Image generated by ChatGTP4-o
As we’ve noted in earlier posts, according to the usually reliable GDPNow forecast from the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, real GDP in the first quarter of 2025 will decline by 2.8 percent. This morning (April 4), the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) released its “Employment Situation” report (often called the “jobs report”) for March. The data in the report show no sign that the U.S. economy is in a recession. We should add two caveats, however: 1. The effects of the unexpectedly large tariff increases announced this week by the Trump Administration are not reflected in the data from this report, and 2. at the beginning of a recession the data in the jobs report can be subject to large revisions.
The jobs report has two estimates of the change in employment during the month: one estimate from the establishment survey, often referred to as the payroll survey, and one from the household survey. As we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 9, Section 9.1 (Economics, Chapter 19, Section 19.1), many economists and Federal Reserve policymakers believe that employment data from the establishment survey provide a more accurate indicator of the state of the labor market than do the household survey’s employment data and unemployment data. (The groups included in the employment estimates from the two surveys are somewhat different, as we discuss in this post.)
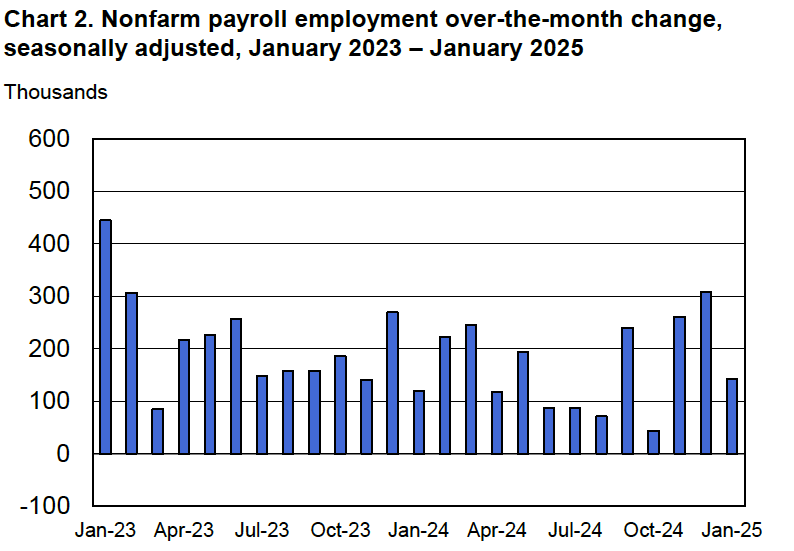
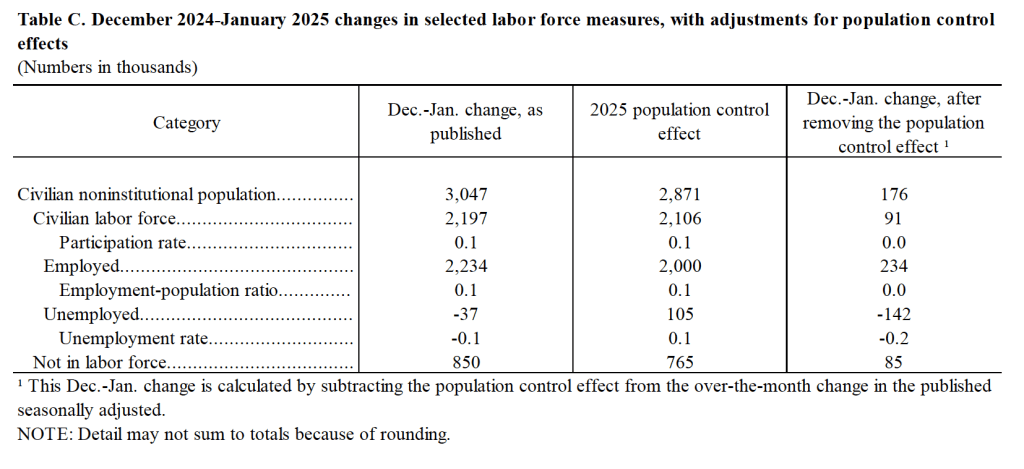
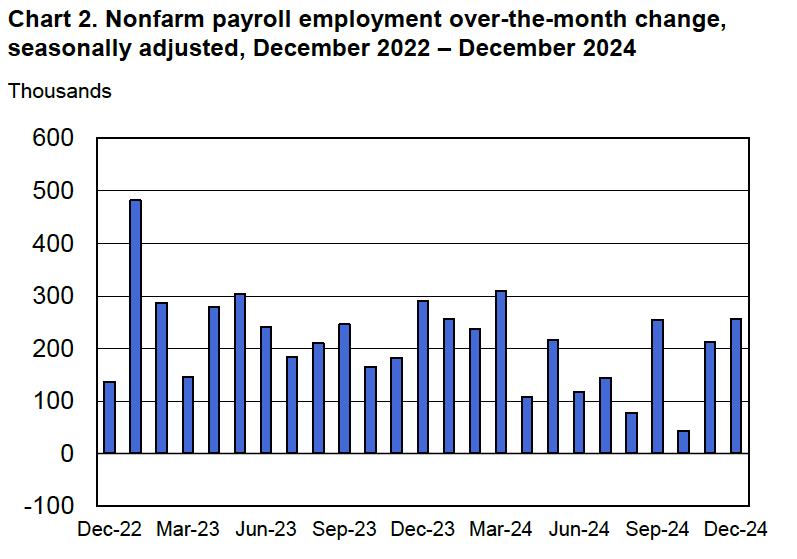
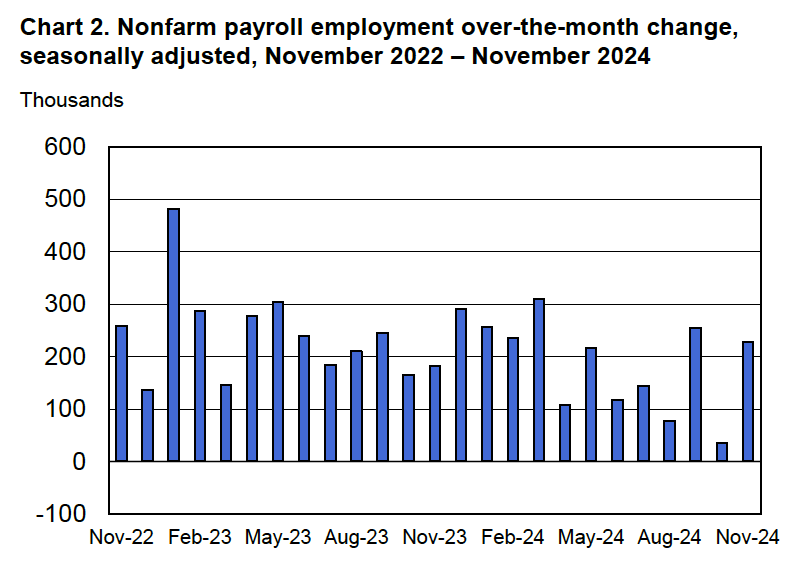
