal Reserve policymakers believe that employment data from the establishment survey provide a more accurate indicator of the state of the labor market than do the household survey’s employment data and unemployment data. (The groups included in the employment estimates from the two surveys are somewhat different, as we discuss in this post.)
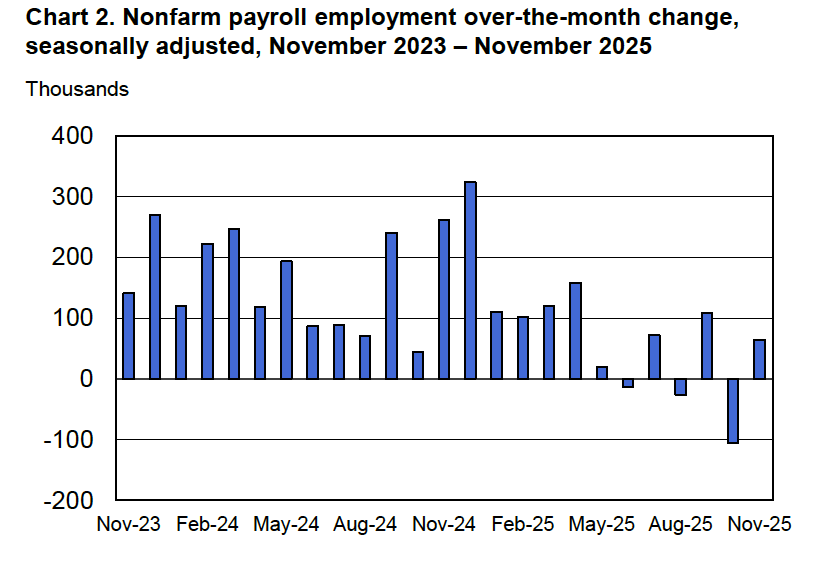
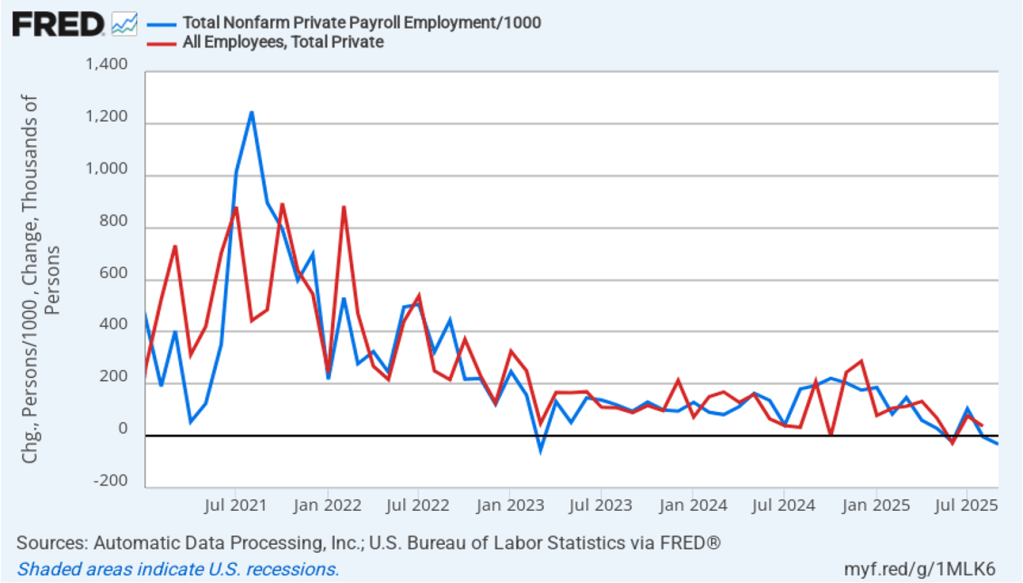
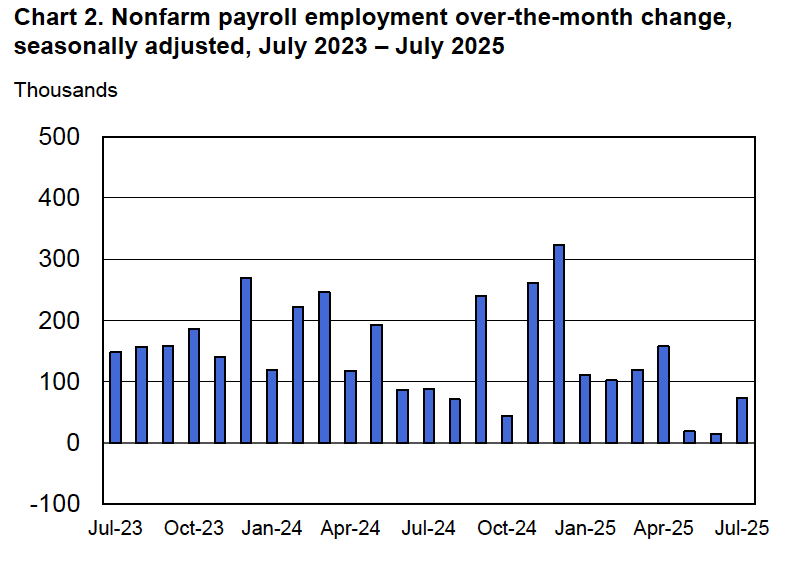
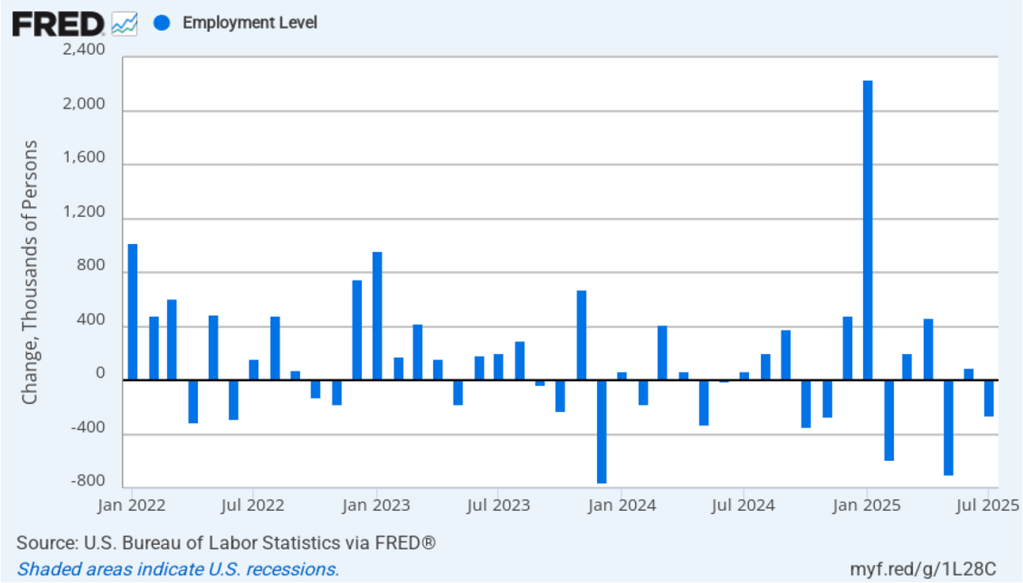
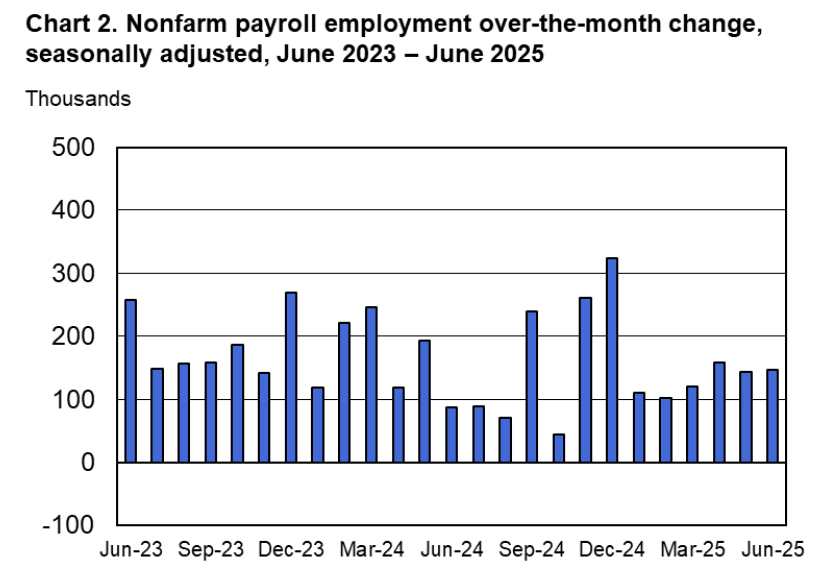
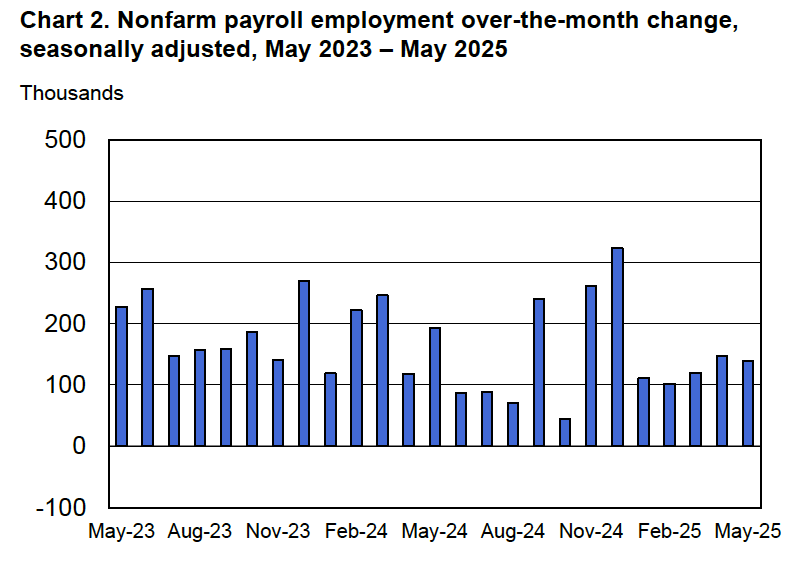
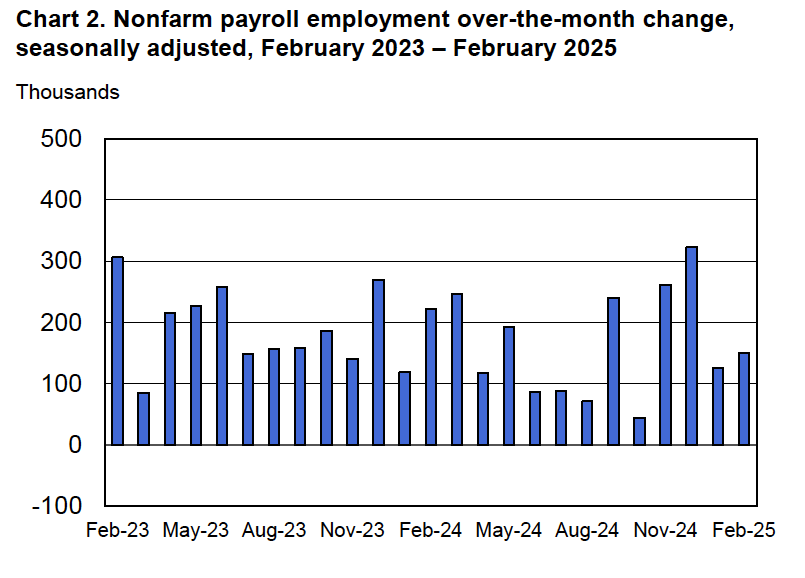
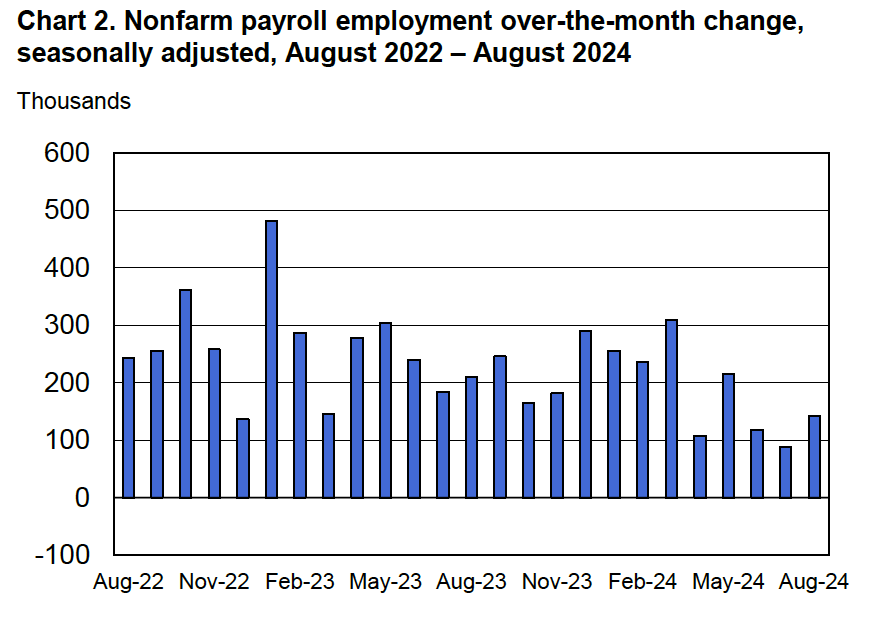
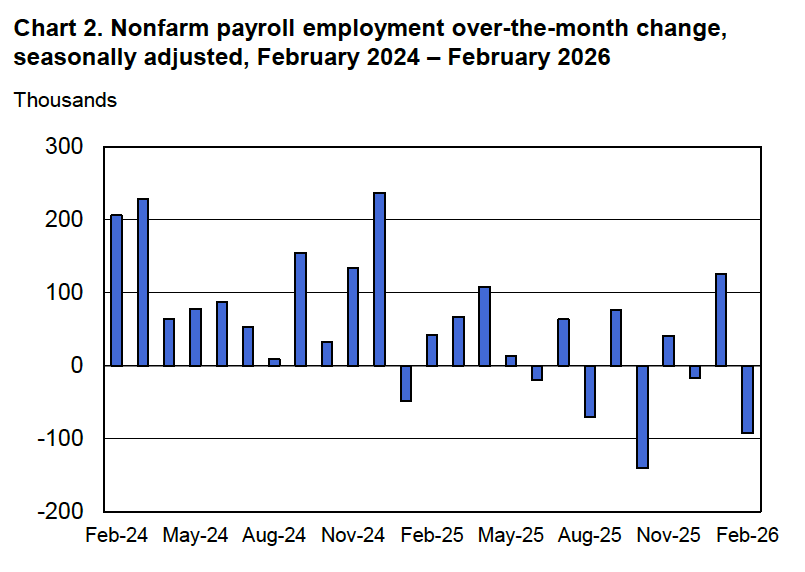
According to the establishment survey, there was a net decrease of 92,000 nonfarm jobs during February. Economists surveyed by the Wall Street Journal had forecast an increase of 50,000 jobs. Economists surveyed by FactSet had a higher forecast of a net increase of 70,000 jobs. The BLS revised downward its previous estimates of employment in December and January by a combined 69,000 jobs. The revised estimate indicates that employment fell in December by 17,000 rather than increasing by 48,000 as in the previous estimate. (The BLS notes that: “Monthly revisions result from additional reports received from businesses and government agencies since the last published estimates and from the recalculation of seasonal factors.”)
