Joel Mokyr (photo from news.northwestern. edu)

Philippe Aghion (photo from philippeaghion.com)

Peter Howitt (photo from brown.edu)
For most of human history there was little to no economic growth. Until the nineteenth century, the average person everywhere in the world lived at a subsistence level. For example, although the Roman Empire controlled most of Southern and Western Europe, the Near East, and North Africa for more than 400 years, the living standard of the average citizen of the Empire was no higher at the end of the Empire than it had been at the beginning.
Economists typically measure economic growth by the rate of increase in real GDP per capita. The following figure, updated from Chapter 11 of Macroeconomics (Chapter 21 of Economics), shows the slow pace of growth in real GDP per capita in the world economy from the year 1 to the year 1820 and the much faster rates of growth over the following periods. As discussed in Chapter 11, the figure relies on data compiled by Angus Maddison of University of Groningen in the Netherlands and—for recent years—data from the World Bank.
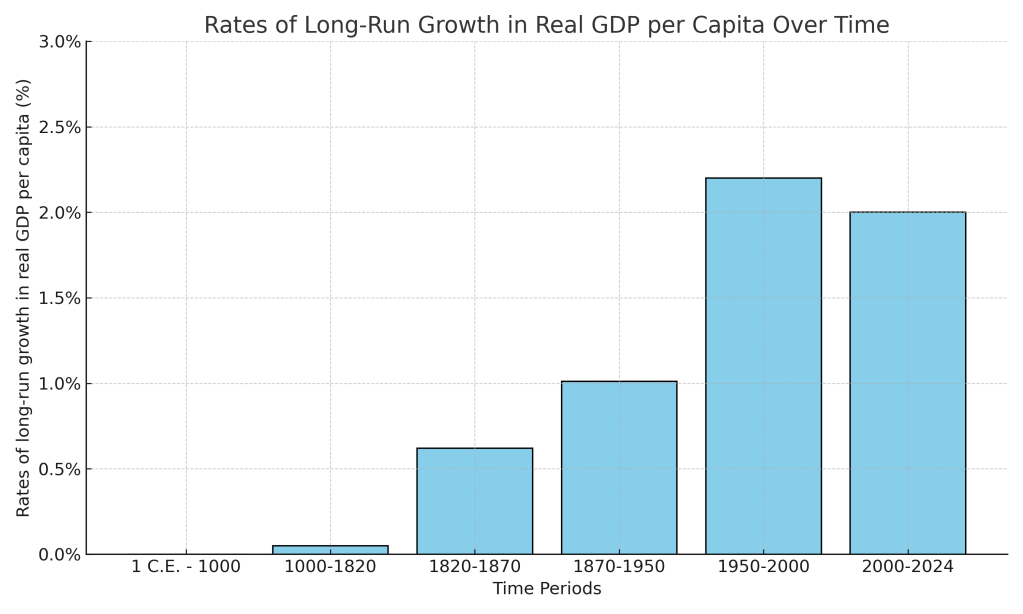
This year’s three Nobelists have contributed to understanding why economic growth accelerated sharply in the nineteenth century and why England was the first country to experienced sustained increases in real GDP per capita—an event labeled the Industrial Revolution. Joel Mokyr of Northwestern University has conducted decades of research into which innovations were crucial to economic growth and the institutional and economic advantages that allowed entrepreneurs in England to use those innovations to expand production much more rapidly than had happened before. Philippe Aghion of Collège de France and INSEAD and Peter Howitt of Brown University have focused on formally modeling the process of creative destruction that underlies sustained economic growth. The classic discussion of creative destruction appears in Joseph Schumpeter’s book Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy, published in 1942.
In Macroeconomics Chapter 21, we discuss the process of creative destruction in the context of economic growth. Creative destruction occurs as technological change results in new products that drive firms producing older products out of business. Examples are automobiles driving out of business producers of horse-drawn carriages in the early twentieth century. Or Netflix and other movie streaming sites driving video rental stores out of business in more recent years.
The Nobel Committee’s announcement of the prize can be found here. A longer discussion of the Nobelists’ work can be found here. The scope of their research can be seen by reviewing their curricula vitae, which can be found here, here, and here. The amount of the prize this years is 11 million Swedish kronor (about $1.2 million). Mokyr receives half and Aghion and Howitt receive the other half.