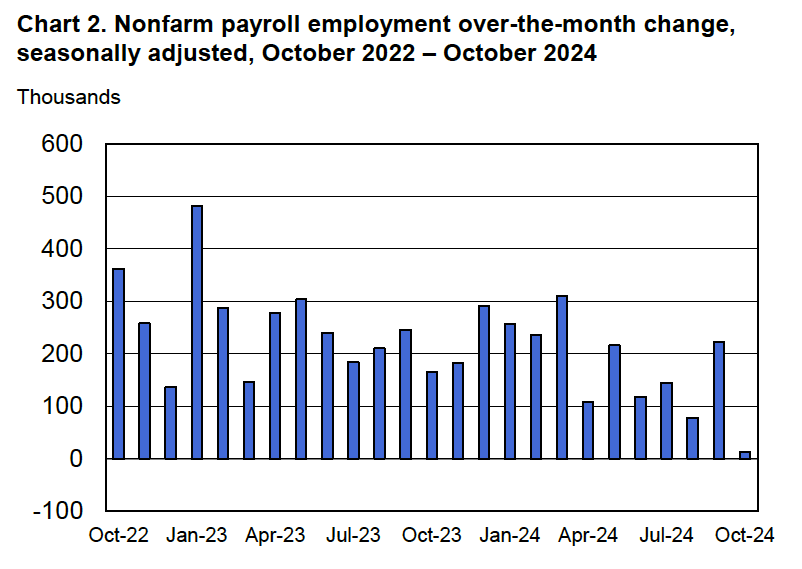
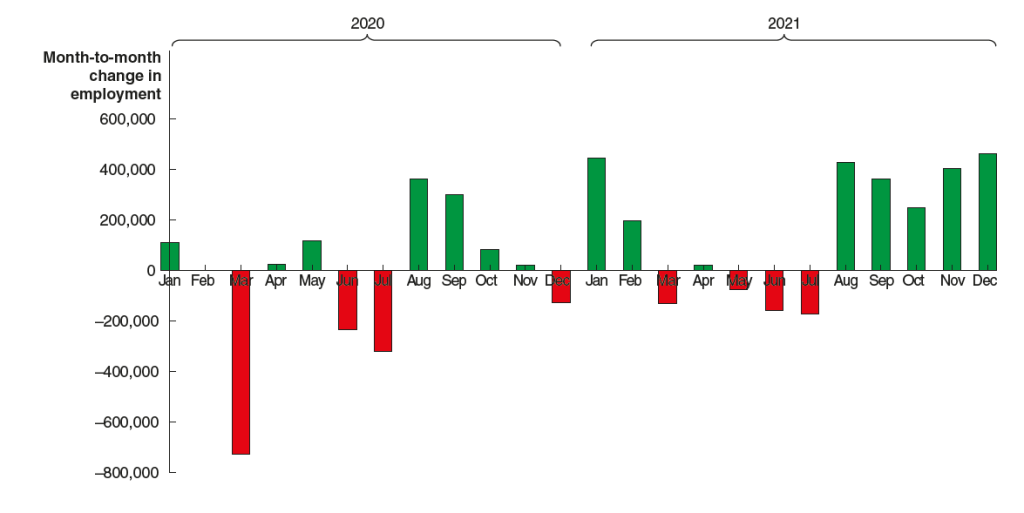
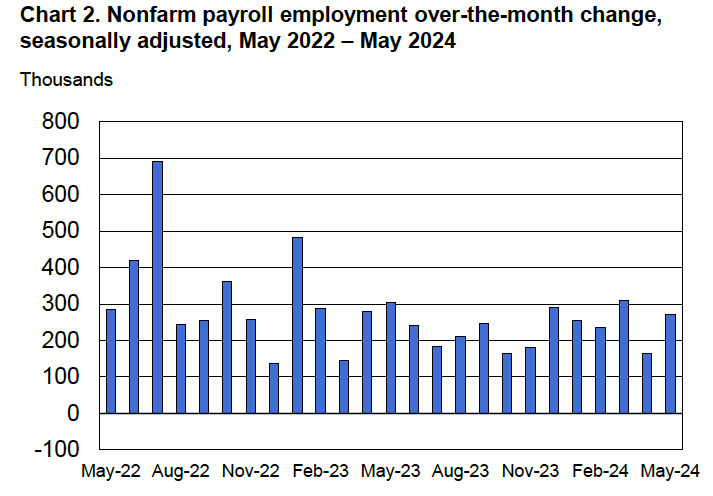
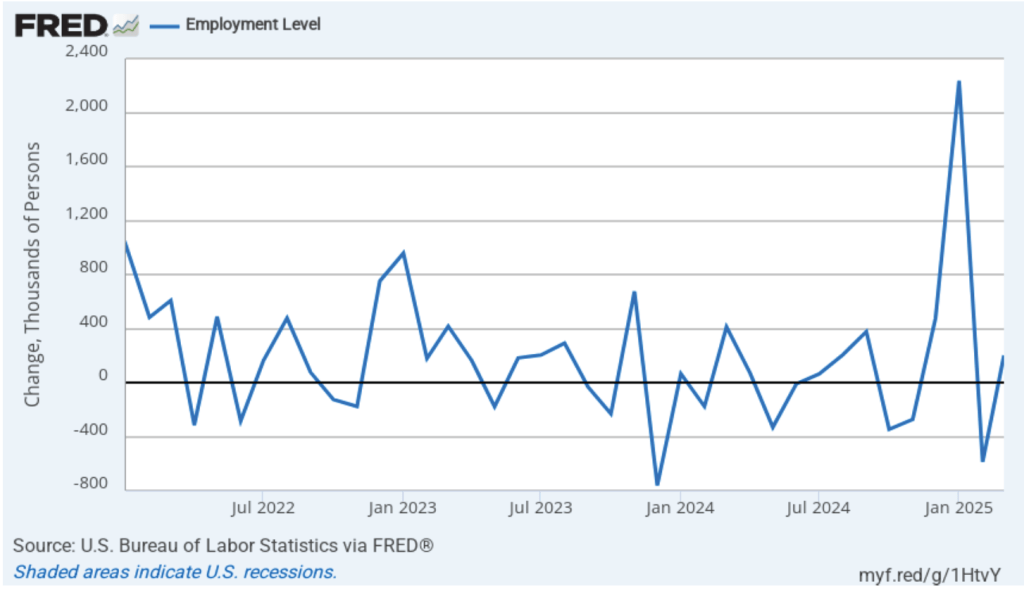
According to the establishment survey, there was a net increase of 228,000 jobs during March. This increase was well above the increase of 140,000 that economists had forecast. Somewhat offsetting this unexpectedly large increase was the BLS revising downward its previous estimates of employment in January and February by a combined 48,000 jobs. (The BLS notes that: “Monthly revisions result from additional reports received from businesses and government agencies since the last published estimates and from the recalculation of seasonal factors.”) The following figure from the jobs report shows the net change in payroll employment for each month in the last two years.