The following figure from the jobs report shows the net change in nonfarm payroll employment for each month in the last two years. The current estimates show a net decrease in employment during five of the last nine months.
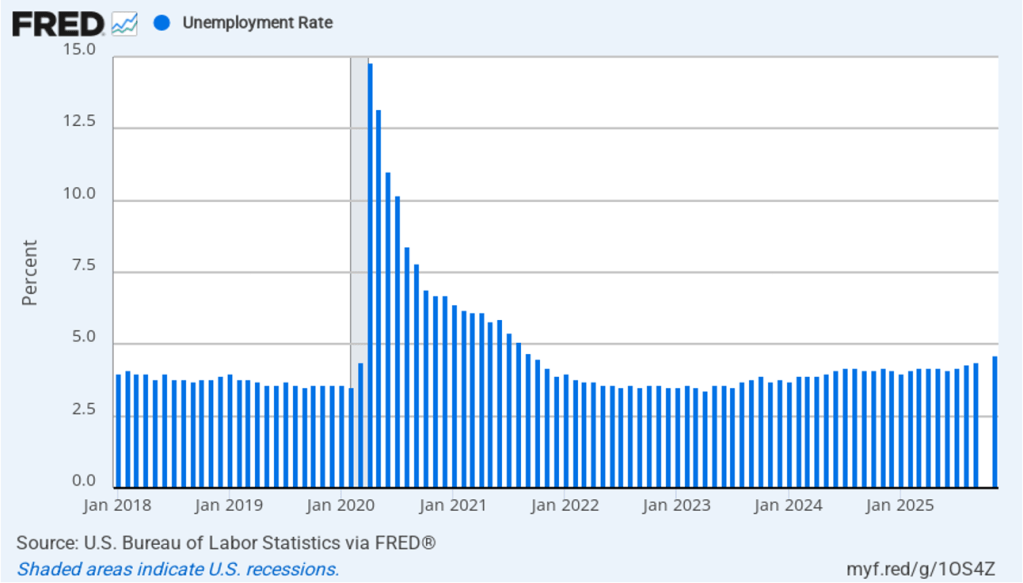
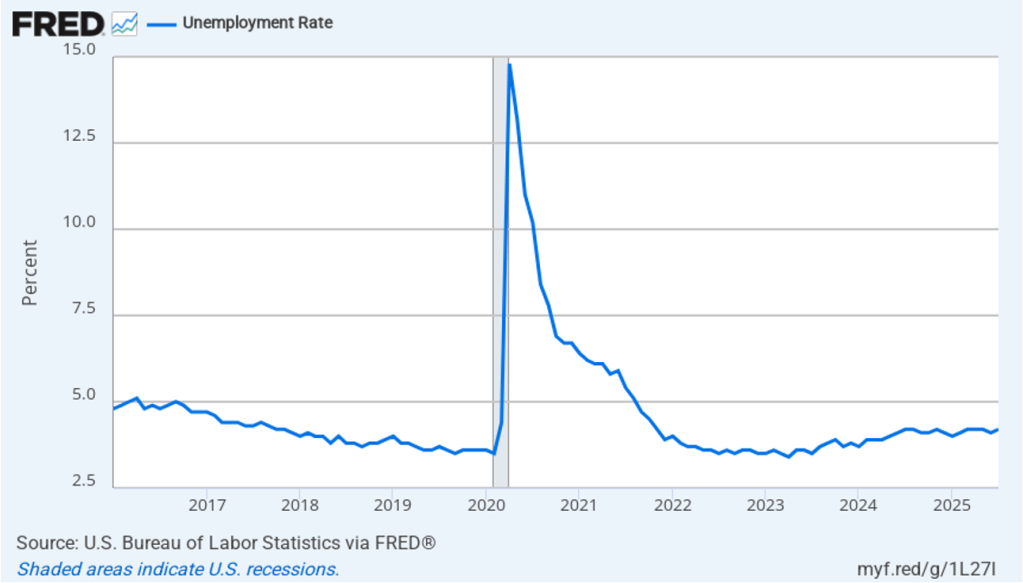
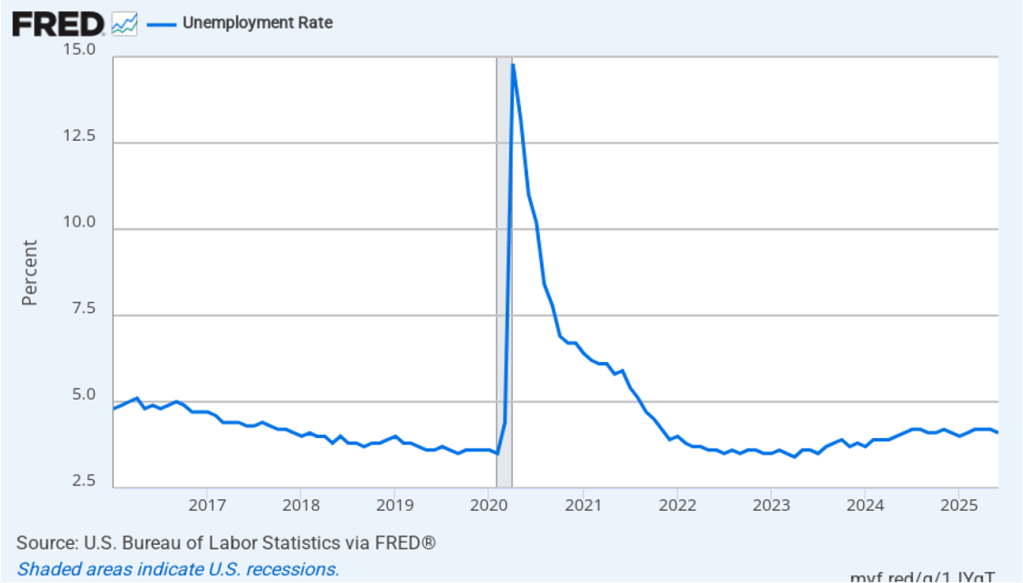
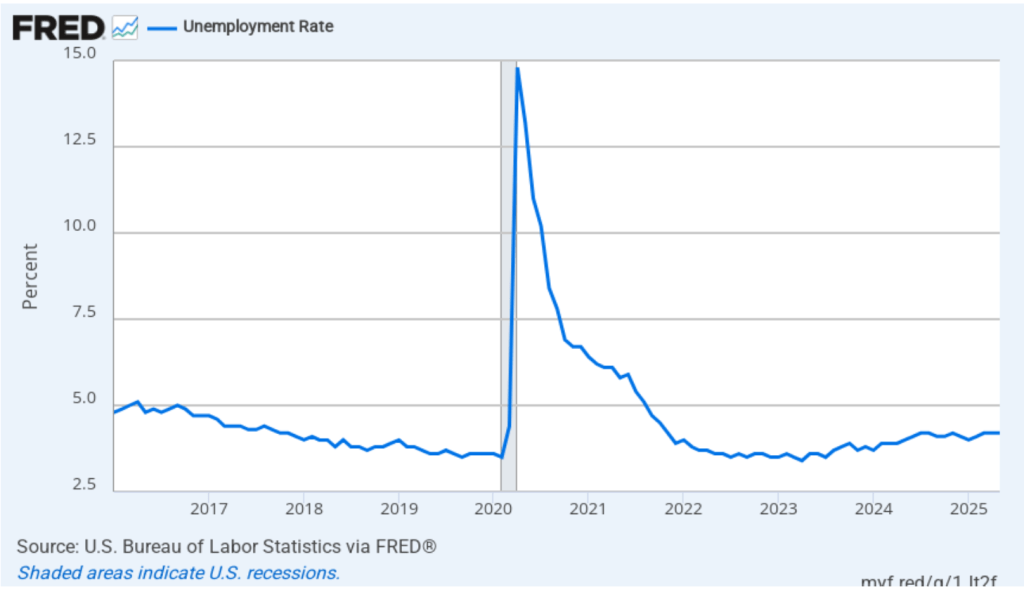
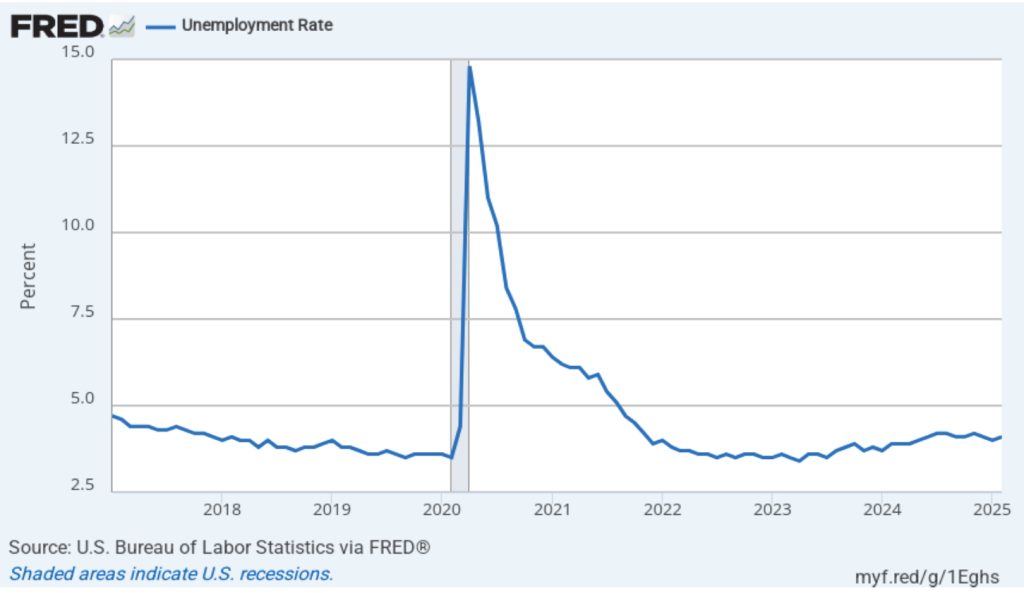
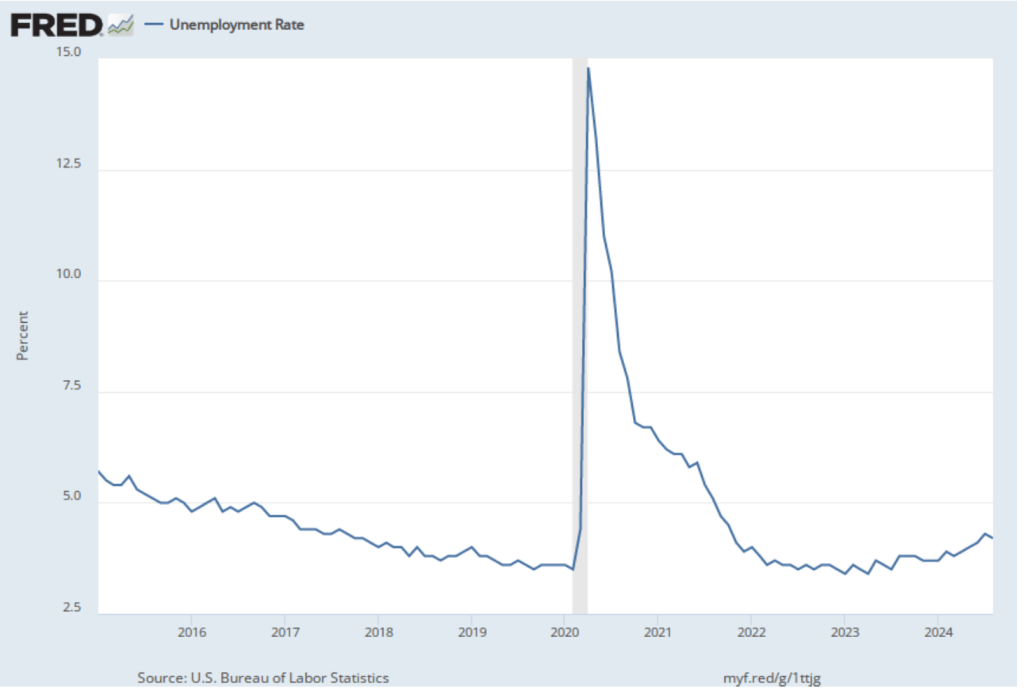
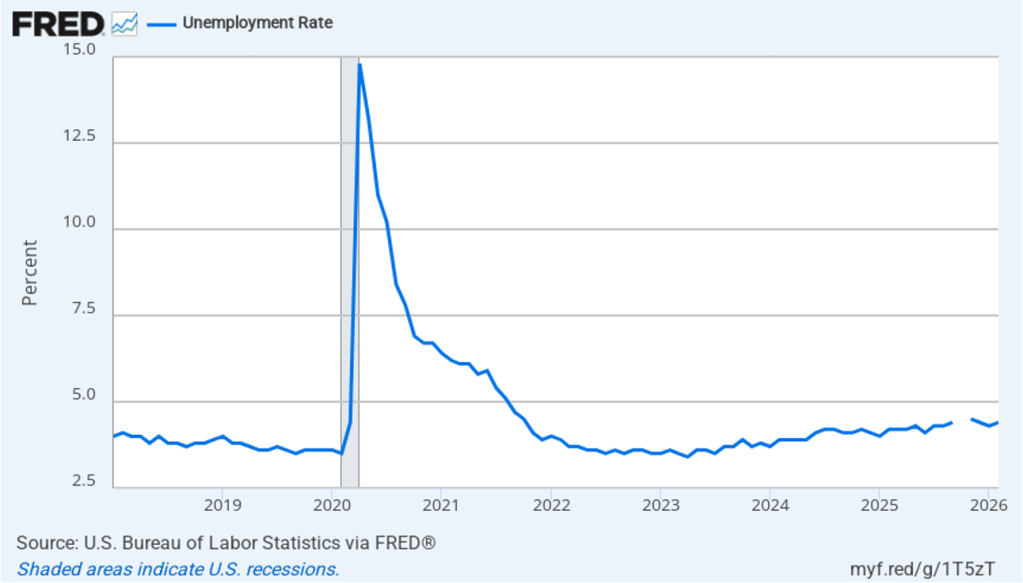
The unemployment rate, which is calculated from data in the household survey, increased to 4.4 percent in February for 4.3 percent in January. As the following figure shows, the unemployment rate has been remarkably stable over the past year and a half, staying between 4.0 percent and 4.4 percent in each month since May 2024. The Federal Open Market Committee’s current estimate of the natural rate of unemployment—the normal rate of unemployment over the long run—is 4.2 percent. So, unemployment is slightly above that estimate of the natural rate. (We discuss the natural rate of unemployment in Macroeconomics, Chapter 9 and Economics, Chapter 19.)
