Image illustrating inflation generated by GTP-4o.
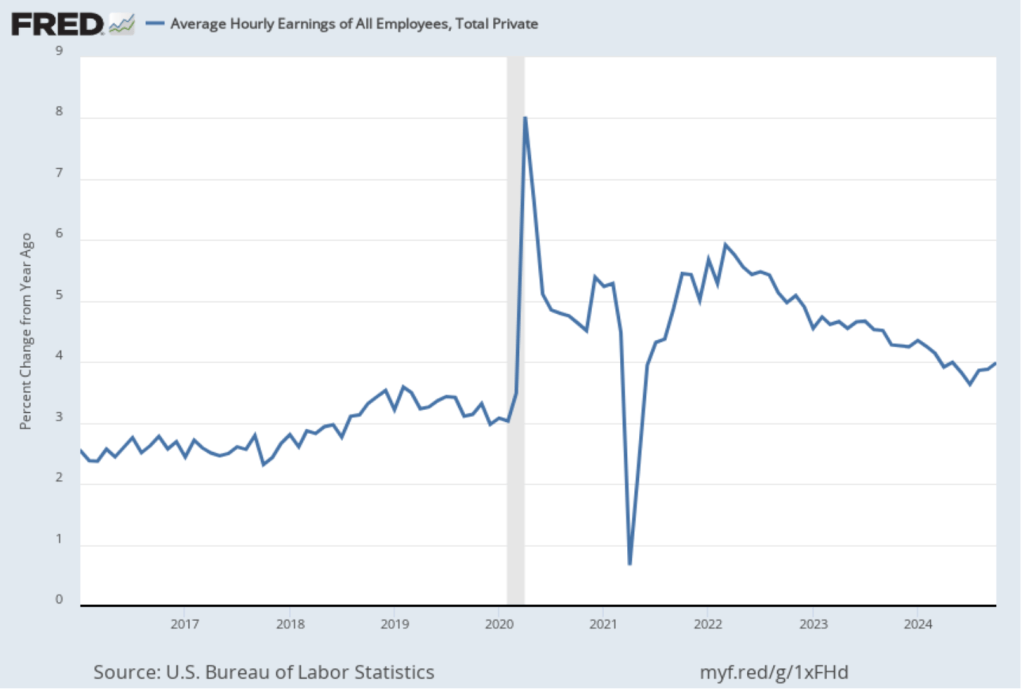
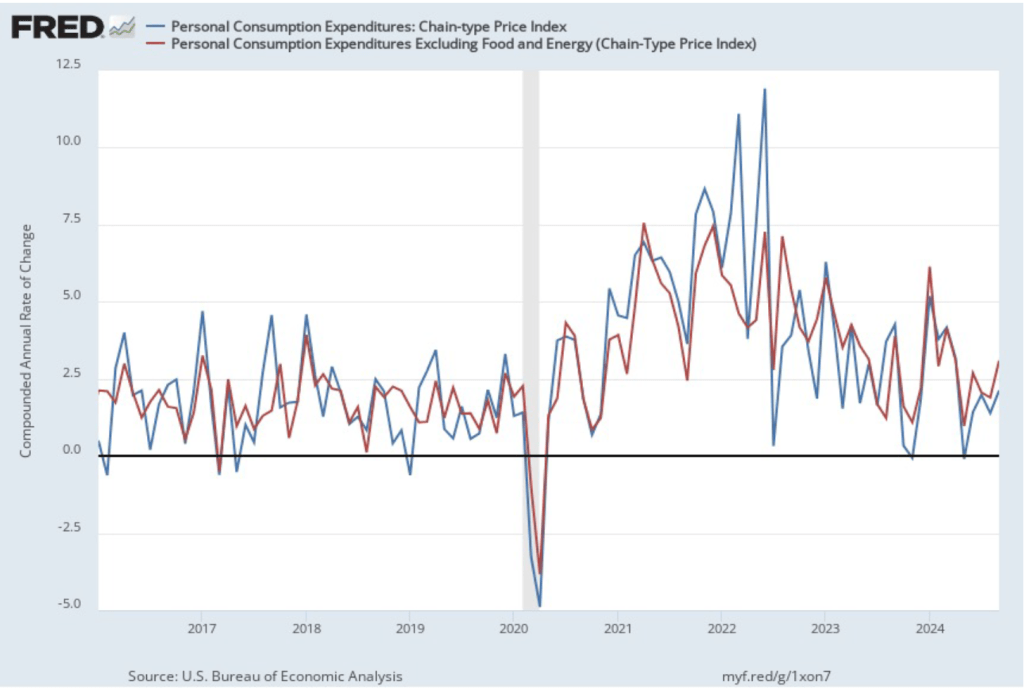
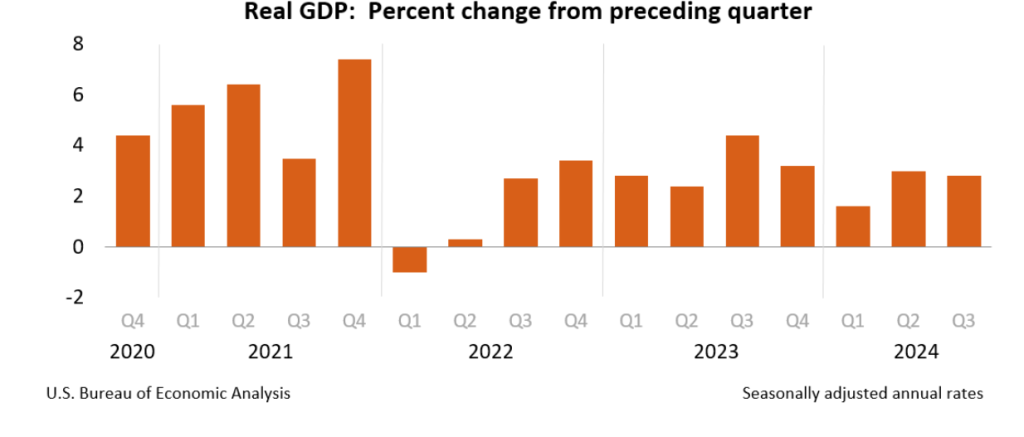
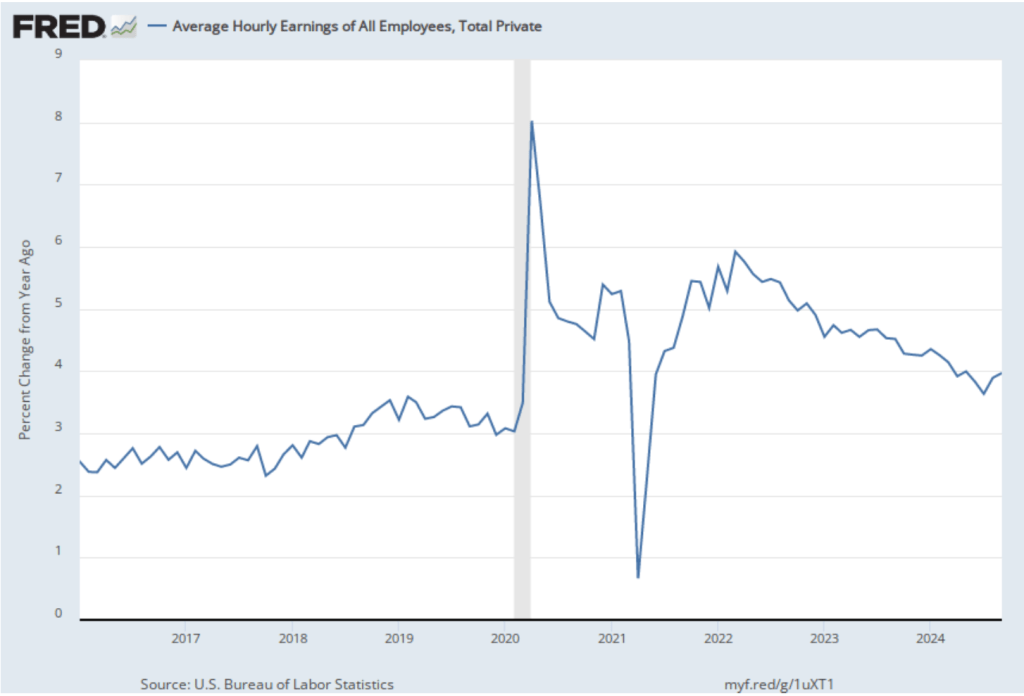
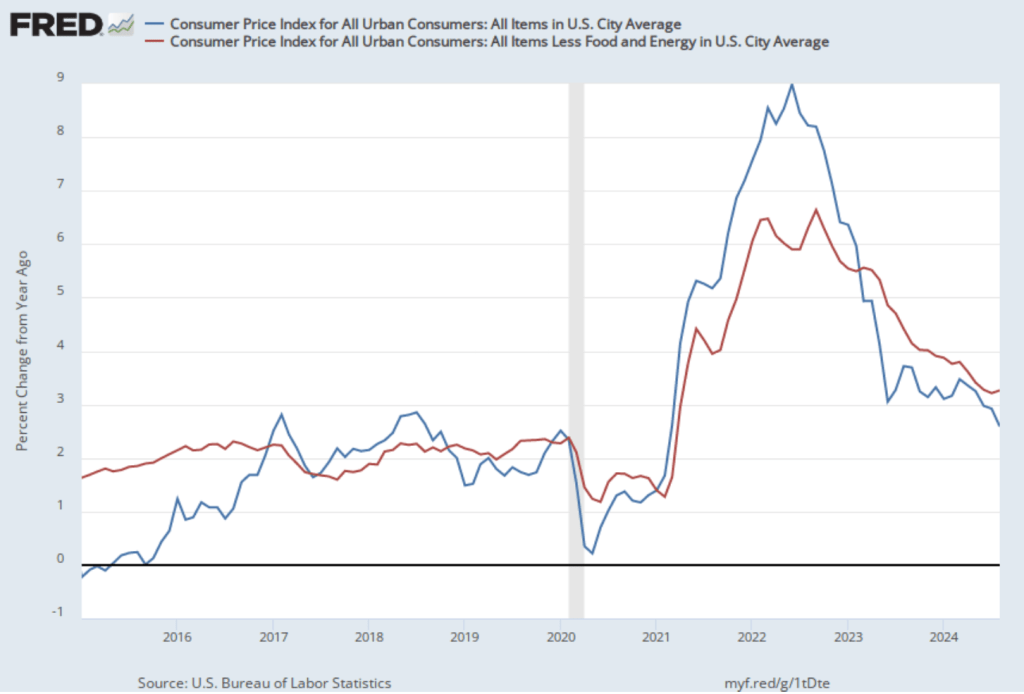
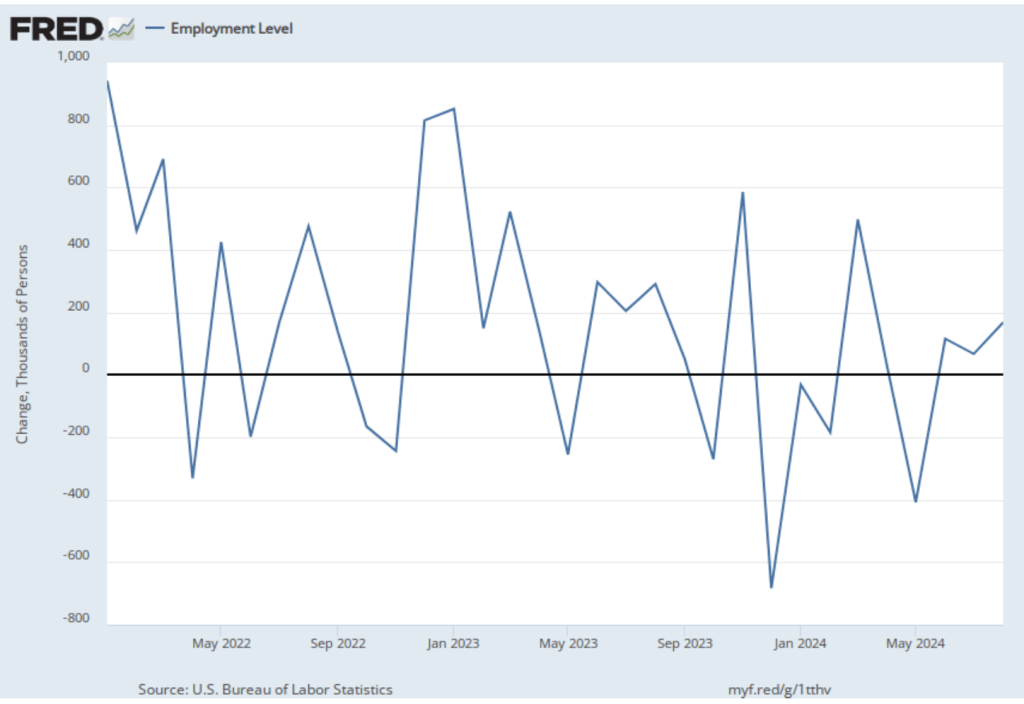