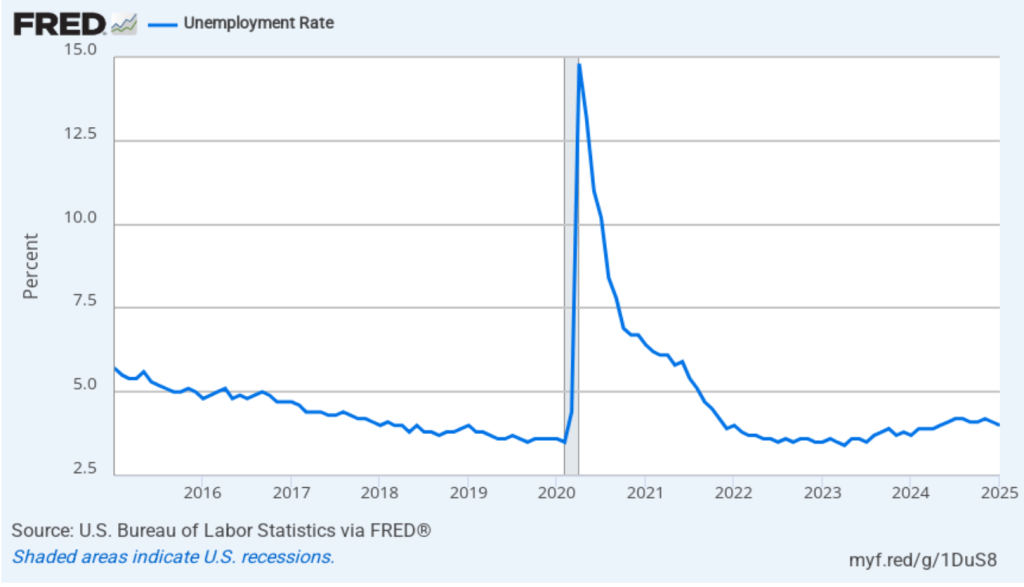
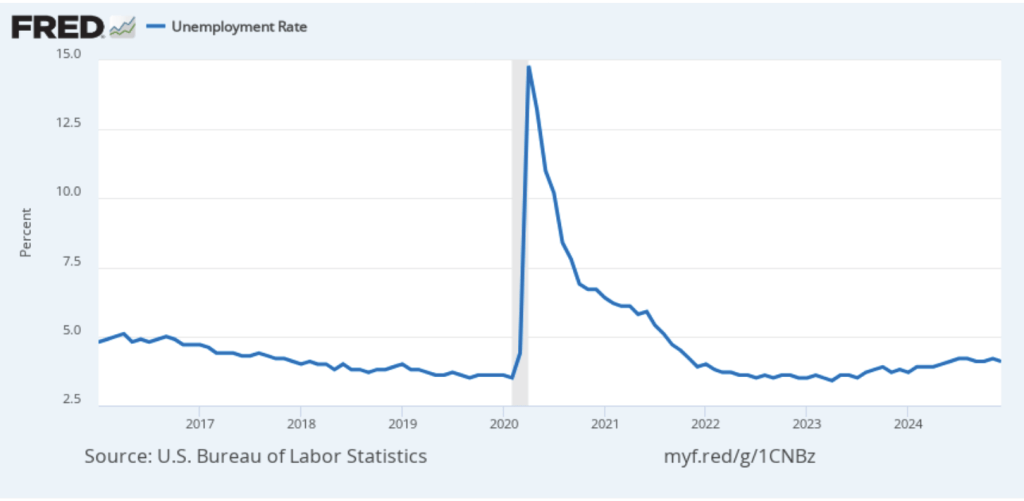
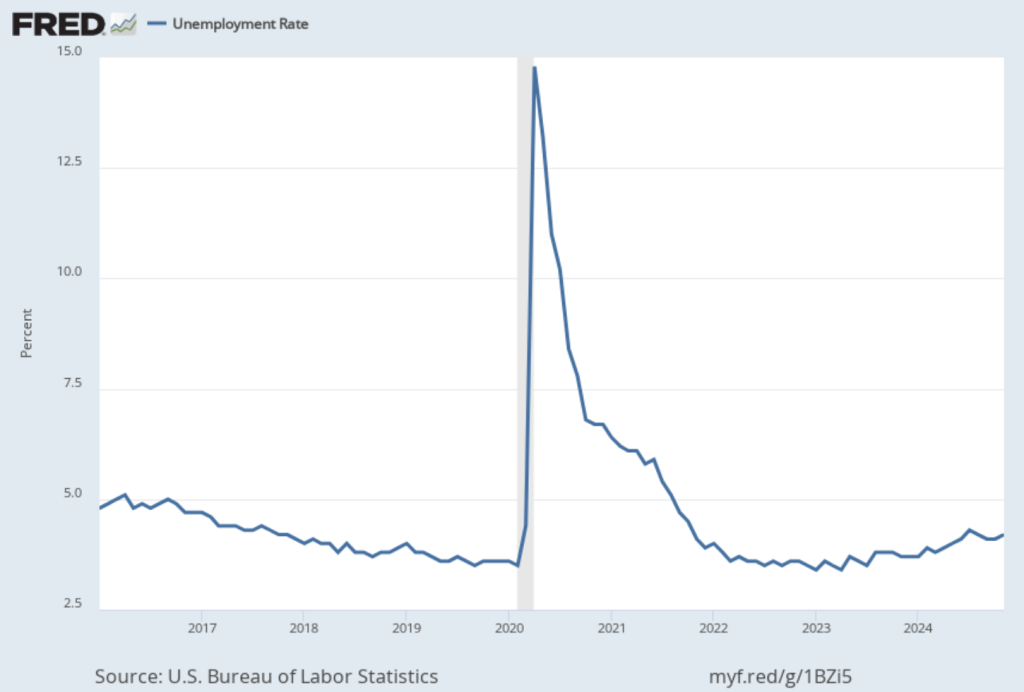
The unemployment rate rose slightly to 4.2 percent in March from 4.1 percent in February. As the following figure shows, the unemployment rate has been remarkably stable in recent months, staying between 4.0 percent and 4.2 percent in each month since May 2024. In March, the members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) forecast that the unemployment rate for 2025 would average 4.4 percent.