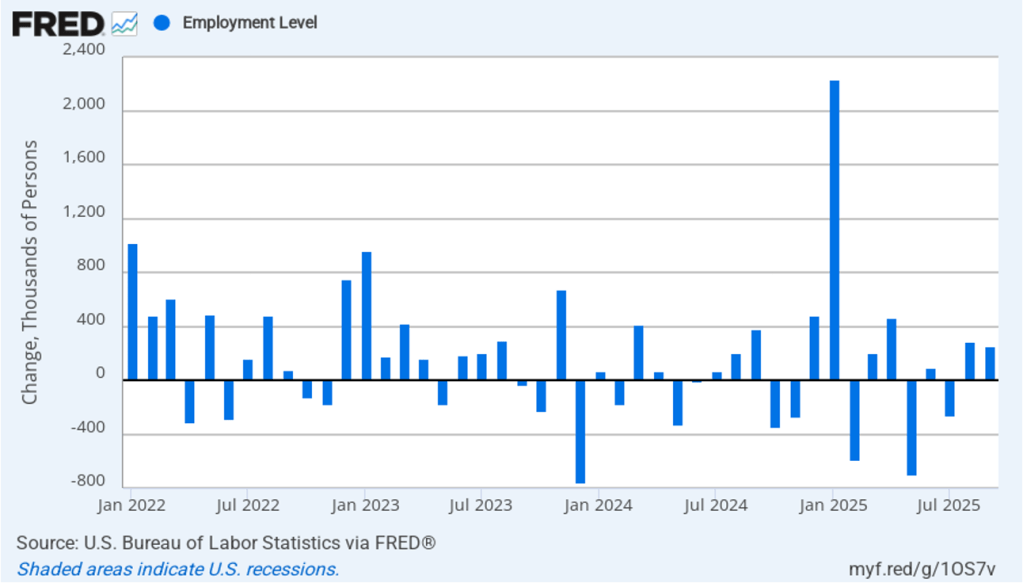
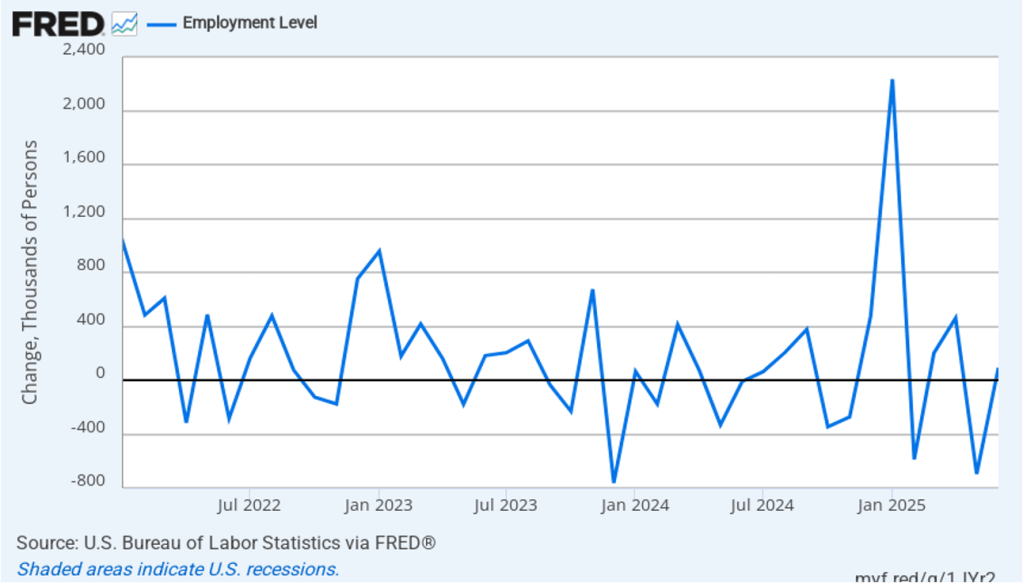
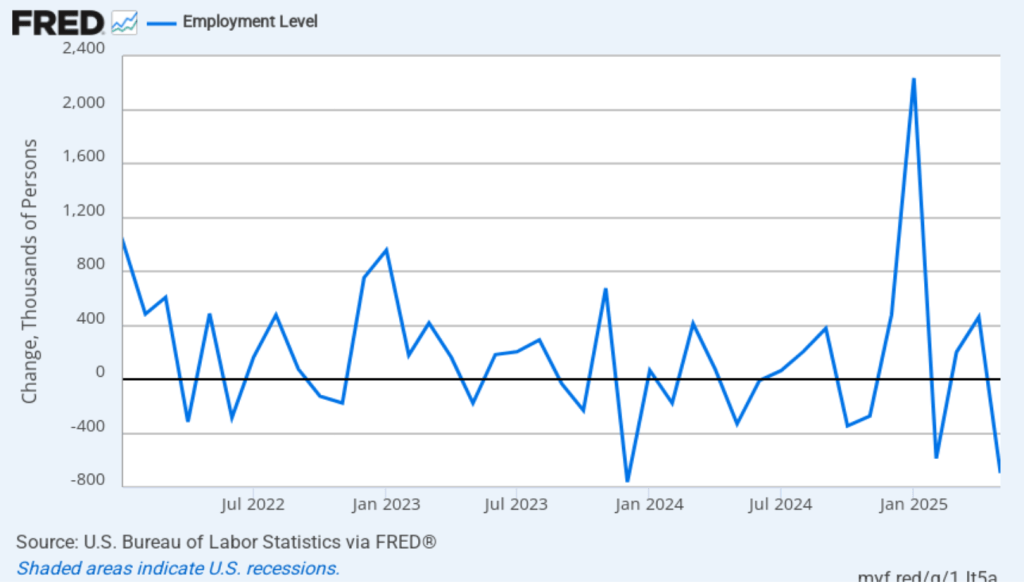
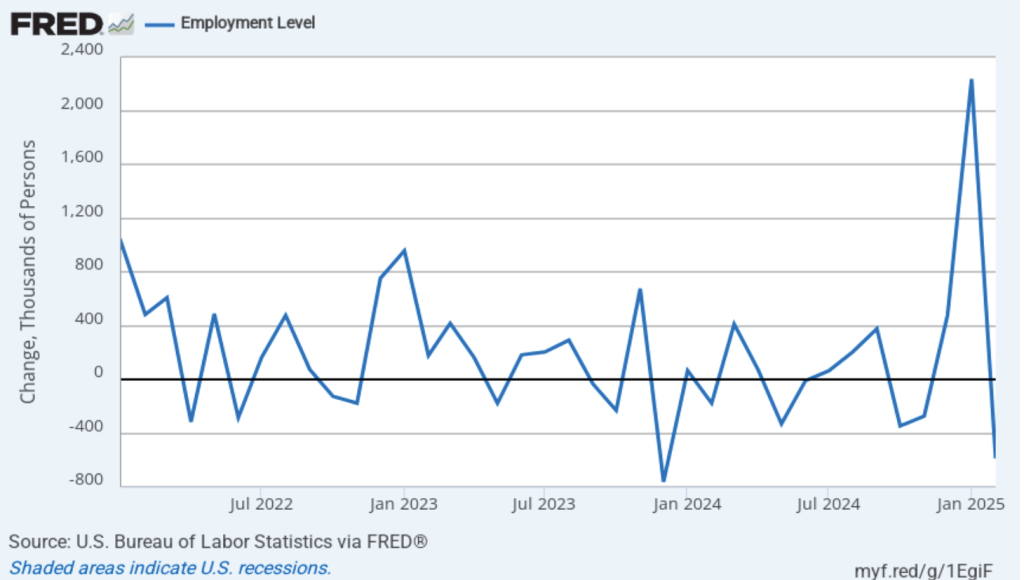
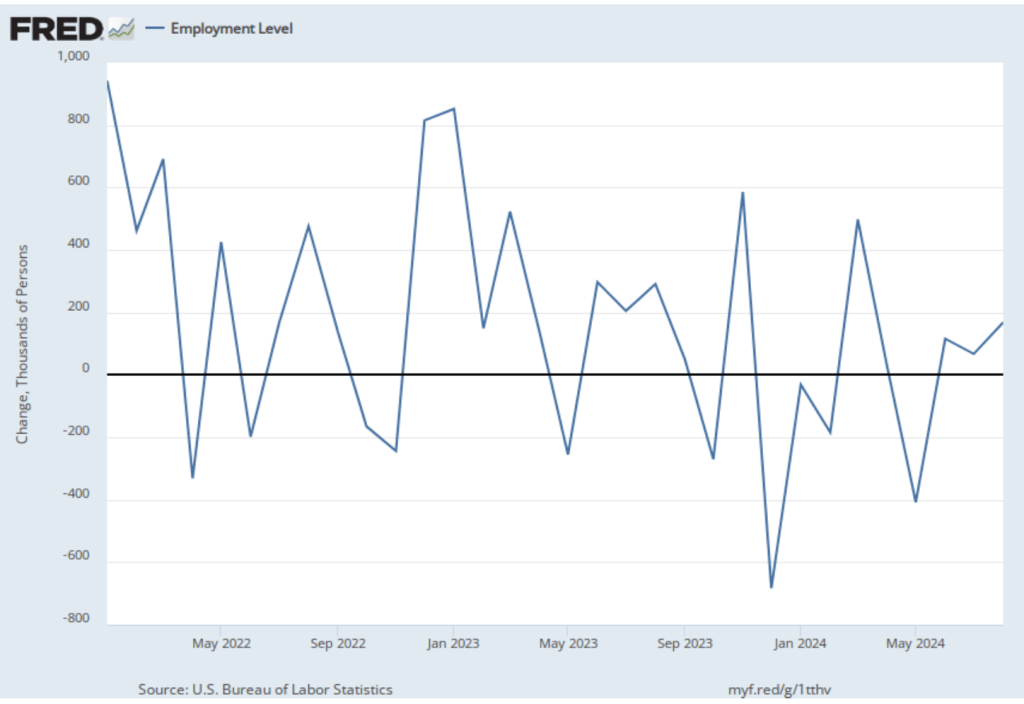
As the following figure shows, the monthly net change in jobs from the household survey moves much more erratically than does the net change in jobs from the establishment survey. As measured by the household survey, there was a net decrease of 185,000 in February. (Note that because of last year’s shutdown of the federal government, there are no data for October or November.) In any particular month, the story told by the two surveys can be inconsistent. In this case, both surveys indicate a net decline in employment. (In this blog post, we discuss the differences between the employment estimates in the two surveys.)