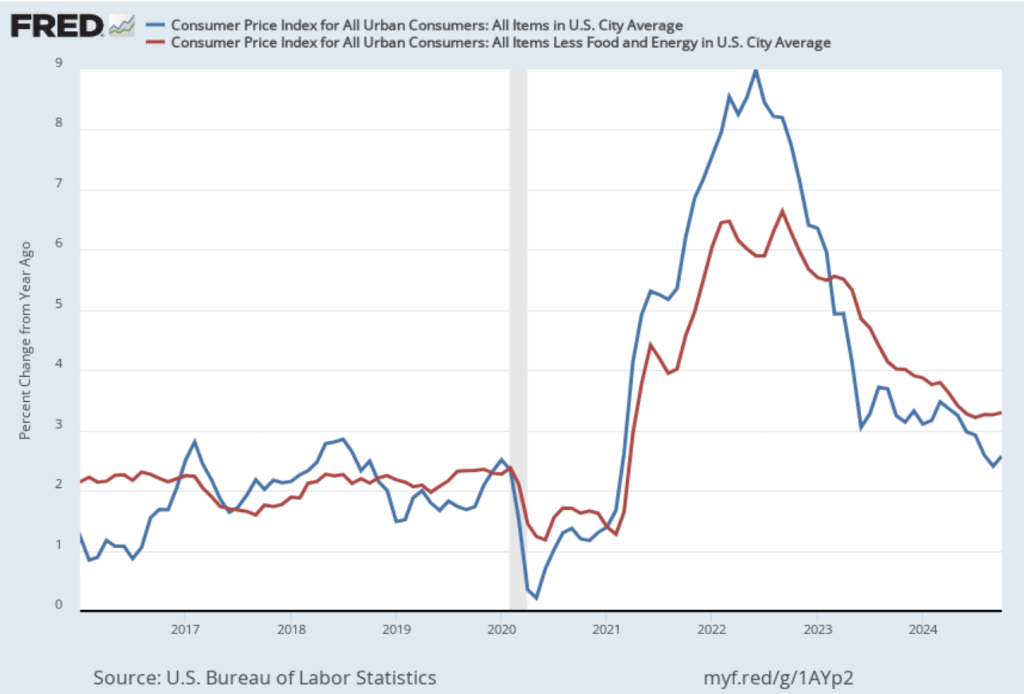
On November 13, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its monthly report on the consumer price index (CPI). The following figure compares headline inflation (the blue line) and core inflation (the red line).
