
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell at Jackson Hole, Wyoming, August 2023 (Photo from the Associated Press.)
Congress has given the Federal Reserve a dual mandate to achieve price stability and high employment. To reach its goal of price stability, the Fed has set an inflation target of 2 percent, with inflation being measured by the percentage change in the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index.
It’s reasonable to ask whether “price stability” is achieved only when the price level is constant—that is, at a zero inflation rate. In practice, Congress has given the Fed wide latitude in deciding when price stability and high employment has been achieved. The Fed didn’t announce a formal inflation target of 2 percent until 2012. But the members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) had agreed to set a 2 percent inflation target much earlier—in 1996—although they didn’t publicly announce it at the time. (The transcript of the FOMC’s July 2-3, 1996 meeting includes a discussion of the FOMC’s decision to adopt an inflation target.) Implicitly, the FOMC had been acting as if it had a 2 percent target since at least the mid–1980s.
But why did the Fed decide on an inflation target of 2 percent rather than 0 percent, 1 percent, 3 percent, or some other rate? There are three key reasons:
- As we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 9, Section 9.4 (Economics, Chapter 19, Section 29.4 and Essentials of Economics, Chapter 13, Section 13.4), price indexes overstate the actual inflation rate by 0.5 percentage point to 1 percentage point. So, a measured inflation of 2 percent corresponds to an actual inflation rate of 1 to 1.5 percent.
- As we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 15, Section 15.5 (Economics, Chapter 25, Section 25.5), the FOMC has a target for the long-run real federal funds rate. Although the target has been as high as 2 percent, in recent years it has been 0.5 percent. With an inflation target of 2 percent, the long-run nominal federal funds rate target is 2.5 percent. (The FOMC’s long-run target federall funds target can be found in the Summary of Economic Projections here.) As the Fed notes, with an inflation target of less than 2 percent “there would be less room to cut interest rates to boost employment during an economic downturn.”
- An inflation target of less than 2 percent would make it more likely that during recessions, the U.S. economy might experience deflation, or a period during which the price level is falling. Deflation can be damaging if falling prices cause consumers to postpone purchases in the hope of being able to buy goods and services at lower prices in the future. The resulting decline in aggregate demand can make a recession worse. In addition, deflation increases the real interest rate associated with a given nominal interest rate, imposing costs on borrowers, particularly if the deflation is unexpected.
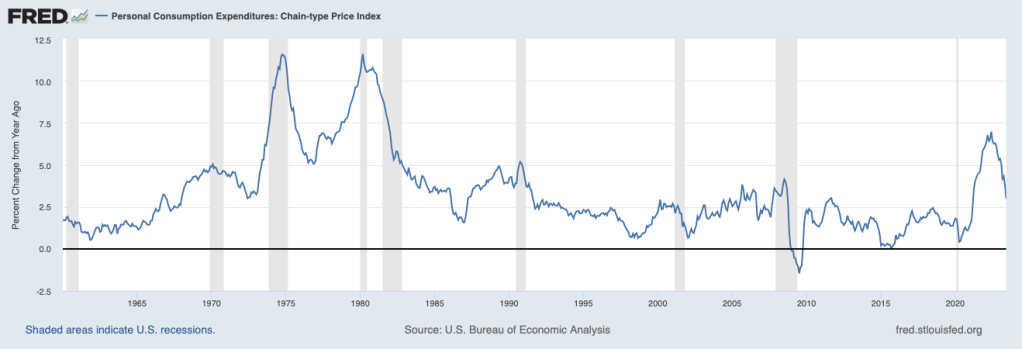
The following figure shows that for most of the period from late 2008 until the spring of 2021, the inflation rate as measured by the PCE was below the Fed’s 2 percent target. Beginning in the spring of 2021, inflation soared, reaching a peak of 7.0 percent in June 2022. Inflation declined over the following year, falling to 3.0 in June 2023.
On August 25, at the Fed’s annual monetary policy symposium in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, Fed Chair Jerome Powell made clear that the Fed intended to continue a restrictive monetary policy until the inflation rate had returned to 2 percent: “It is the Fed’s job to bring inflation down to our 2 percent goal, and we will do so.” (The text of Powell’s speech can be found here.) Some economists have been arguing that once the Fed had succeeded in pushing the inflation rate back to 2 percent it should, in the future, consider raising its inflation target to 3 percent. At Jackson Hole, Powell appeared to rule out this possibility: “Two percent is and will remain our inflation target.”
Why might a 3 percent inflation target be preferrable to a 2 percent inflation target? Proponents of the change point to two key advantages:
- Reducing the likelihood of monetary policy being constrained by the zero lower bound. Because the federal funds rate can’t be negative, zero provides a lower bound on how much the FOMC can cut its federal funds rate target in a recession. Monetary policy was constrained by the zero lower bound during both the Great Recession of 2007–2009 and the Covid recession of 2020. Because an inflation target of 3 percent could likely be achieved with a federal funds rate that is higher than the FOMC’s current long-run target of 2.5 percent, the FOMC should have more room to cut its target during a recession.
- During a recession, firms attempting to reduce costs can do so by cutting workers’ nominal wages. But, as we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 13, Section 13.2 (Economics, Chapter 23, Section 23.2 and Essentials of Economics, Chapter 15, Section 15.2), most workers dislike wage cuts. Some workers will quit rather than accept a wage cut and the productivity of workers who remain may decline. As a result, firms often use a policy of freezing wages rather than cutting them. Freezing nominal wages when inflation is occurring results in cuts to real wages. The higher the inflation rate, the greater the decline in real wages and the more firms can reduce their labor costs without laying off workers.
Why would Powell rule out increasing the Fed’s target for the inflation rate? Although he didn’t spell out the reasons in his Jackson Hole speech, these are two main points usually raised by those who favor keeping the target at 2 percent:
- A target rate above 2 percent would be inconsistent with the price stability component of the Fed’s dual mandate. During the years between 2008 and 2021 when the inflation rate was usually at or below 2 percent, most consumers, workers, and firms found the inflation rate to be low enough that it could be safely ignored. A rate of 3 percent, though, causes money to lose its purchasing power more quickly and makes it less likely that people will ignore it. To reduce the effects of inflation people are likely to spend resources in ways such as firms reprinting menus or price lists more frequently or labor unions negotiating for higher wages in multiyear wage contracts. The resources devoted to avoiding the negative effects of inflation represent an efficiency loss to the economy.
- Raising the target for the inflation rate might undermine the Fed’s credibility in fighting inflation. One of the reasons that the Fed was able to bring down the inflation rate without causing a recession—at least through August 2023—was that the expectations of workers, firms, and investors remained firmly anchored. That is, there was a general expectation that the Fed would ultimately succeed in bringing the inflation back down to 2 percent. If expectations of inflation become unanchored, fighting inflation becomes harder because workers, firms, and investors are more likely to take actions that contribute to inflation. For instance, lenders won’t assume that inflation will be 2 percent in the future and so will require higher nominal interest rates on loans. Workers will press for higher nominal wages to protect themselves from the effects of higher inflation, thereby raising firms’ costs. Raising its inflation target to 3 percent may also cause workers, firms, and investors to question whether during a future period of high inflation the Fed will raise its target to an even higher rate. If that happens, inflation may be more persistent than it was during 2022 and 2023.
It seems unlikely that the Fed will raise its target for the inflation rate in the near future. But the Fed is scheduled to review its current monetary policy strategy in 2025. It’s possible that as part of that review, the Fed may revisit the issue of its inflation target.