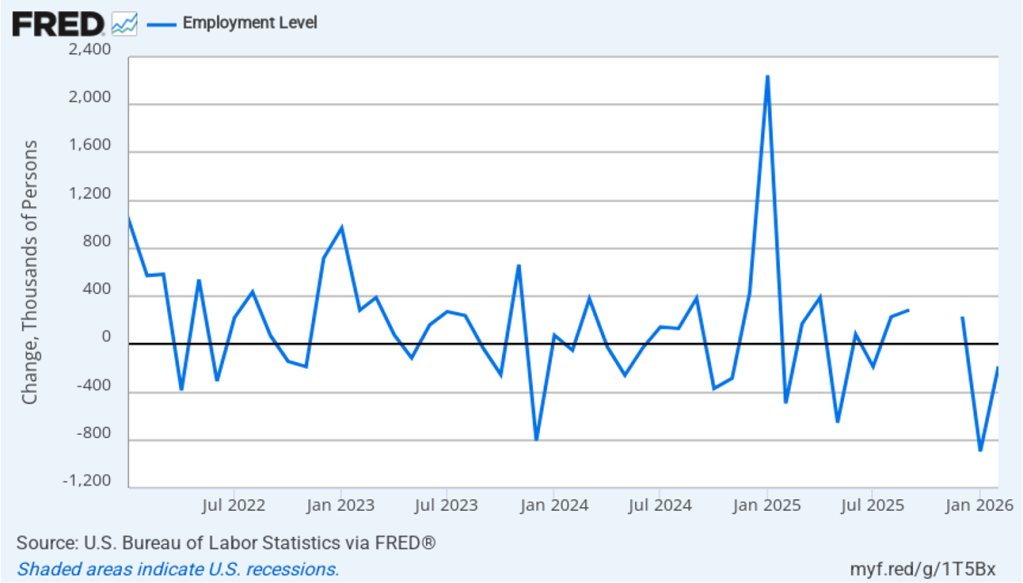
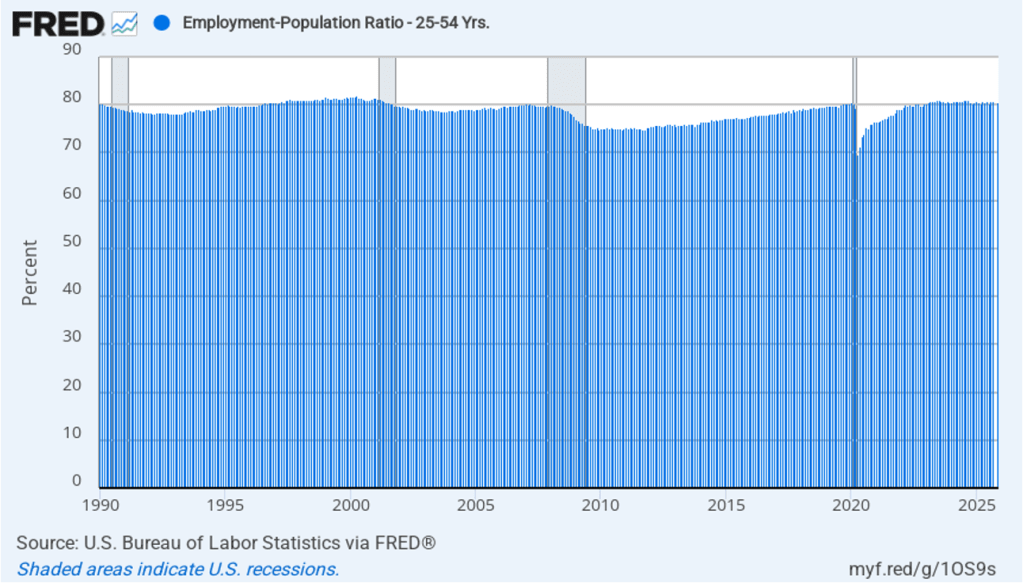
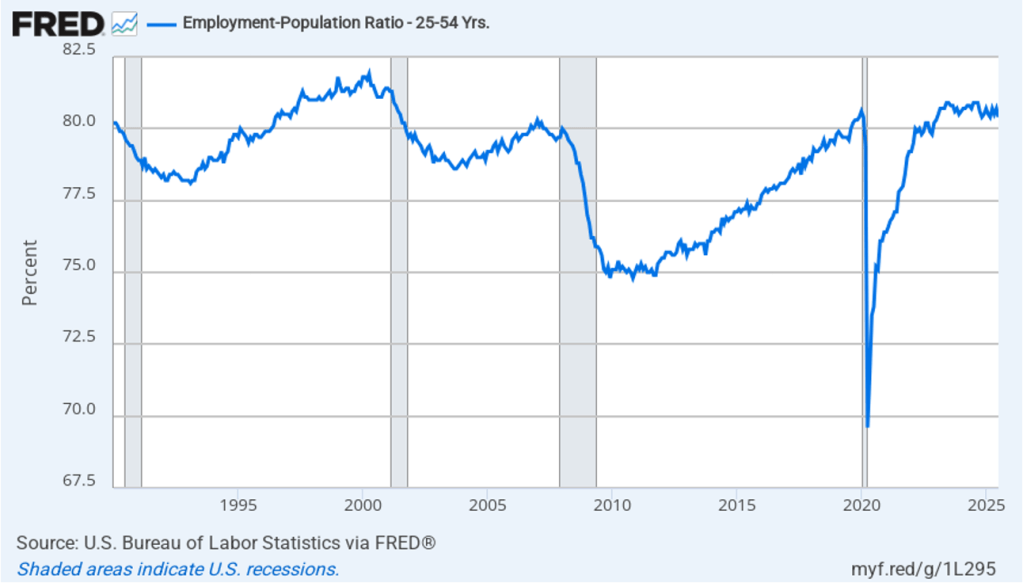
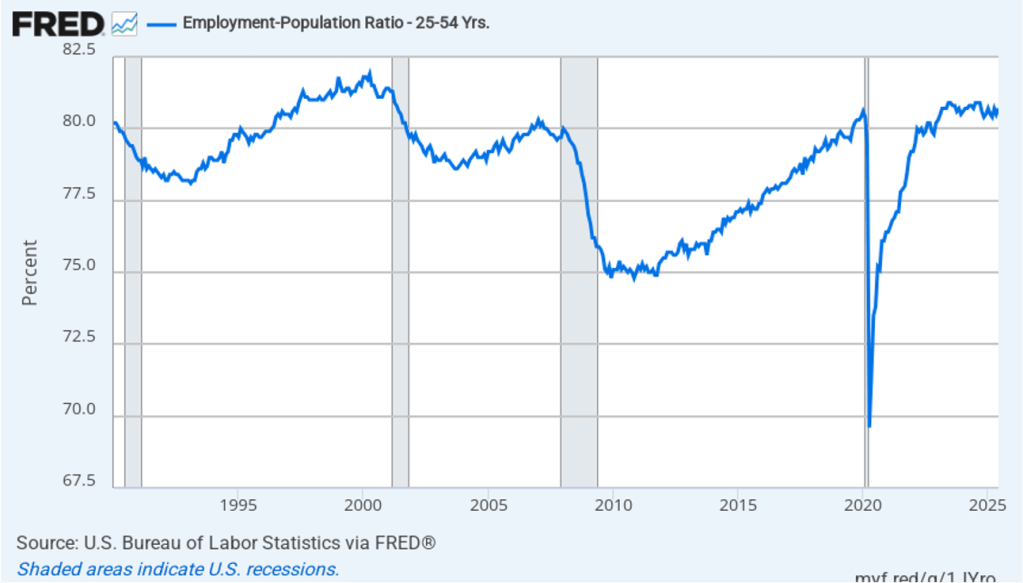
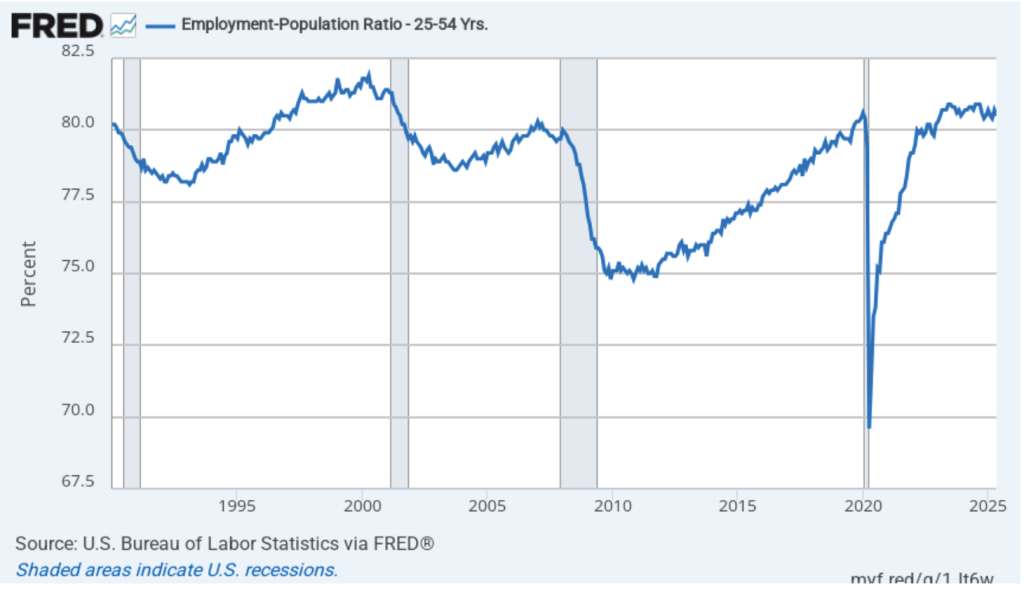
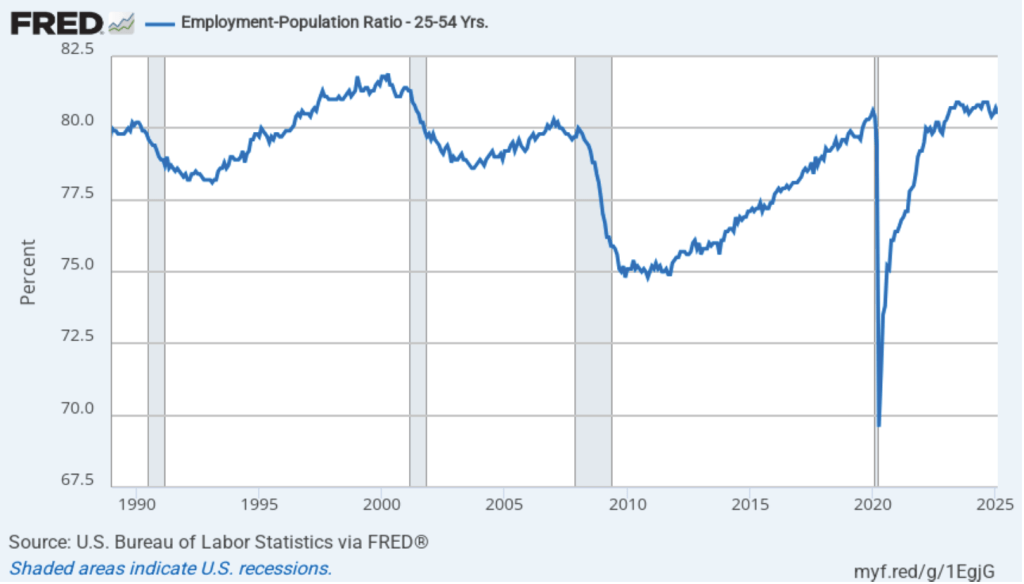
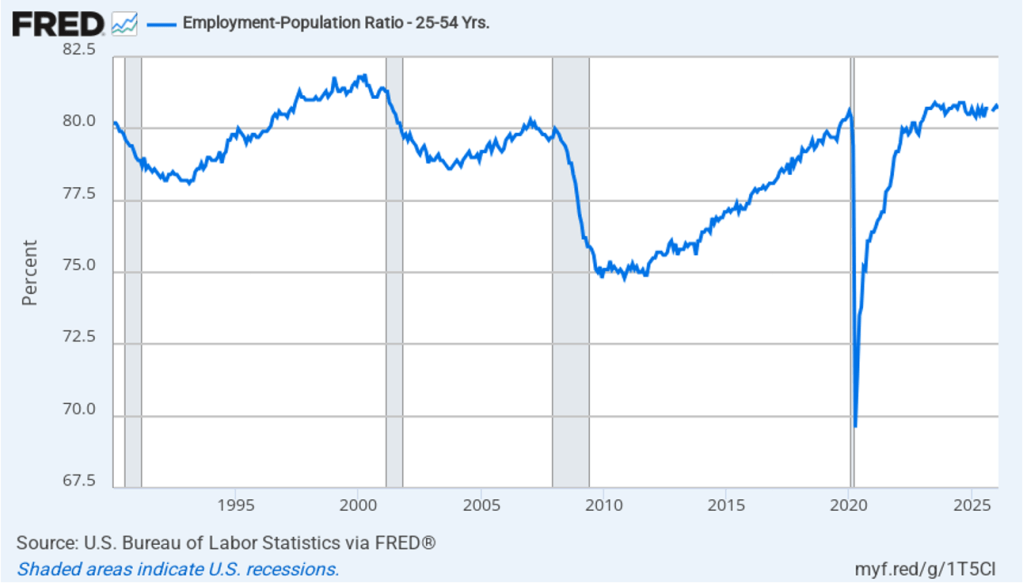
The household survey has another important labor market indicator: the employment-population ratio for prime age workers—those workers aged 25 to 54. In February the ratio was 80.7 percent, down slightly from 80.8 percent in January. The prime-age population ratio remains above its value for most of the period since 2001. The continued high levels of the prime-age employment-population ratio indicate some continuing strength in the labor market.