- The headline inflation rate, which is measured by the percentage change in the CPI from the same month in the previous month, was 2.6 percent—up from 2.4 percent in September.
- The core inflation rate, which excludes the prices of food and energy, was unchanged at 3.3 percent for the third month in a row.
Both headline inflation and core inflation were the values that economists surveyed by the Wall Street Journal had expected.
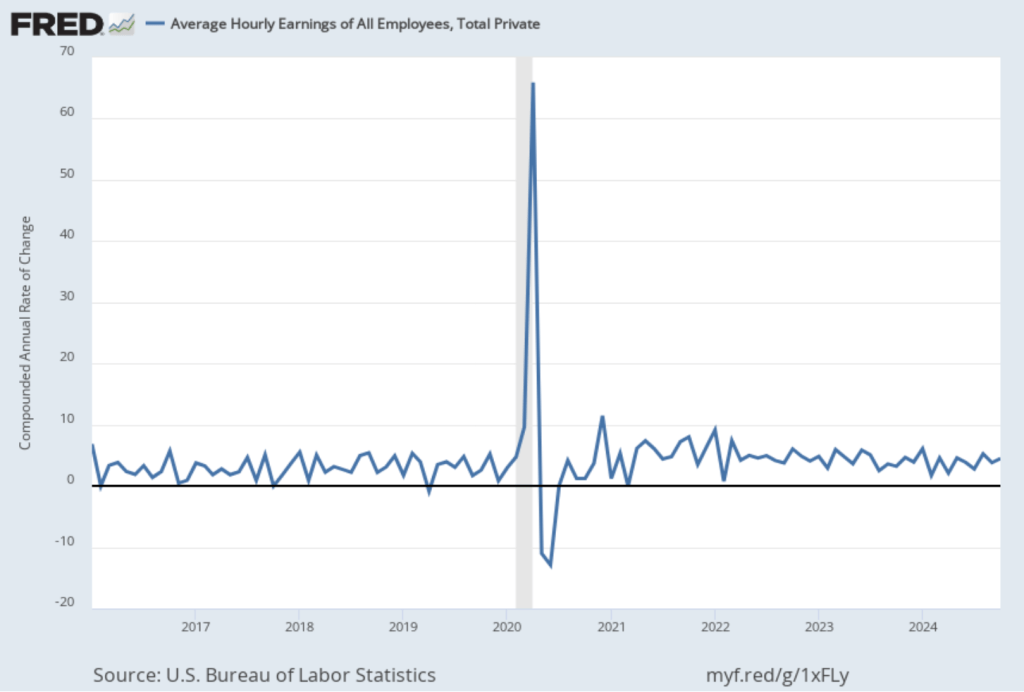
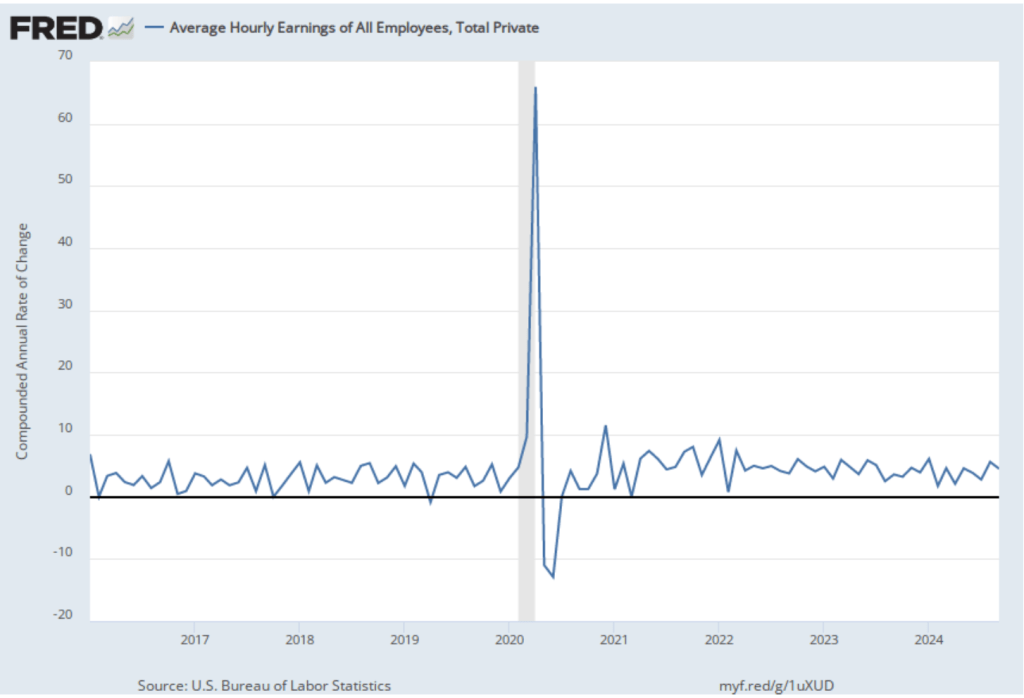
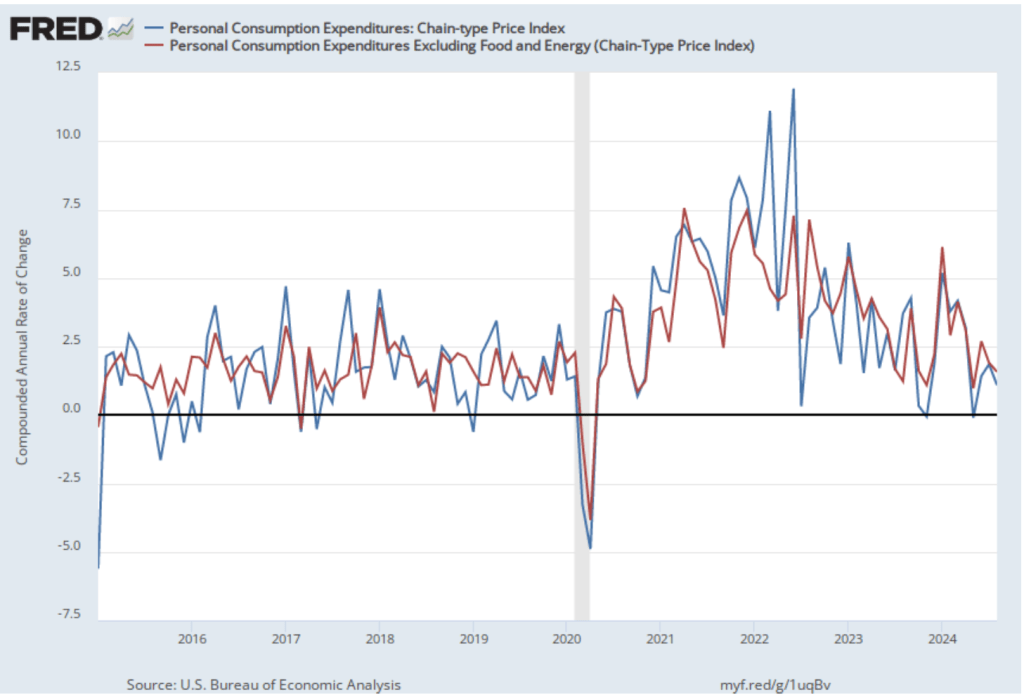
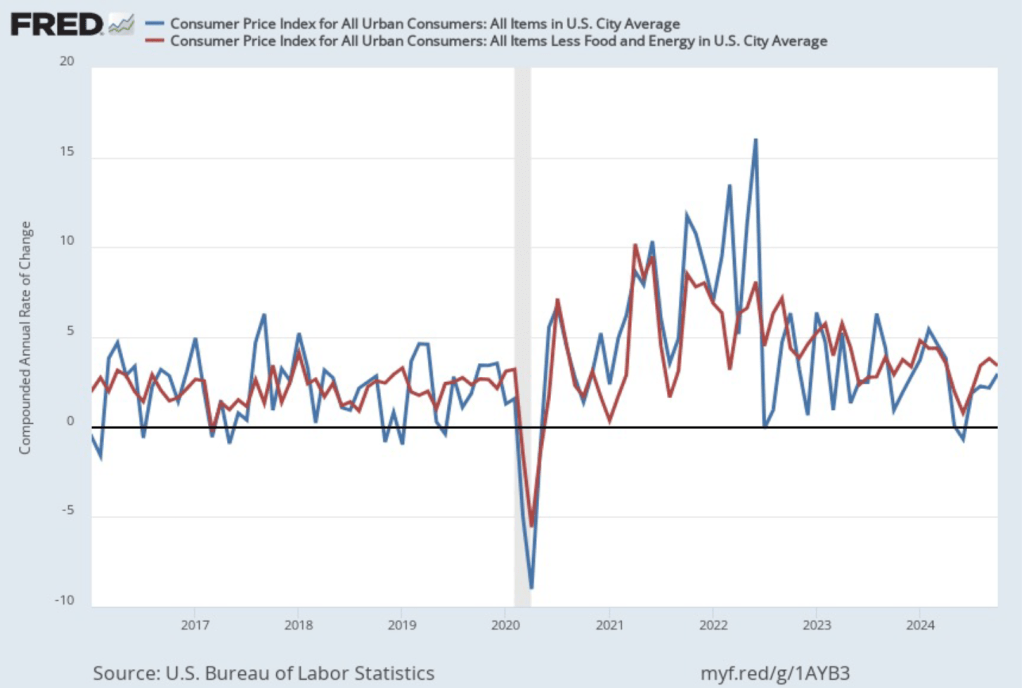
In the following figure, we look at the 1-month inflation rate for headline and core inflation—that is the annual inflation rate calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. Calculated as the 1-month inflation rate, headline inflation (the blue line) increased from 2.2 percent in September to 3.0 percent in October. Core inflation (the red line) fell from 3.8 percent in September to 3.4 percent in October.
Overall, considering 1-month and 12-month inflation together, the U.S. economy may still be on course for a soft landing—with the annual inflation rate returning to the Fed’s 2 percent target without the economy being pushed into a recession. However, progress on lowering inflation may have slowed or, possibly, stalled. The relatively high rates of core inflation in both the 12-month and 1-month measures are concerning because most economists believe that core inflation is a better indicator of the underlying inflation rate than is headline inflation. It’s important not to overinterpret the data from a single month, although this is the third month in a row that core inflation has been above 3 percent. (Note, that the Fed uses the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, rather than the CPI in evaluating whether it is hitting its 2 percent inflation target.)