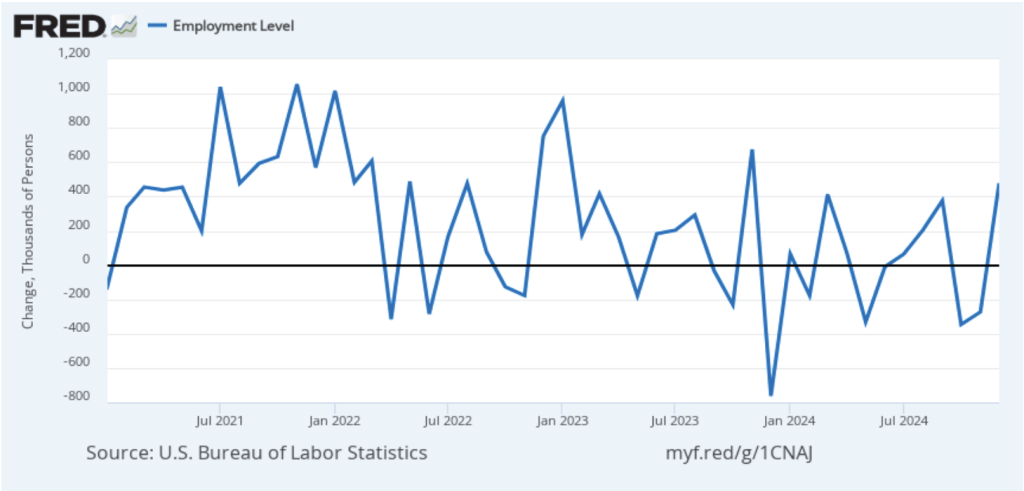
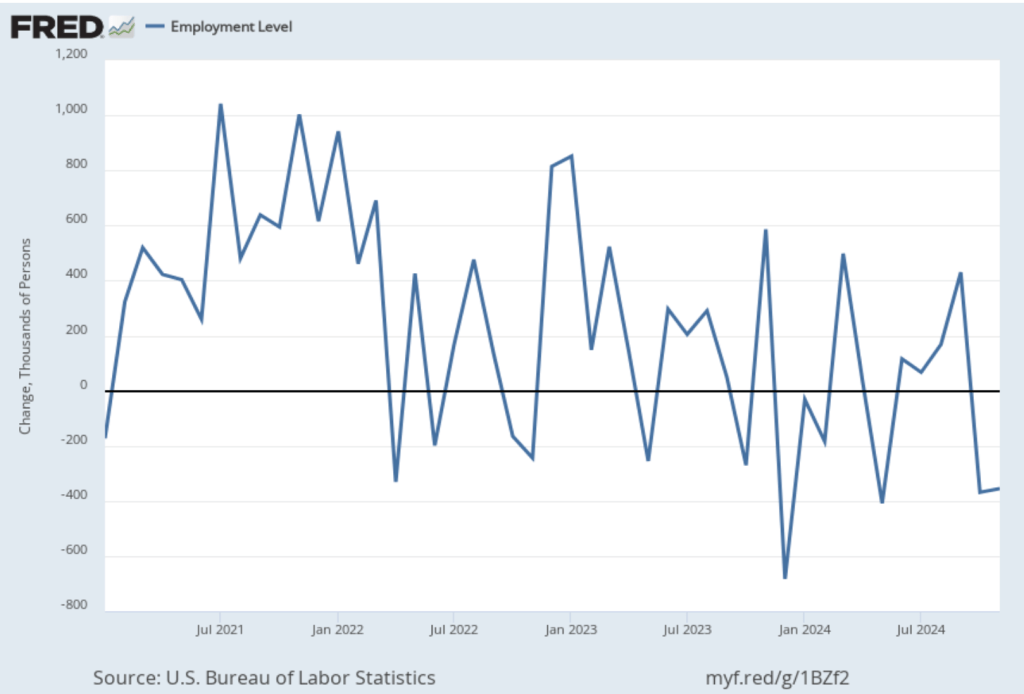
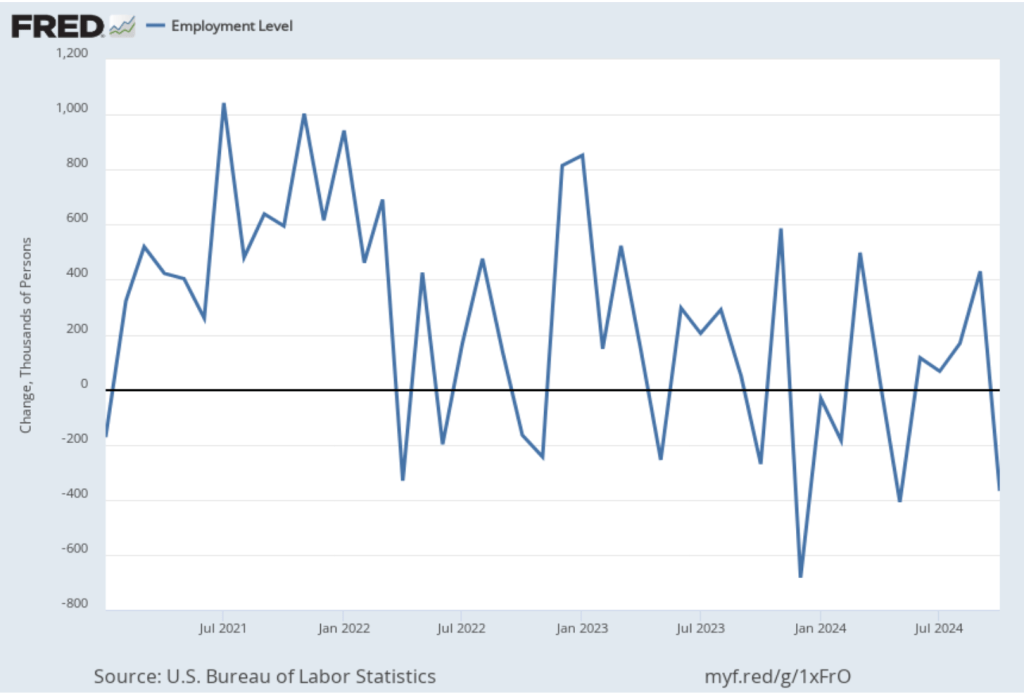
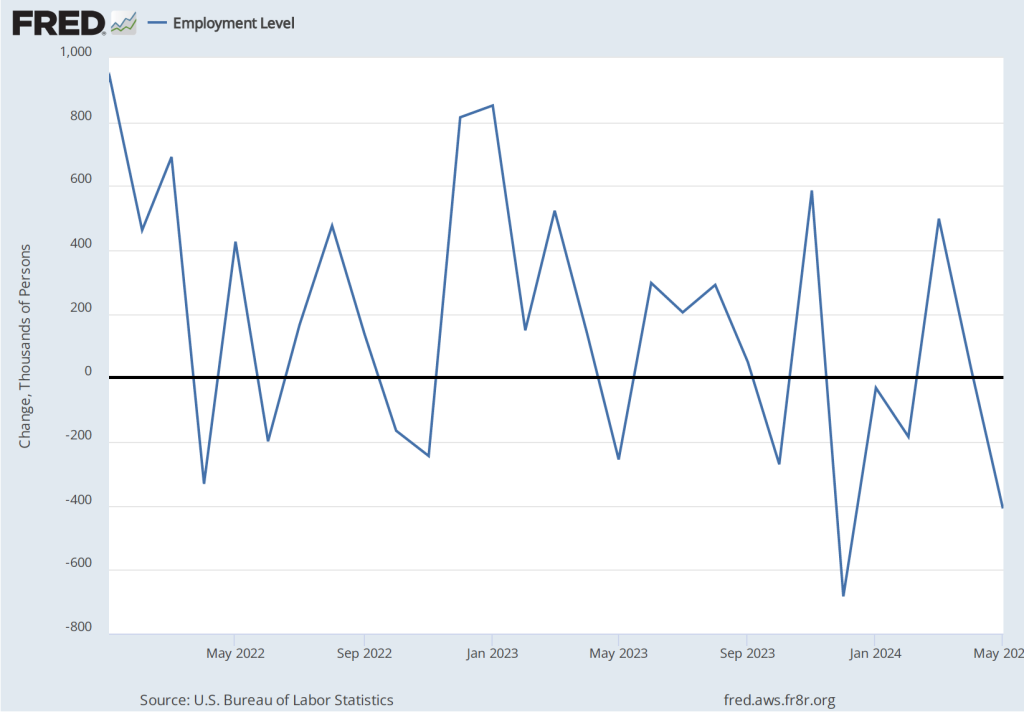
As the following figure shows, the monthly net change in jobs from the household survey moves much more erratically than does the net change in jobs from the establishment survey. As measured by the household survey, there was a net increase of 201,000 jobs in March, following a sharp decrease of 588,000 jobs in February. In any particular month, the story told by the two surveys can be inconsistent with employment increasing in one survey while falling in the other. This month, however, both surveys showed roughly the same net job increase. (In this blog post, we discuss the differences between the employment estimates in the two surveys.)