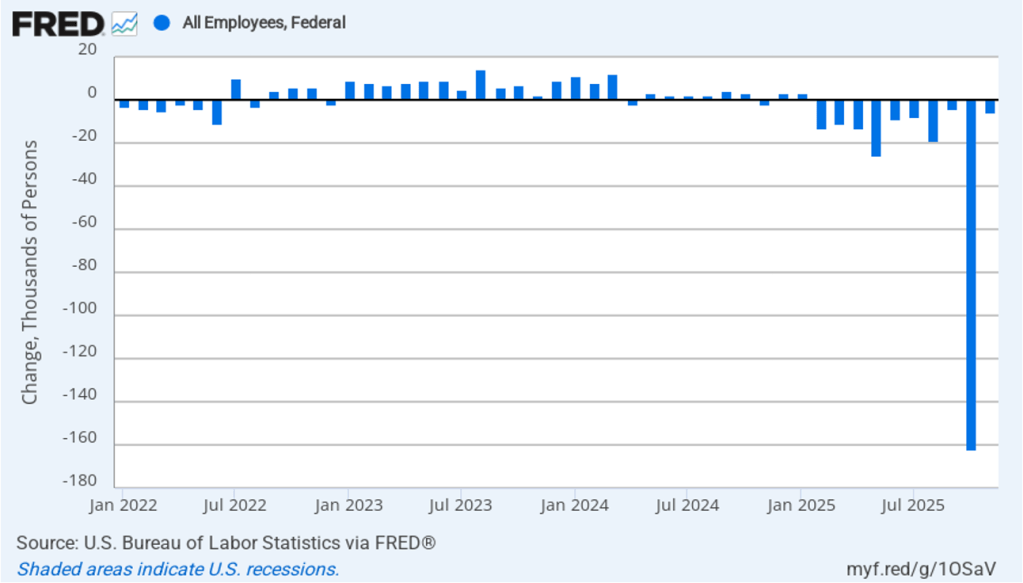
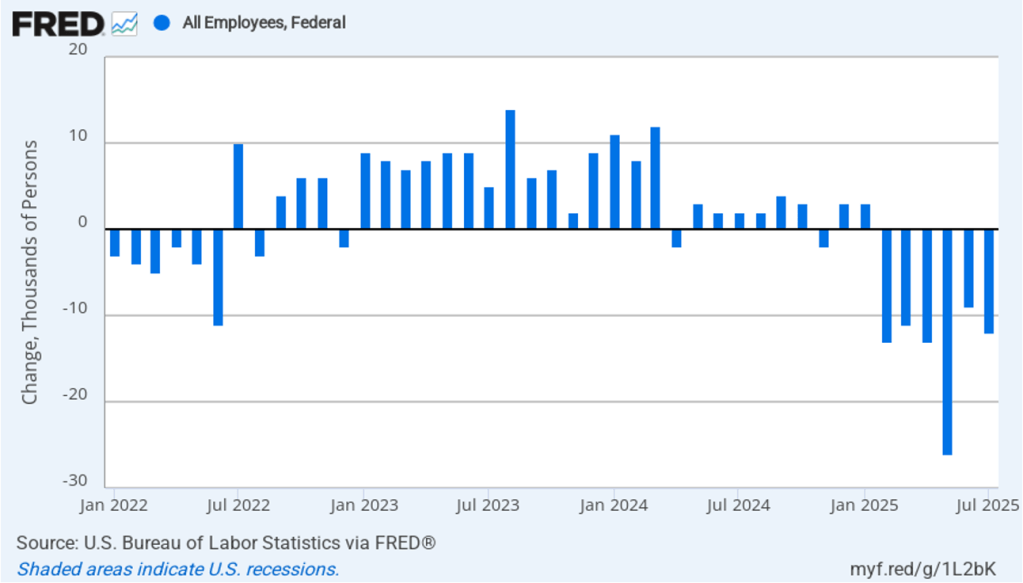
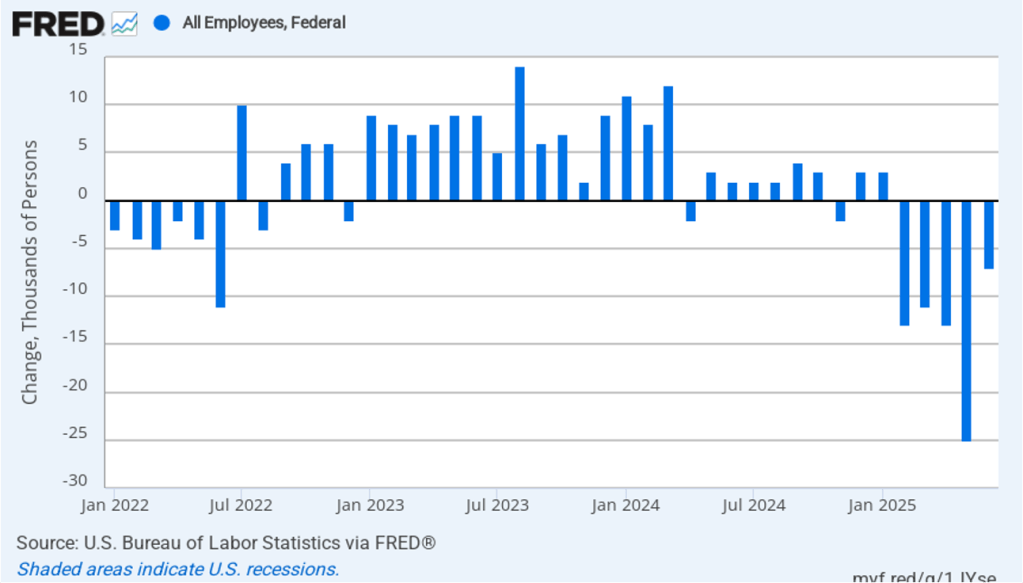
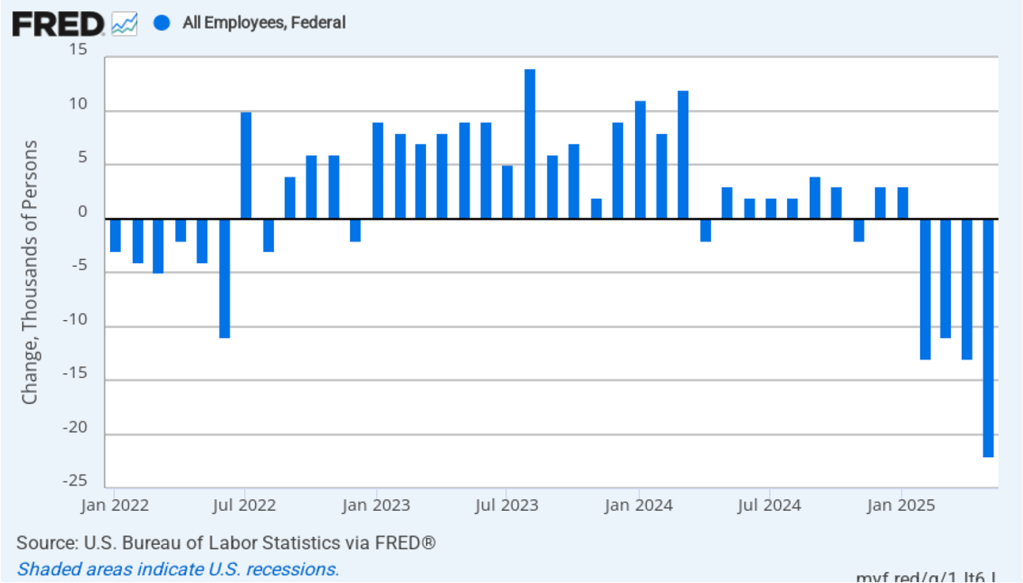
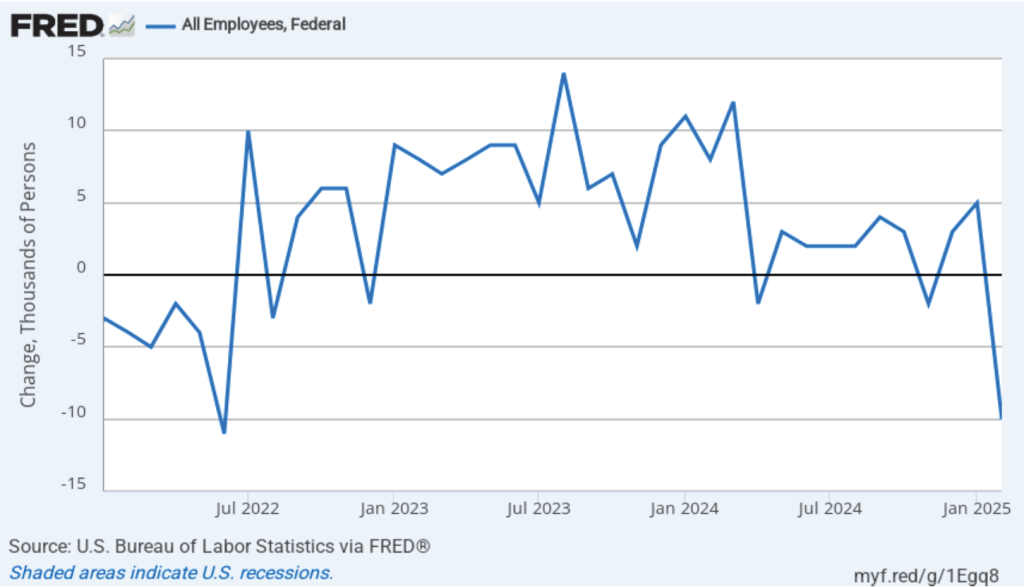
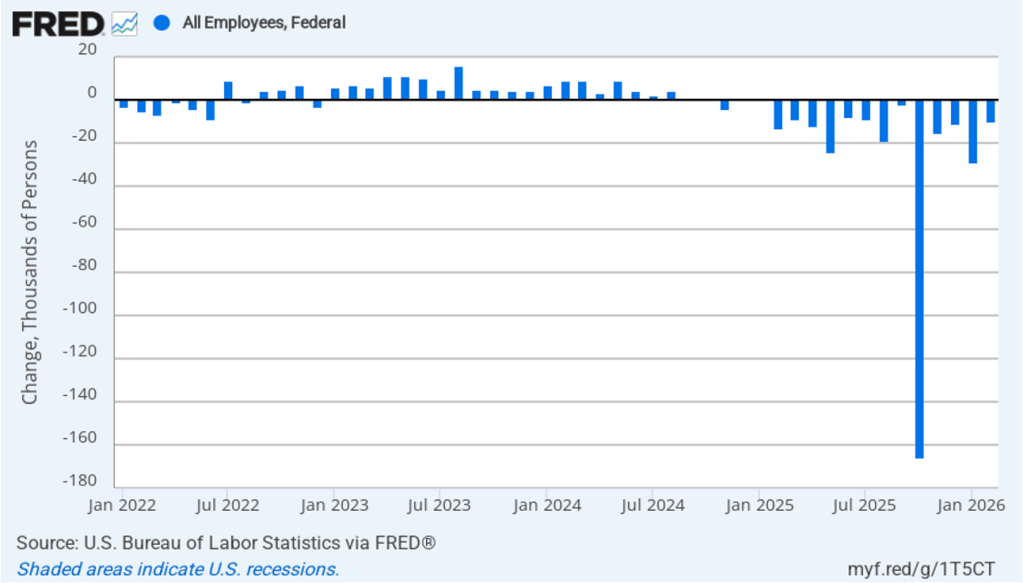
The Trump Administration’s layoffs of some federal government workers are clearly shown in the estimate of total federal employment for October, when many federal government employees exhausted their severance pay. (The BLS notes that: “Employees on paid leave or receiving ongoing severance pay are counted as employed in the establishment survey.”) As the following figure shows, there was a decline in federal government employment of 166,000 in October, with additional declines in the following four months. The total decline in federal government employment since the beginning of February 2025 is 327,000. But the decline has been slowing, with a net decrease of 10,000 jobs in February.