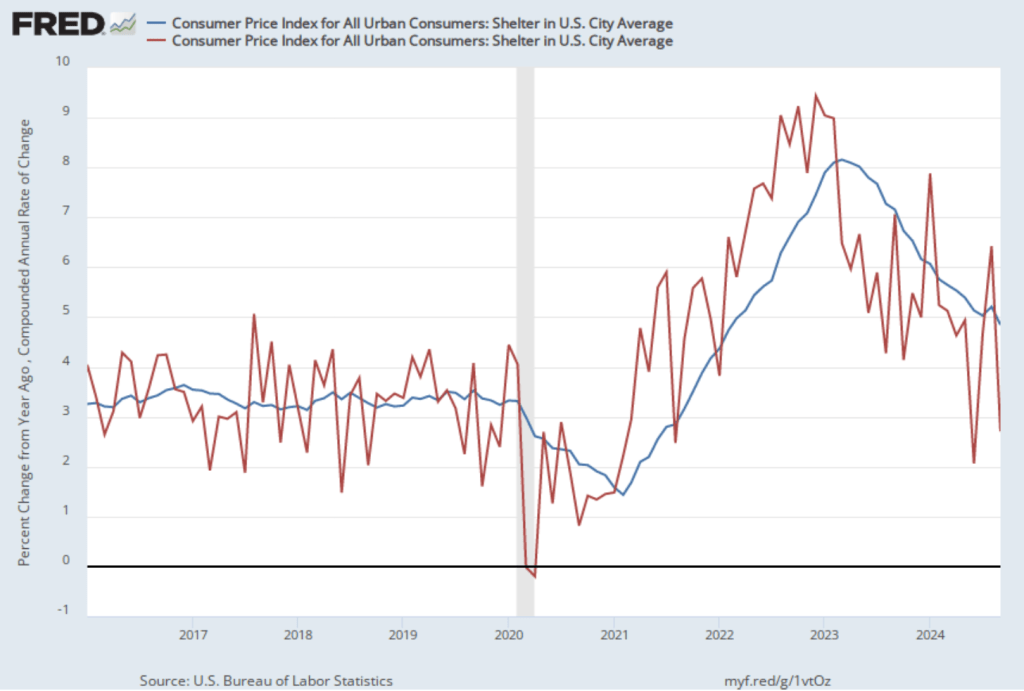
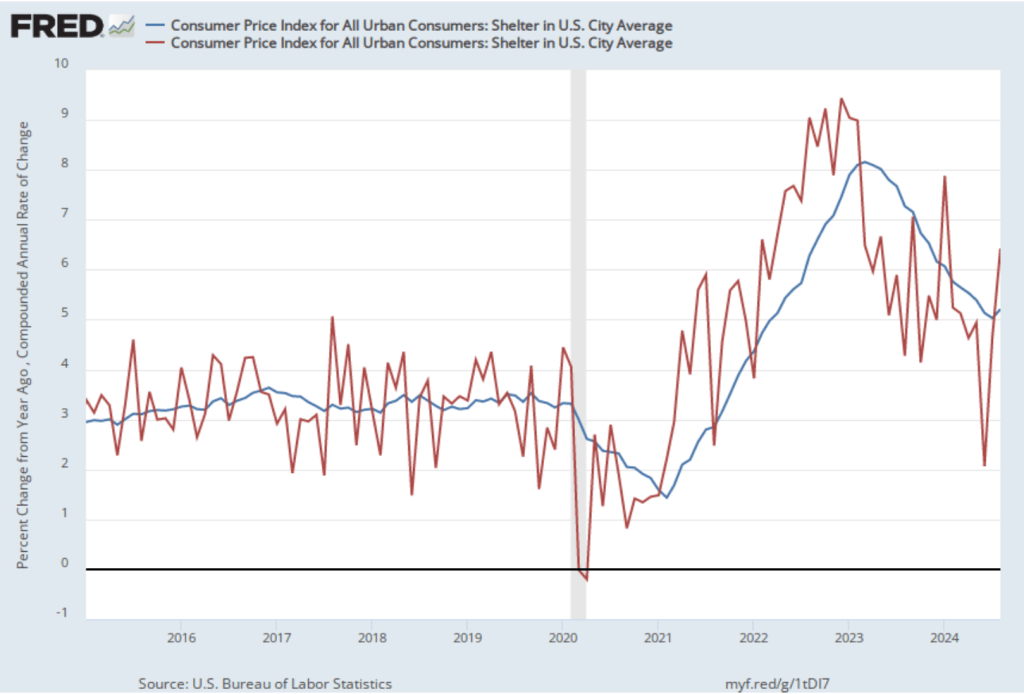
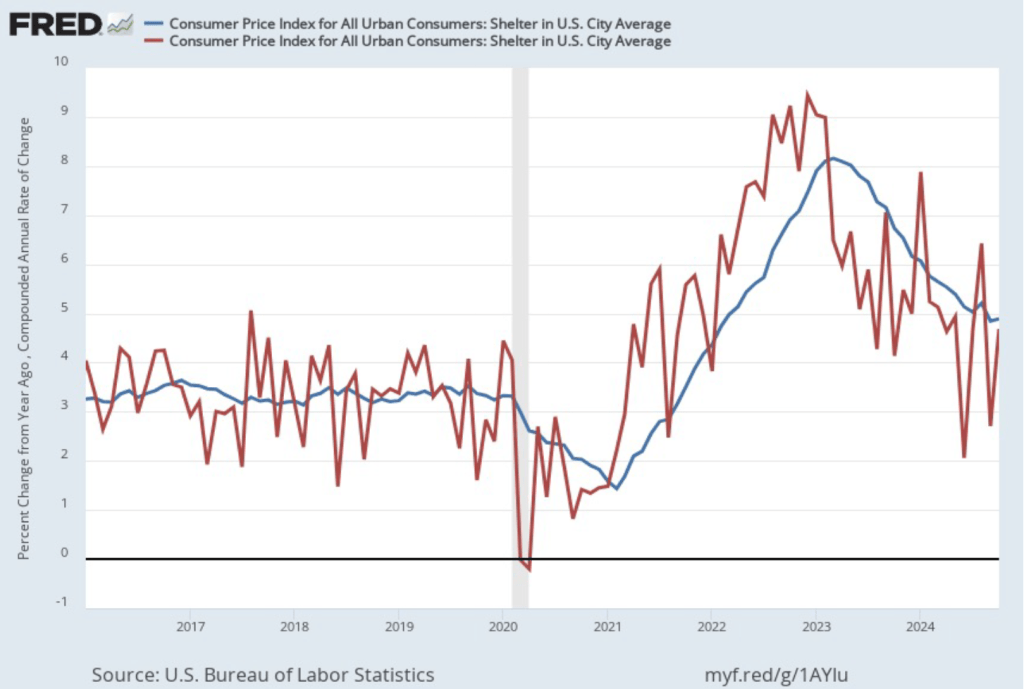
As we’ve discussed in previous blog posts, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell and his colleagues on the Fed’s policymaking Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) have been closely following inflation in the price of shelter. The price of “shelter” in the CPI, as explained here, includes both rent paid for an apartment or house and “owners’ equivalent rent of residences (OER),” which is an estimate of what a house (or apartment) would rent for if the owner were renting it out. OER is included in the CPI to account for the value of the services an owner receives from living in an apartment or house.
As the following figure shows, inflation in the price of shelter has been a significant contributor to headline inflation. The blue line shows 12-month inflation in shelter, and the red line shows 1-month inflation in shelter. Twelve-month inflation in shelter has been declining since the spring of 2023, but increased in October to 4.9 percent from 4.8 percent in September. One-month inflation in shelter—which is much more volatile than 12-month inflation in shelter—increased sharply from 2.7 percent in September to 4.7 percent in October.