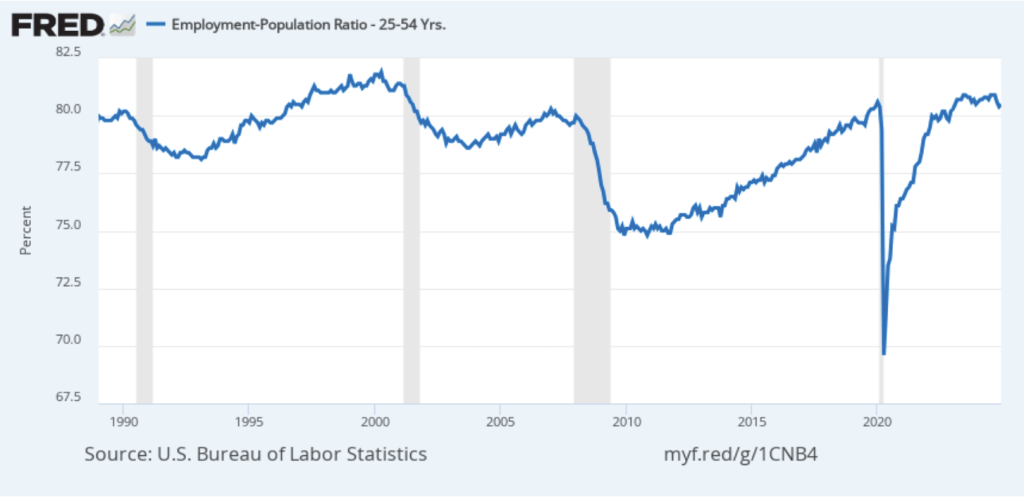
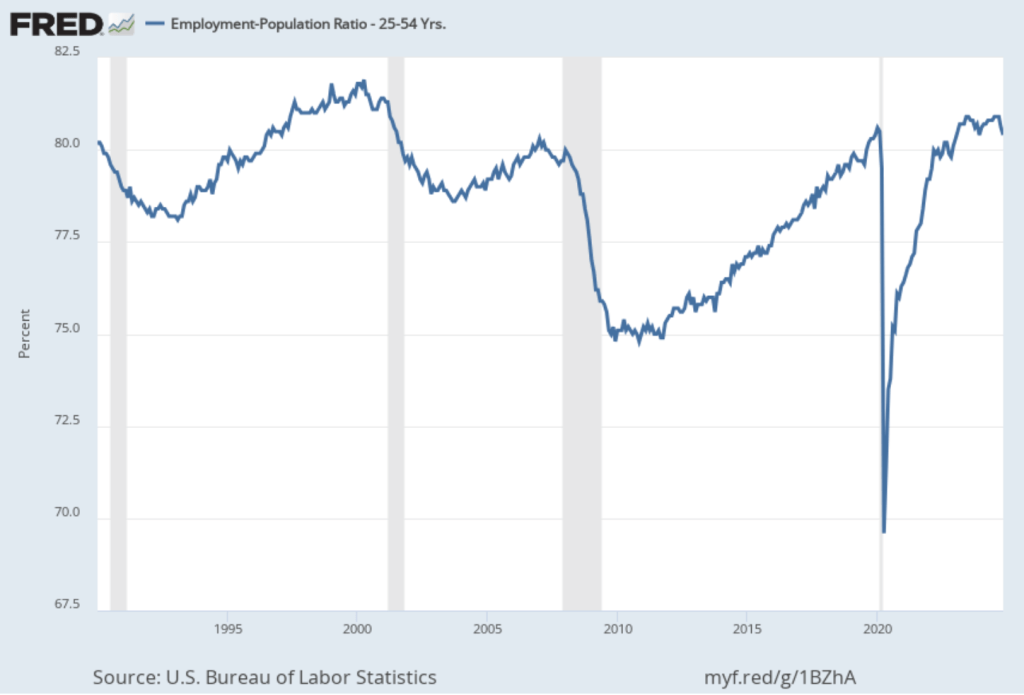
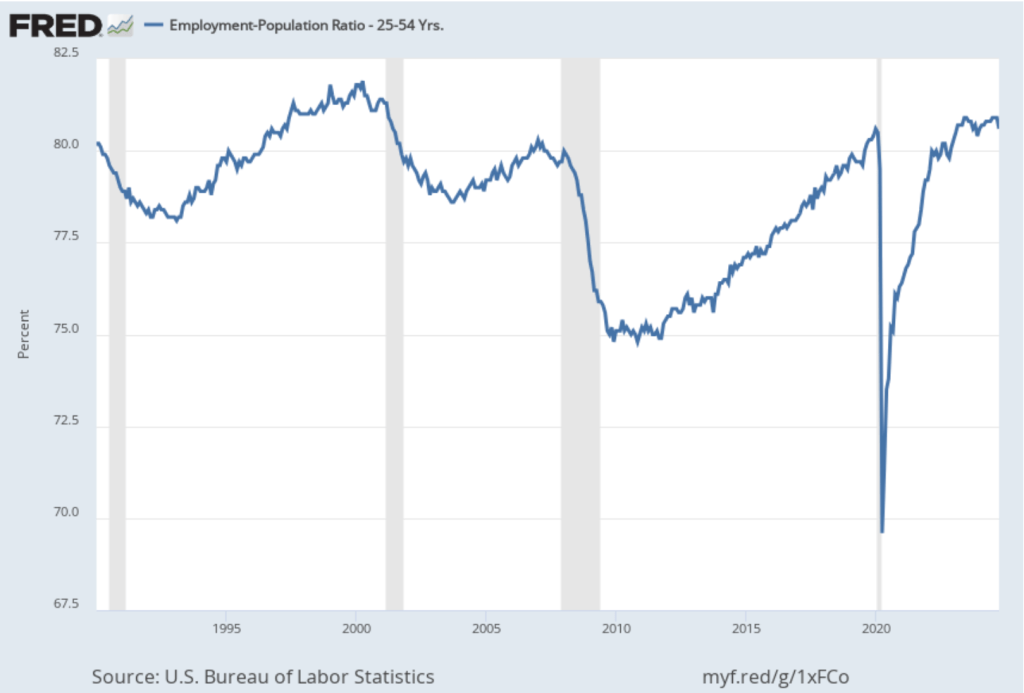
One concerning sign in the household survey is the fall in the employment-population ratio for prime age workers—those aged 25 to 54. The ratio declined from 80.5 percent in February to 80.4 percent in March. Although the prime-age employment-population is still high relative to the average level since 2001, it’s now well below the high of 80.9 percent in mid-2024. Continuing declines in this ratio would indicate a significant softening in the labor market.