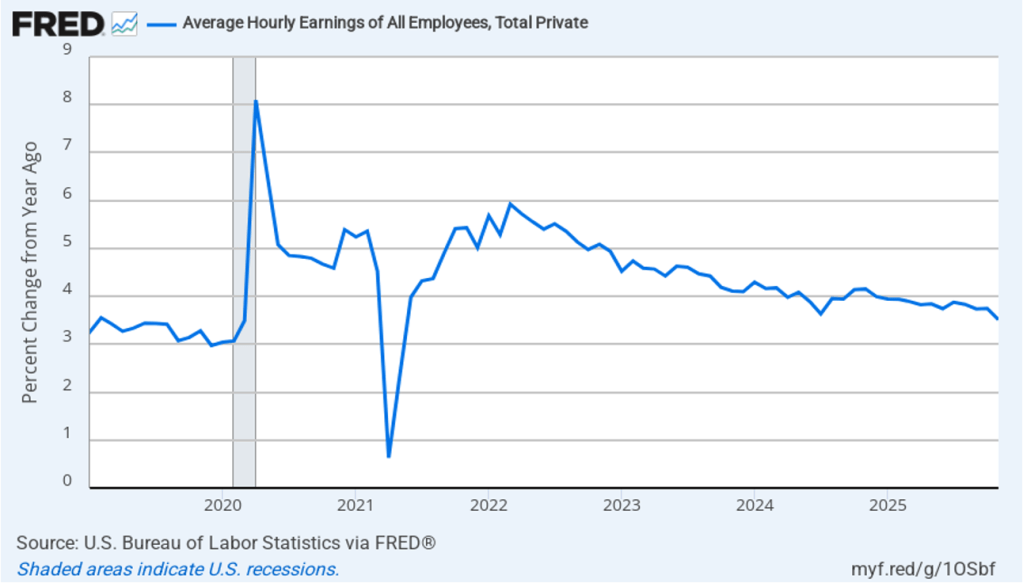
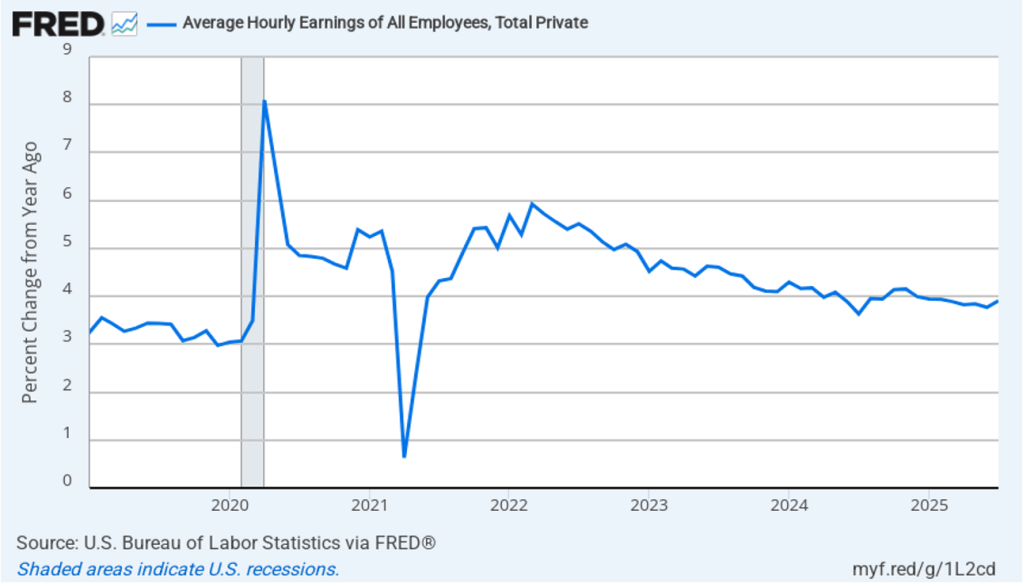
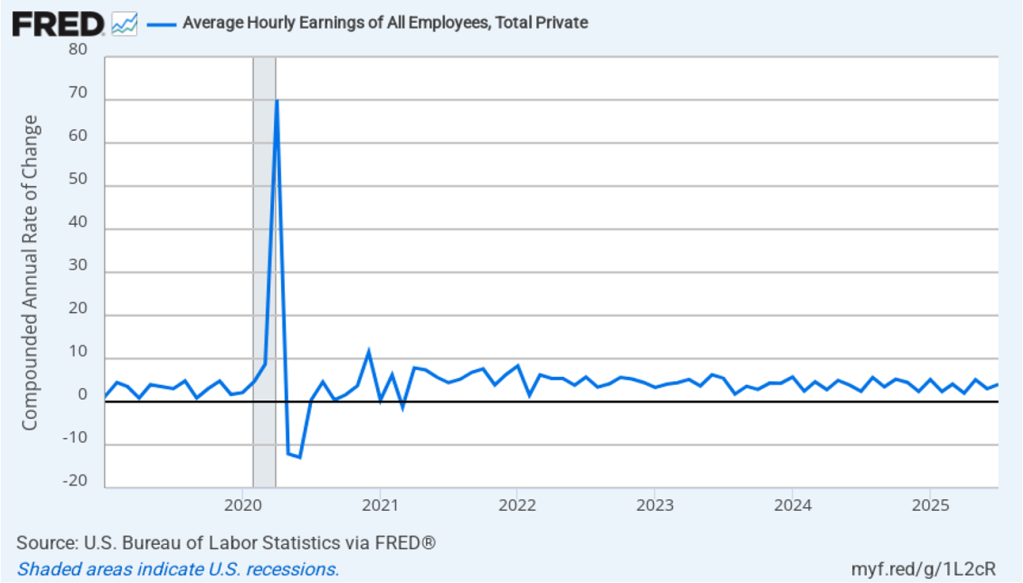
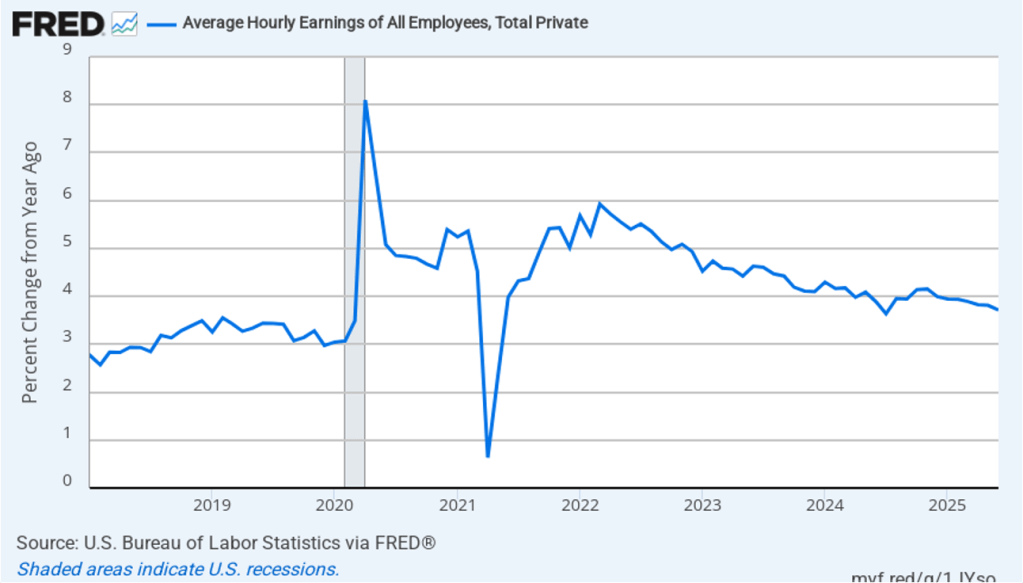
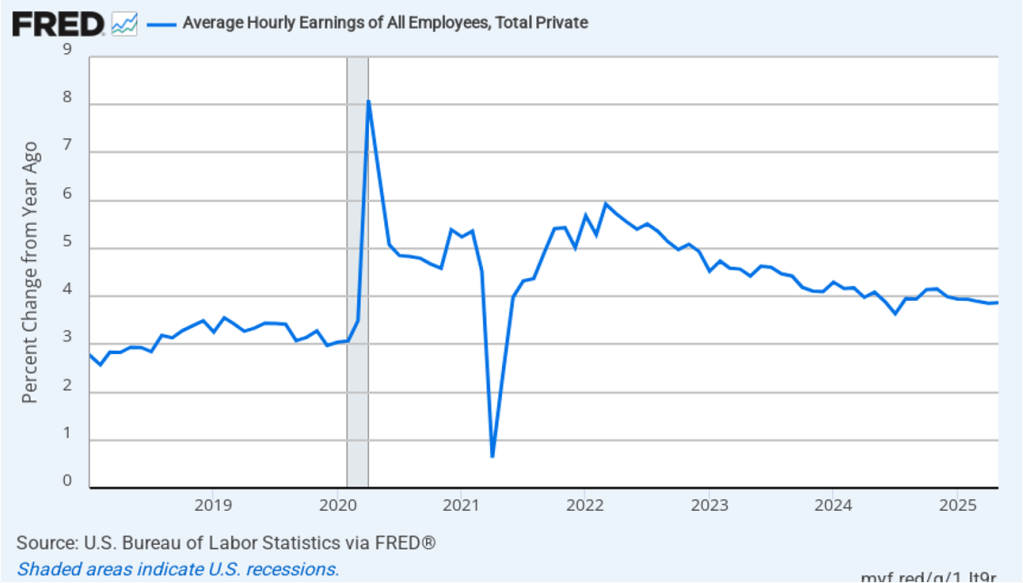
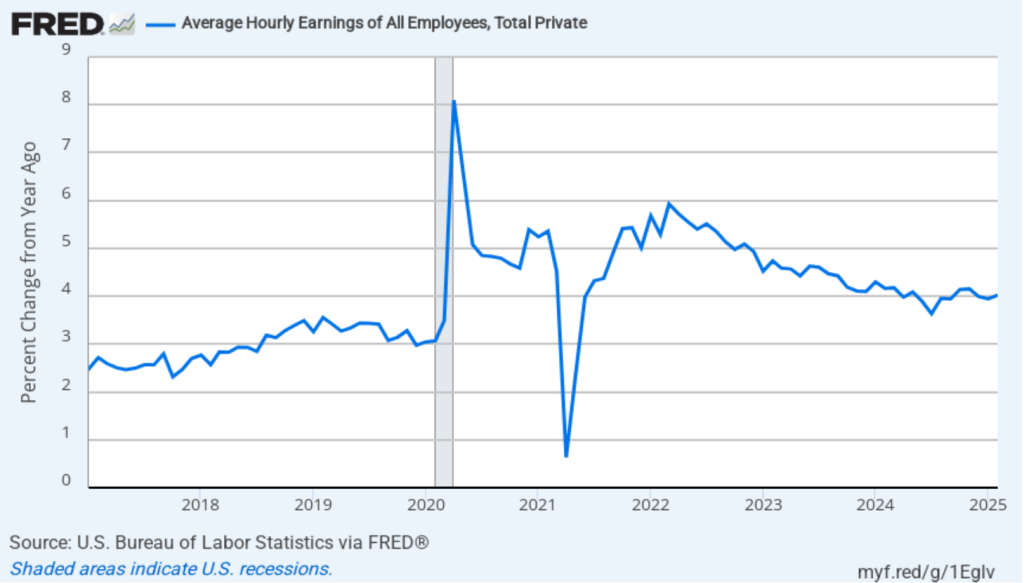
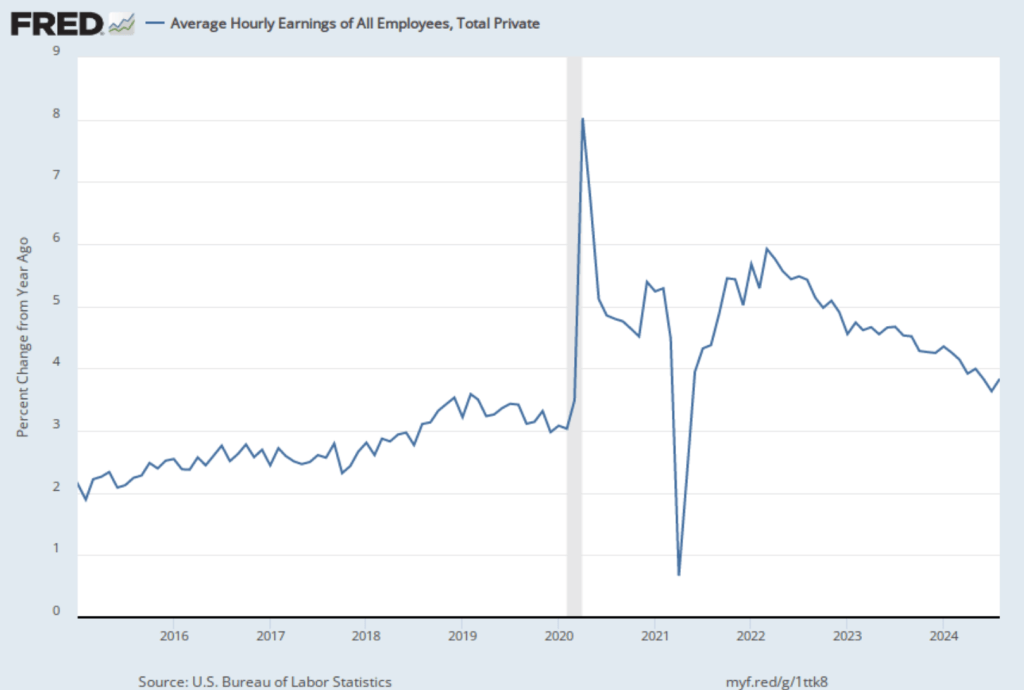
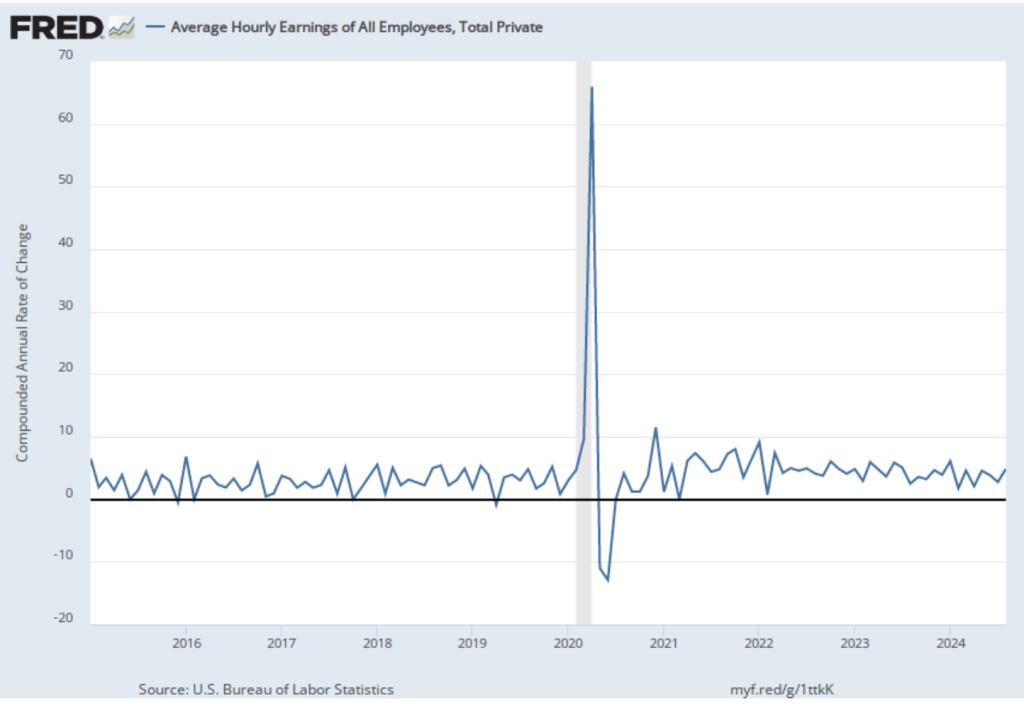
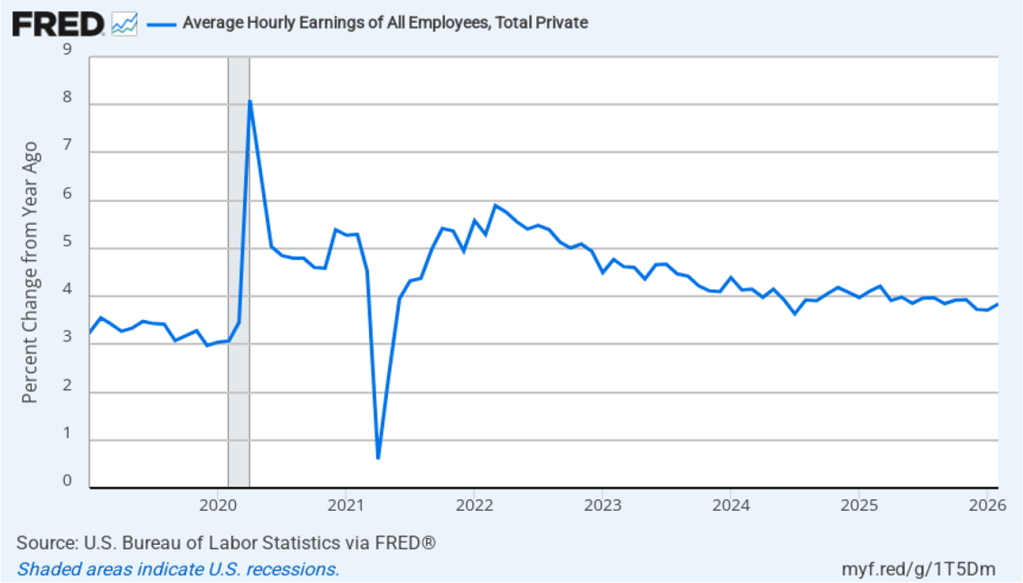
The establishment survey also includes data on average hourly earnings (AHE). As we noted in this post, many economists and policymakers believe the employment cost index (ECI) is a better measure of wage pressures in the economy than is the AHE. The AHE does have the important advantage of being available monthly, whereas the ECI is only available quarterly. The following figure shows the percentage change in the AHE from the same month in the previous year. The AHE increased 3.8 percent in February, up slightly from 3.7 percent in January.