Chair Powell and the other members of the FOMC have been expecting that the inflation in shelter would continue to decline. For instance, in his press conference following the last FOMC meeting on November 7, Powell stated that:
“What’s going on there is, you know, market rents, newly signed leases, are experiencing very low inflation. And what’s happening is older—you know, leases that are turning over are taking several years to catch up to where market leases are; market rent leases are. So that’s just a catch-up problem. It’s not really reflecting current inflationary pressures, it’s reflecting past inflationary pressures.”
The recent uptick in shelter inflation may concern FOMC members as they consider whether, and by how much, to cut their target for the federal funds rate at their next meeting on December 17-18. Bear in mind, though, that shelter has a weight of only 15 percent in the PCE price index that the Fed uses to gauge whether it is hitting its 2 percent inflation target in contrast with the 33 percent weight that shelter has in the CPI.
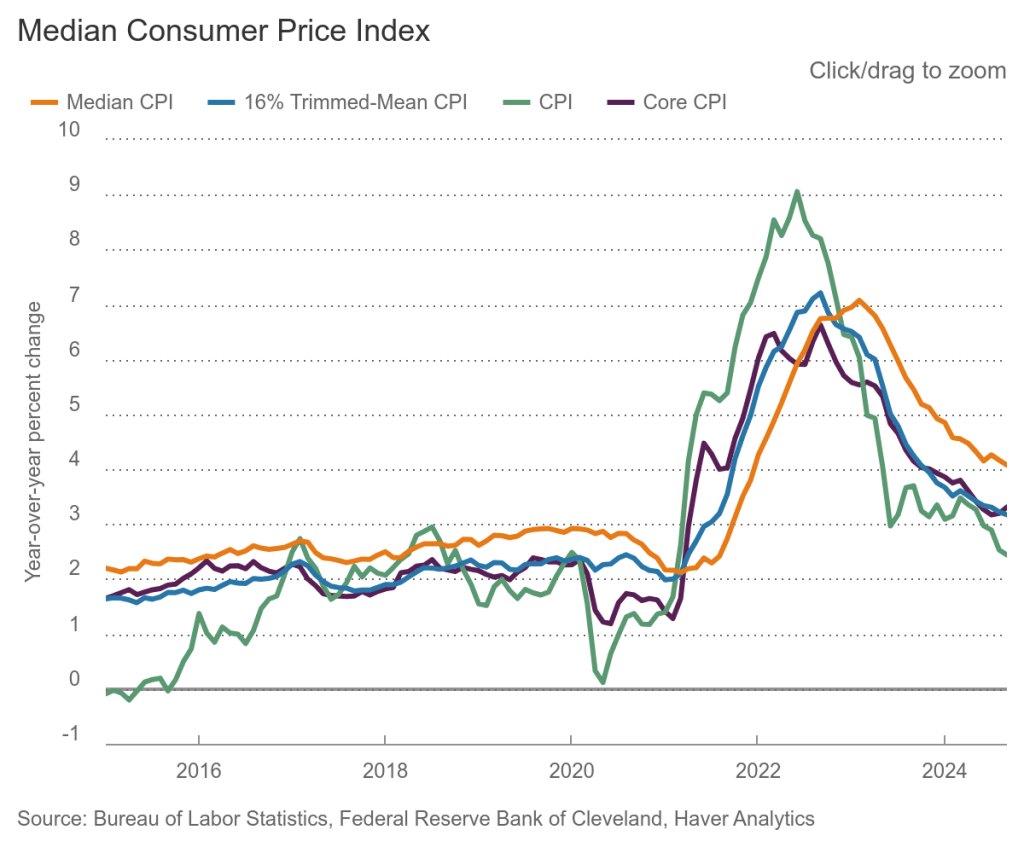
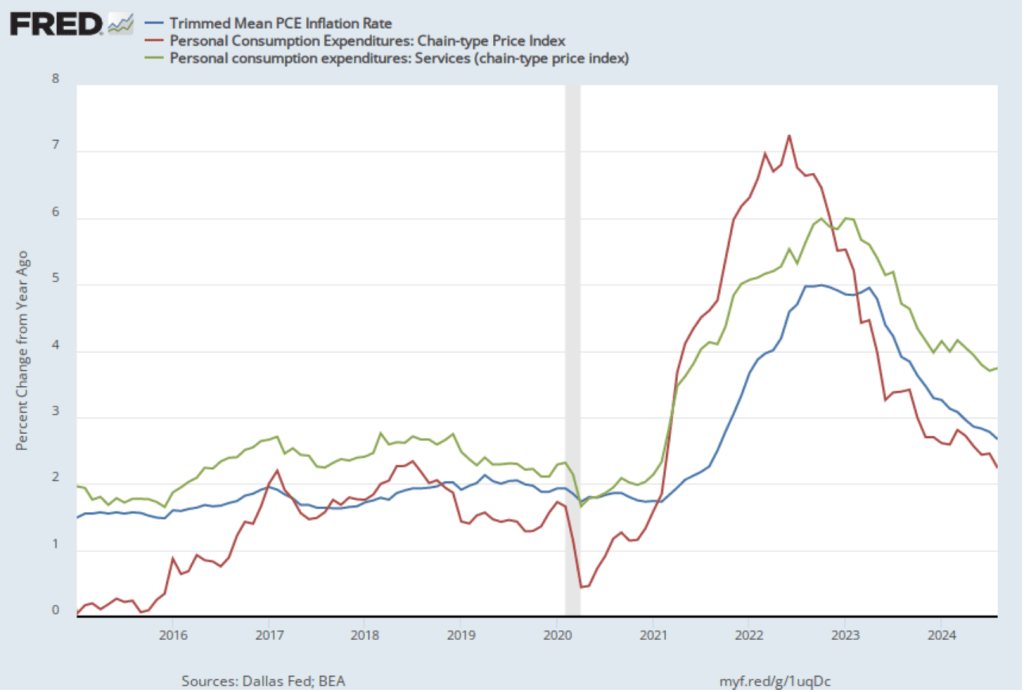
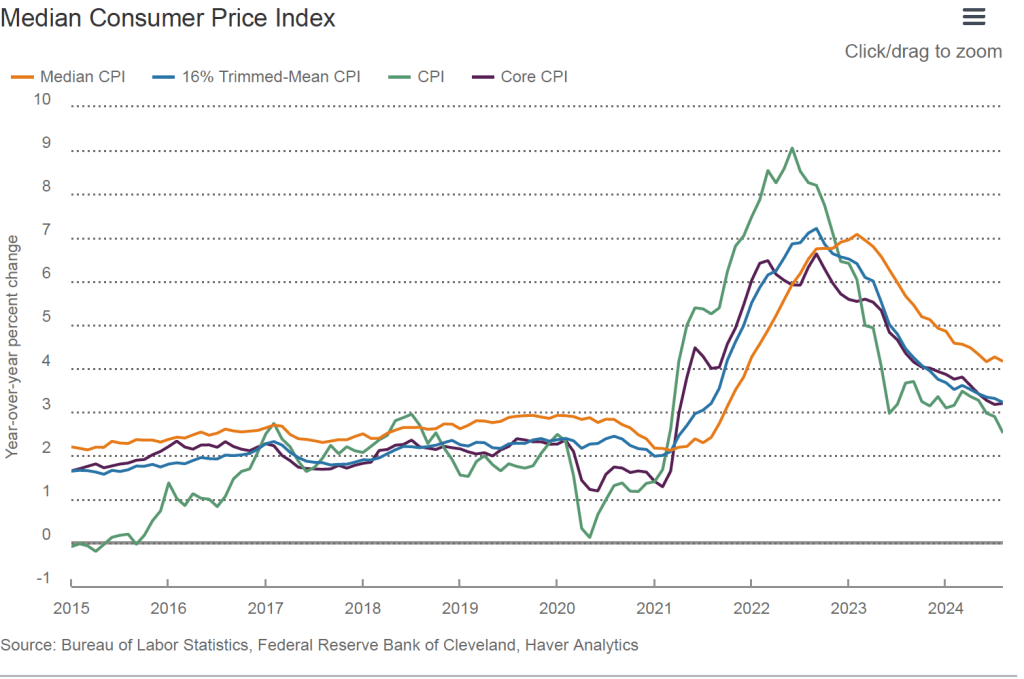
To better estimate of the underlying trend in inflation, some economists look at median inflation and trimmed mean inflation.