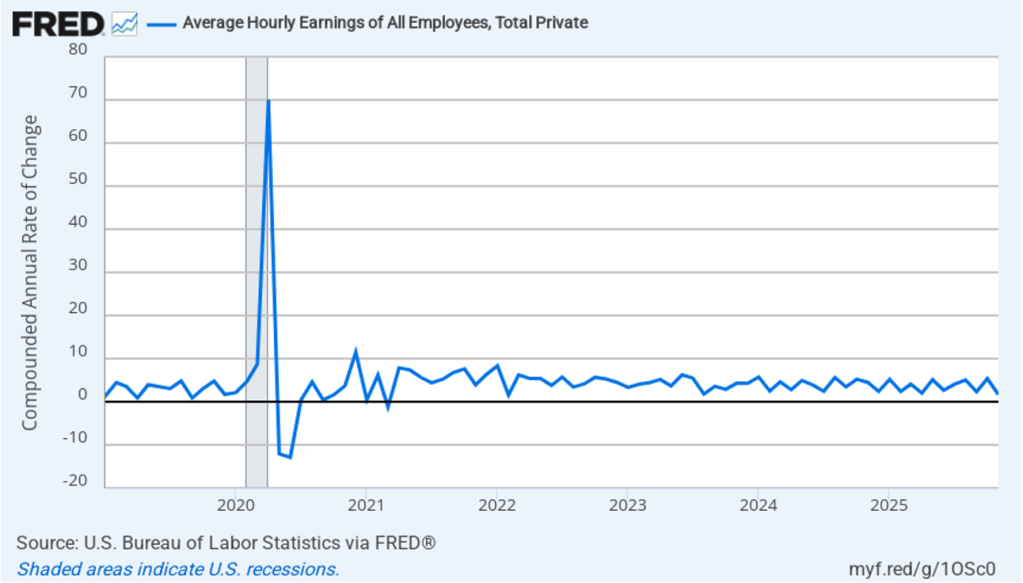
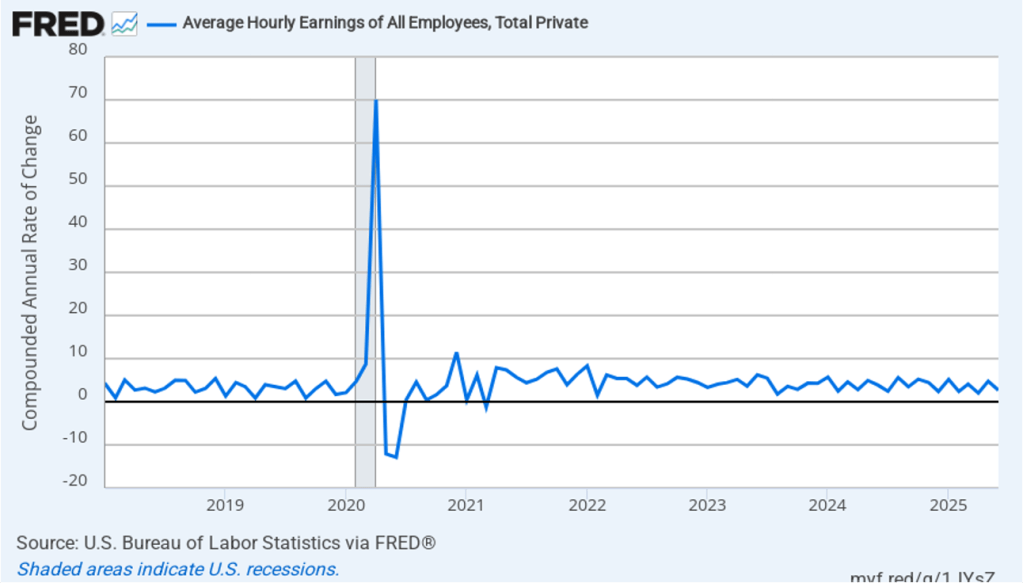
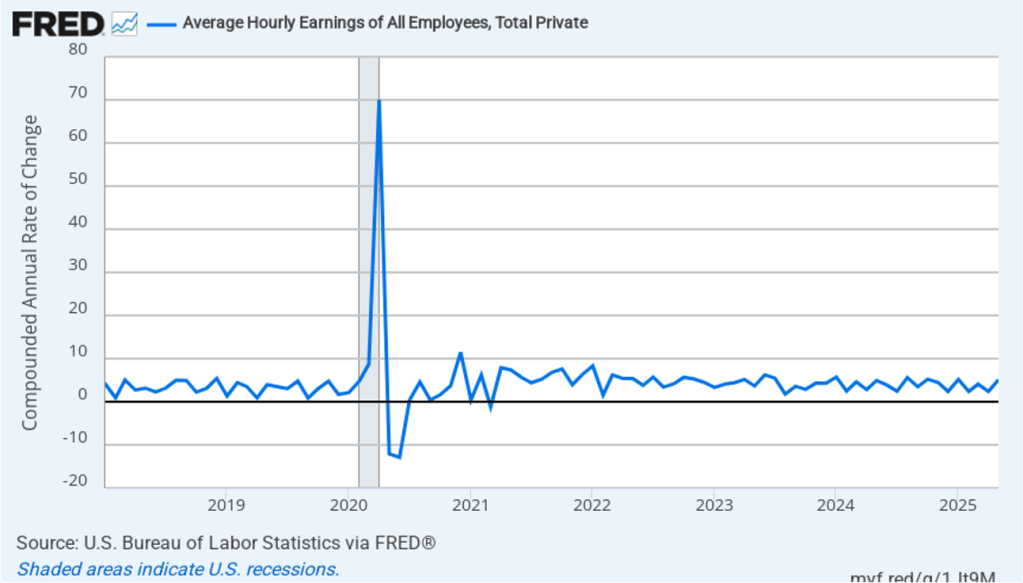
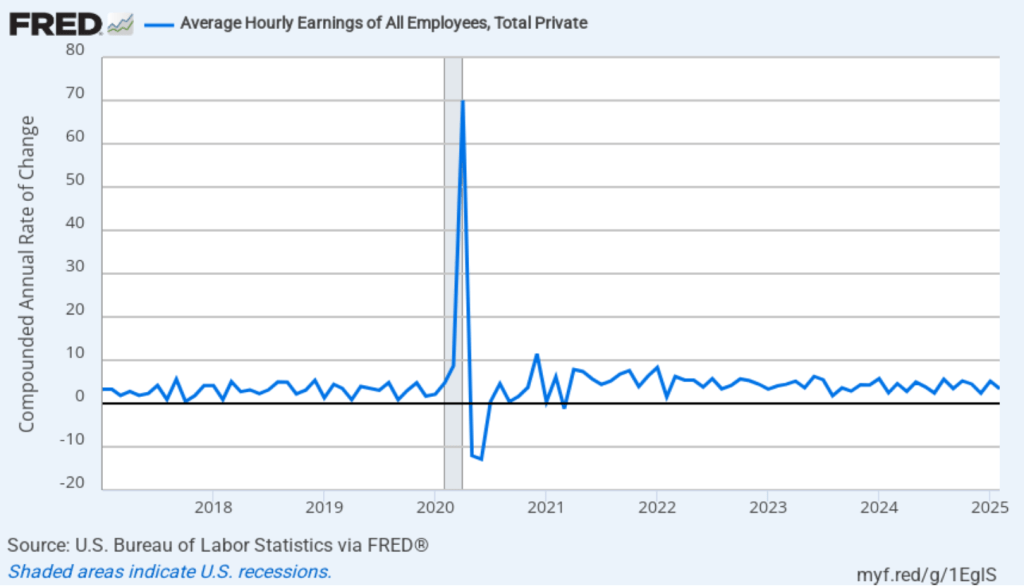
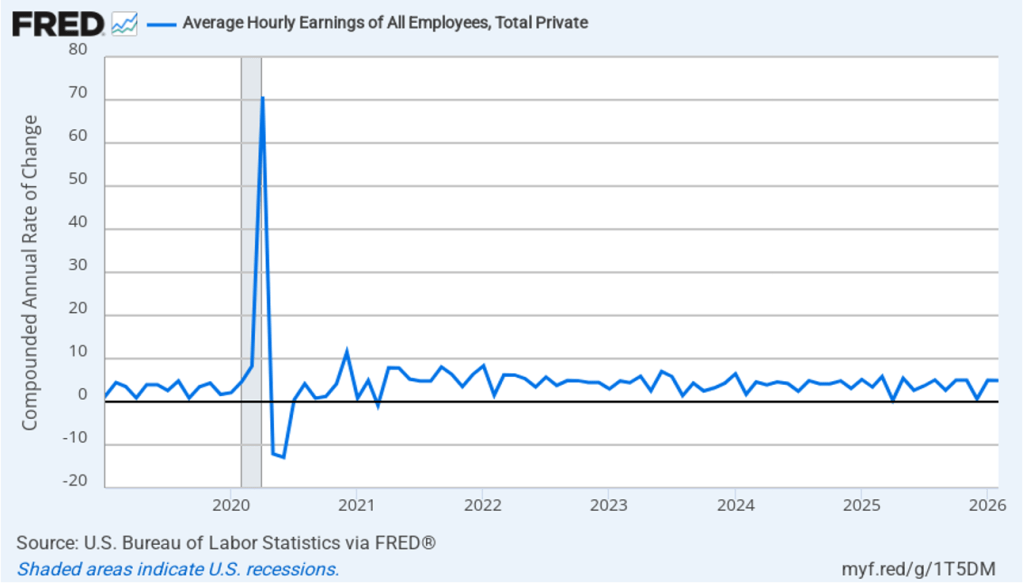
The following figure shows wage inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month wage inflation, whereas this figure shows 1-month wage inflation.) One-month wage inflation is much more volatile than 12-month wage inflation—note the very large swings in 1-month wage inflation in April and May 2020 during the business closures caused by the Covid pandemic. In February, the 1-month rate of wage inflation was 5.0 percent, unchanged from January. This high rate of wage growth is surprising given the decline in employment. But two month’s data from such a volatile series may not accurately reflect longer-run trends in wage inflation.
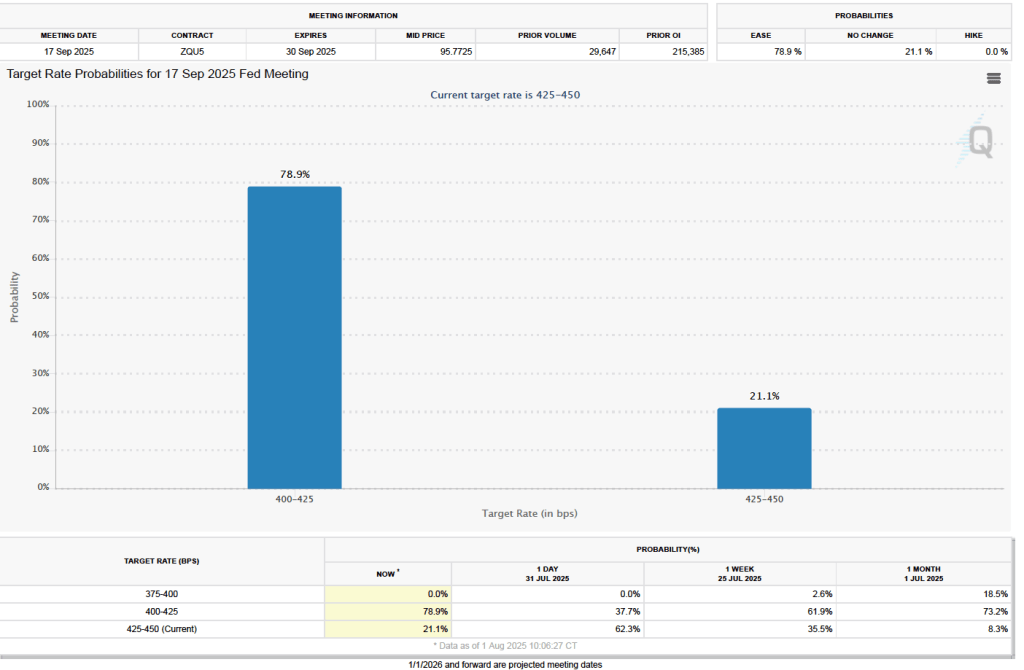
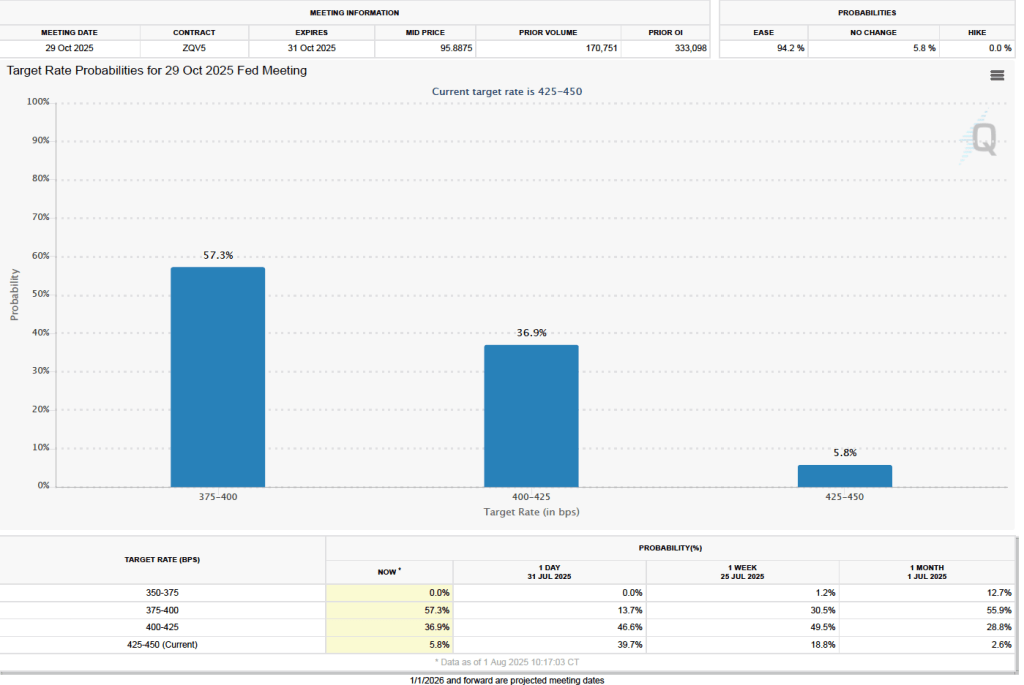
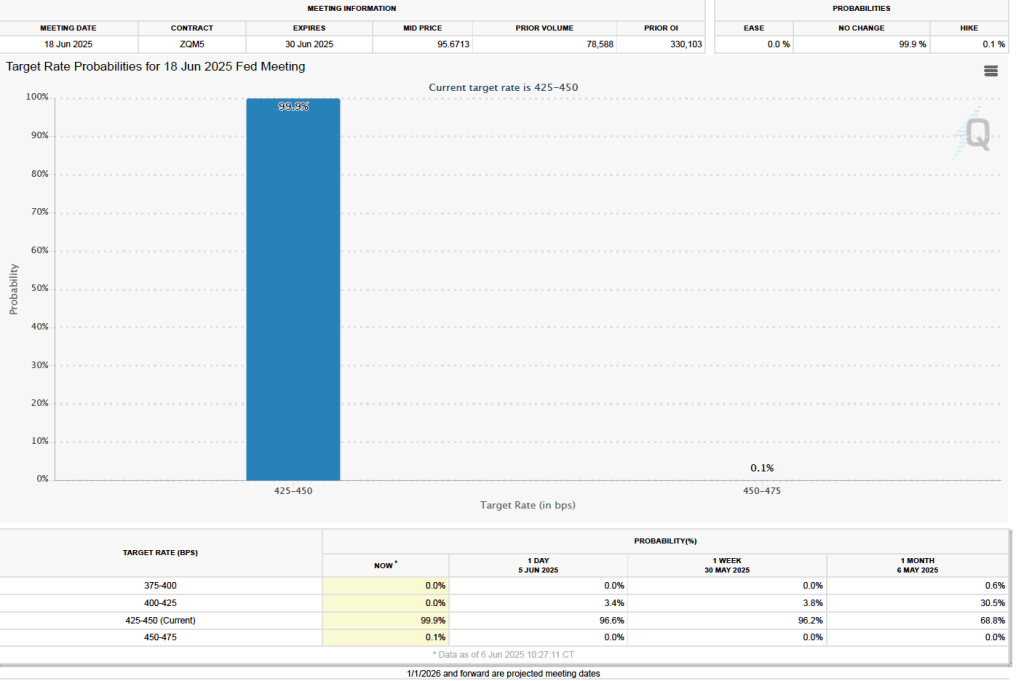
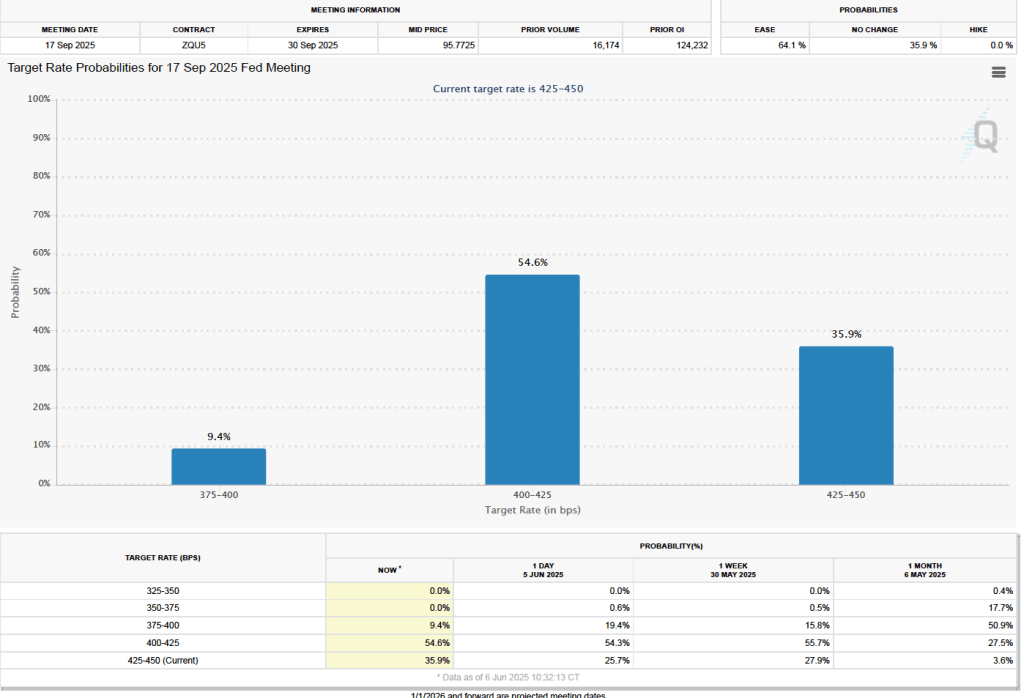
What effect is this weak jobs report likely to have on the decisions of the Federal Reserve’s policymaking Federal Open Market Committee at its next meeting on March 17–18? Taken by itself, employment having fallen in five of the last nine months might be expected to cause the committee to cut its target range for the federal funds rate. But disruptions to the world oil market as a result of the U.S. and Israeli bombing campaign in Iraq have caused oil prices to rise, putting upward pressure on the price level. In addition, wage growth in the United States appears higher than is consistent with price inflation returning to the Fed’s 2 percent annual target. These factors make it likely that the committee will keep its target range for the federal funds rate unchanged at its next meeting.
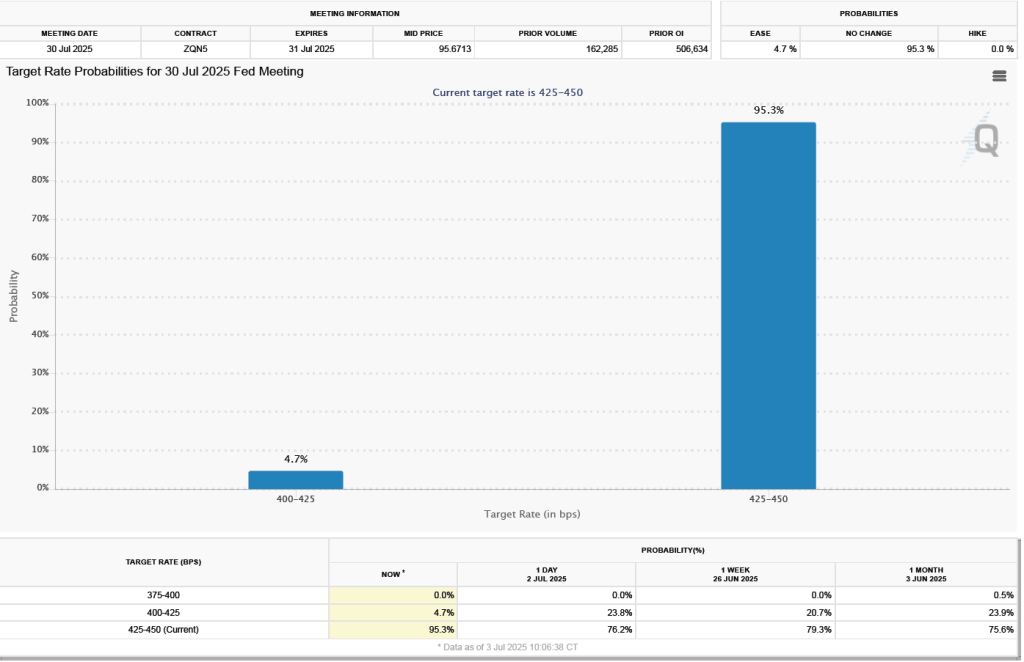
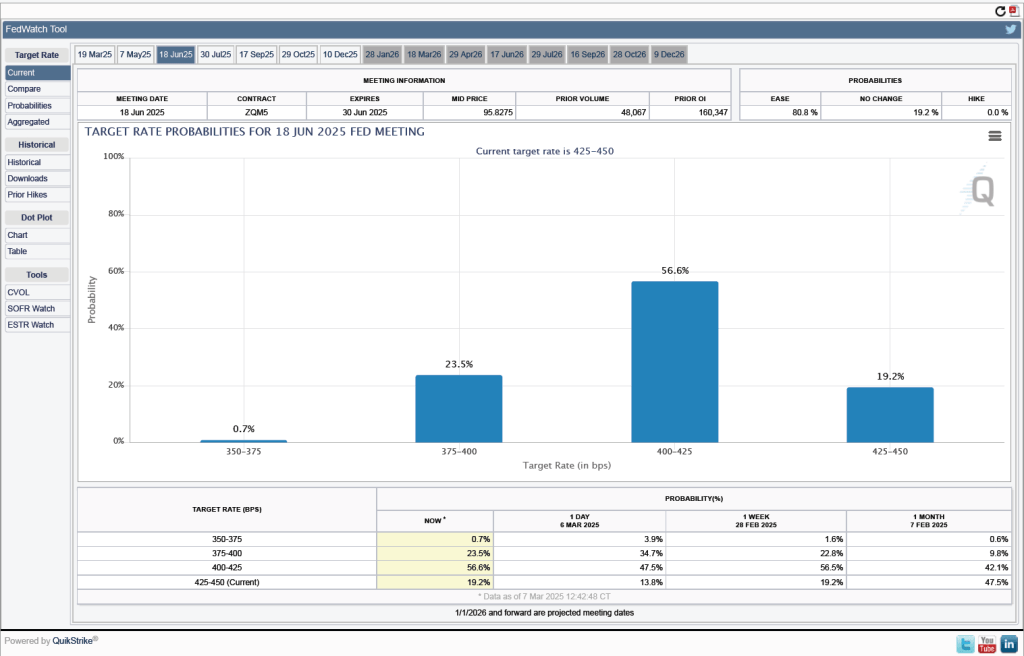
The probability that investors in the federal funds futures market assign to the FOMC keeping its target rate unchanged at its March meeting was largely unchanged this morning at 95.6 percent, only a slight decrease from 96.3 percent yesterday.