- Median inflation is calculated by economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland and Ohio State University. If we listed the inflation rate in each individual good or service in the CPI, median inflation is the inflation rate of the good or service that is in the middle of the list—that is, the inflation rate in the price of the good or service that has an equal number of higher and lower inflation rates.
- Trimmed mean inflation drops the 8 percent of good and services with the highest inflation rates and the 8 percent of goods and services with the lowest inflation rates.
The following figure is from the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland. It shows that median inflation (the orange line) was unchanged in October at 4.1 percent. Trimmed mean inflation (the blue line) was also unchanged at 3.2 percent. These data provide confirmation that (1) core CPI inflation at this point is likely running at least slightly higher than a rate that would be consistent with the Fed achieving its inflation target and (2) that progress toward the target has slowed.

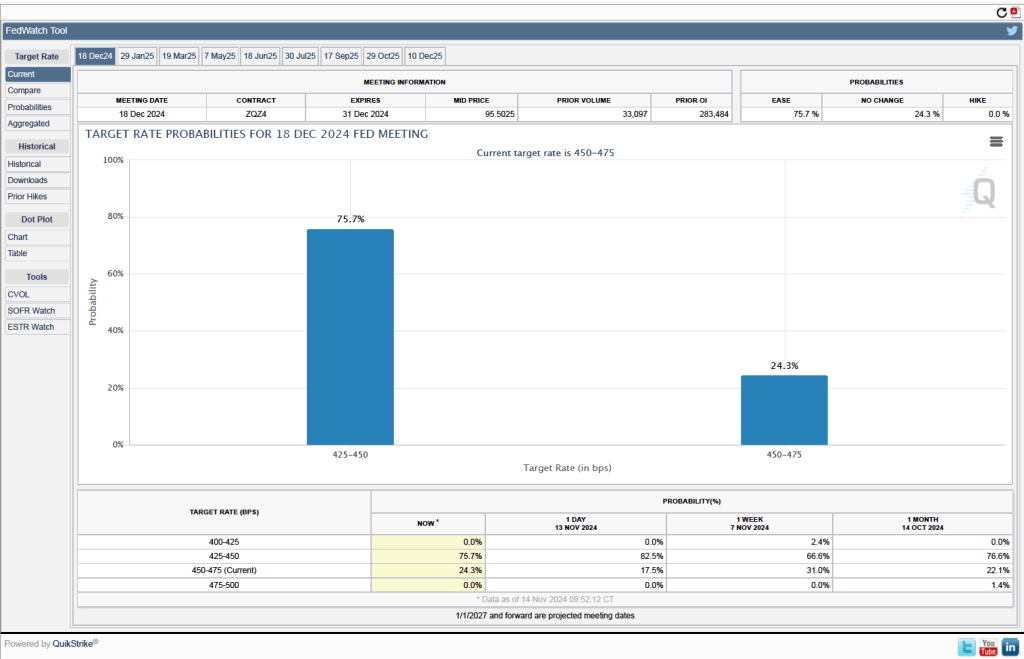
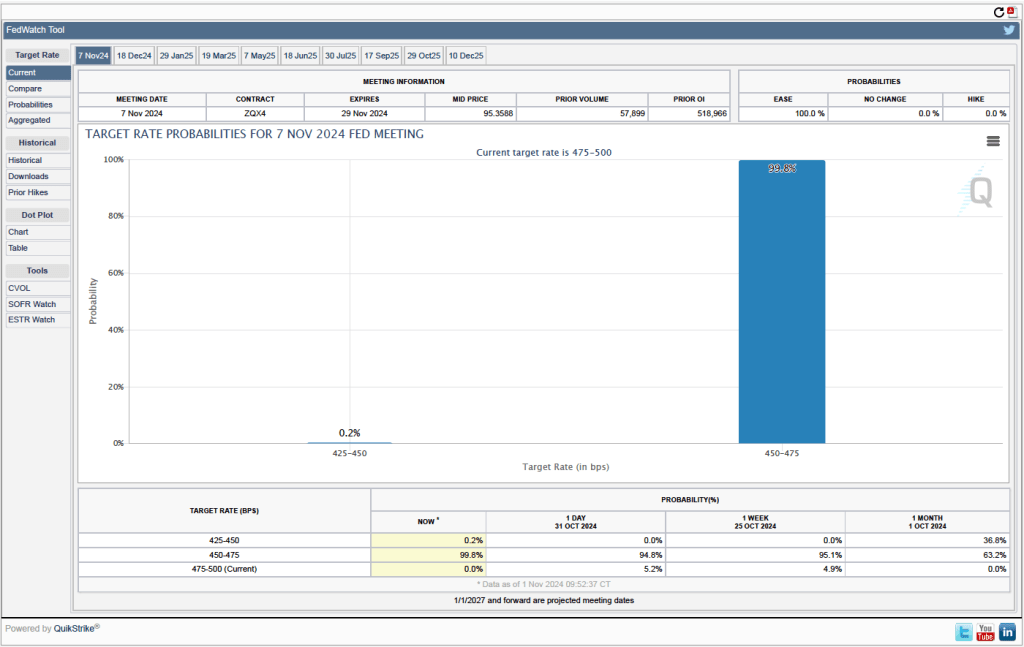
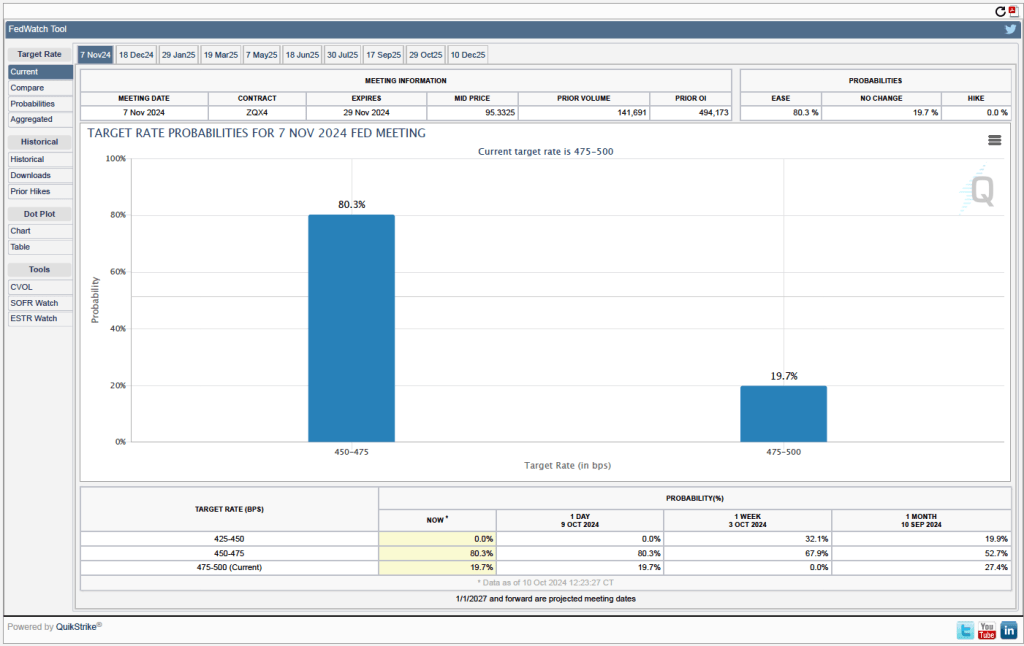
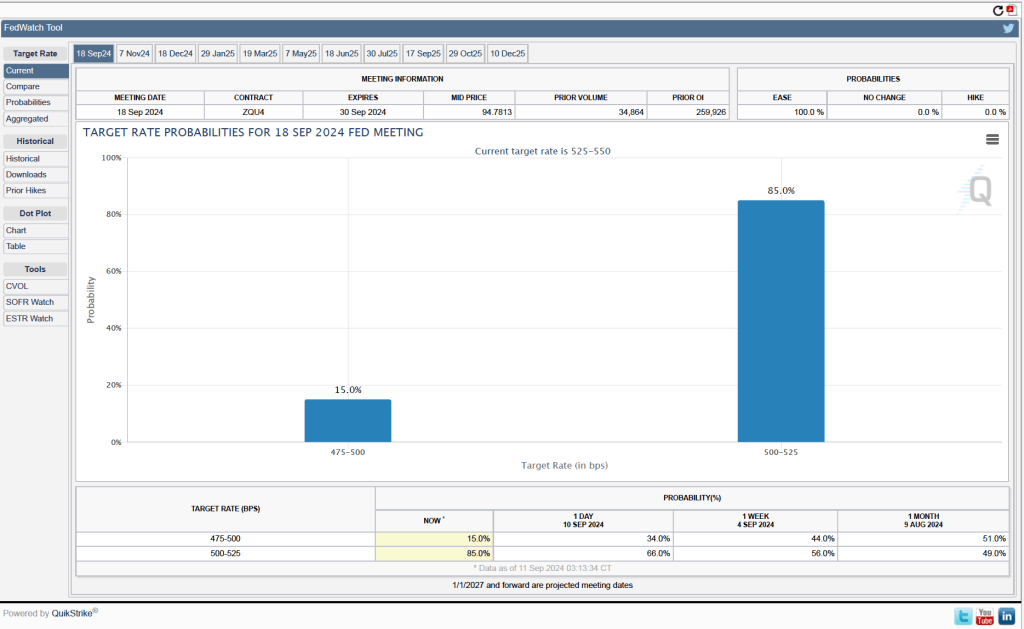
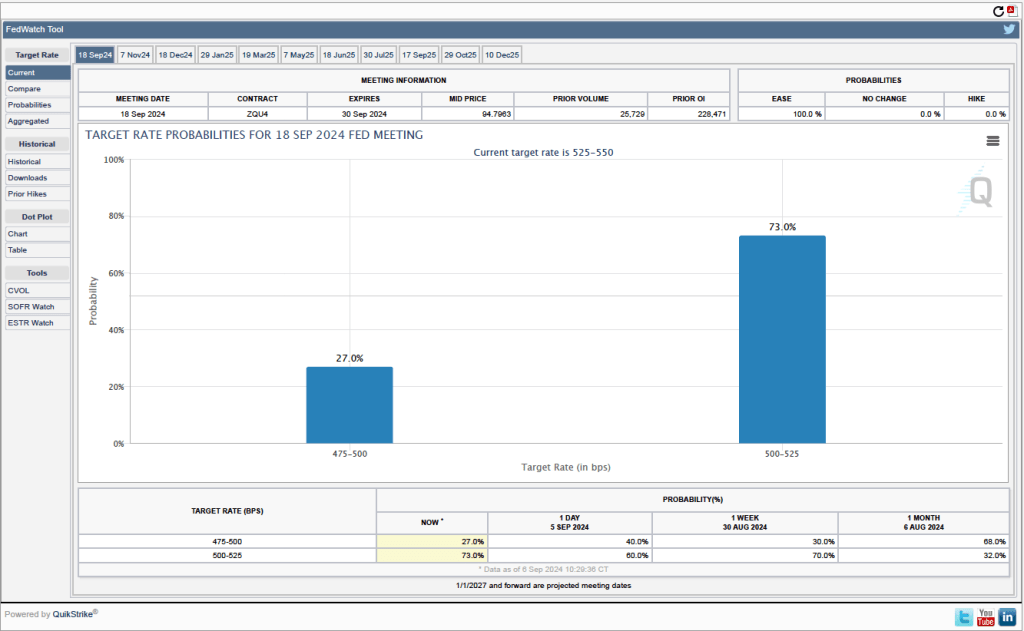
Will this persistence in inflation above the Fed’s 2 percent target cause the FOMC to hold constant its target range for the federal funds rate? Investors who buy and sell federal funds futures contracts expect that the FOMC will cut still cut its target for the federal funds rate by 0.25 percentage point at its December meeting. (We discuss the futures market for federal funds in this blog post.) The following figure that today these investors assign a probability of 75.7 percent to the FOMC cutting its target for the federal funds rate by 0.25 percentage point and a probability of 24.3 percent to the committee leaving its target unchanged at a range of 4.50 percent to 4.75 percent.