It’s unclear how many federal workers have been laid off since the Trump Administration took office. The establishment survey shows a decline in total federal government employment of 4,000 in March. However, the BLS notes that: “Employees on paid leave or receiving ongoing severance pay are counted as employed in the establishment survey.” It’s possible that as more federal employees end their period of receiving severance pay, future jobs reports may find a more significant decline in federal employment.

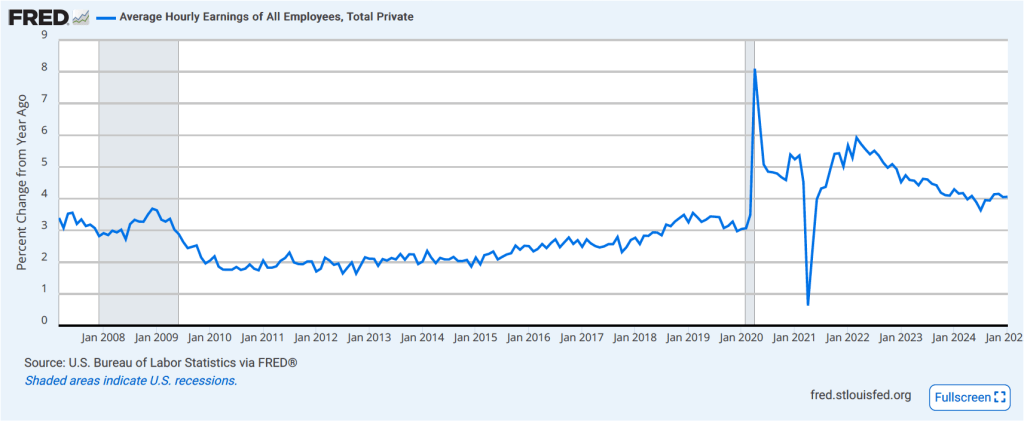
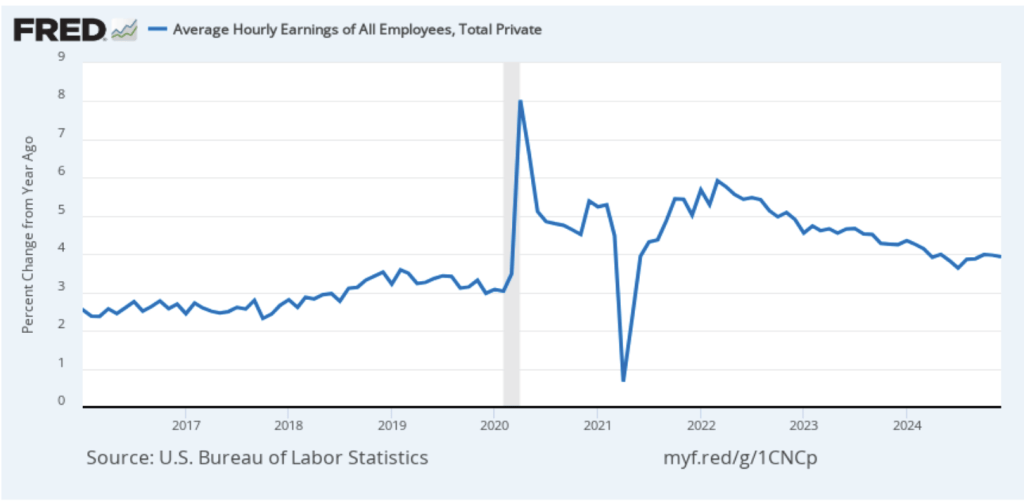
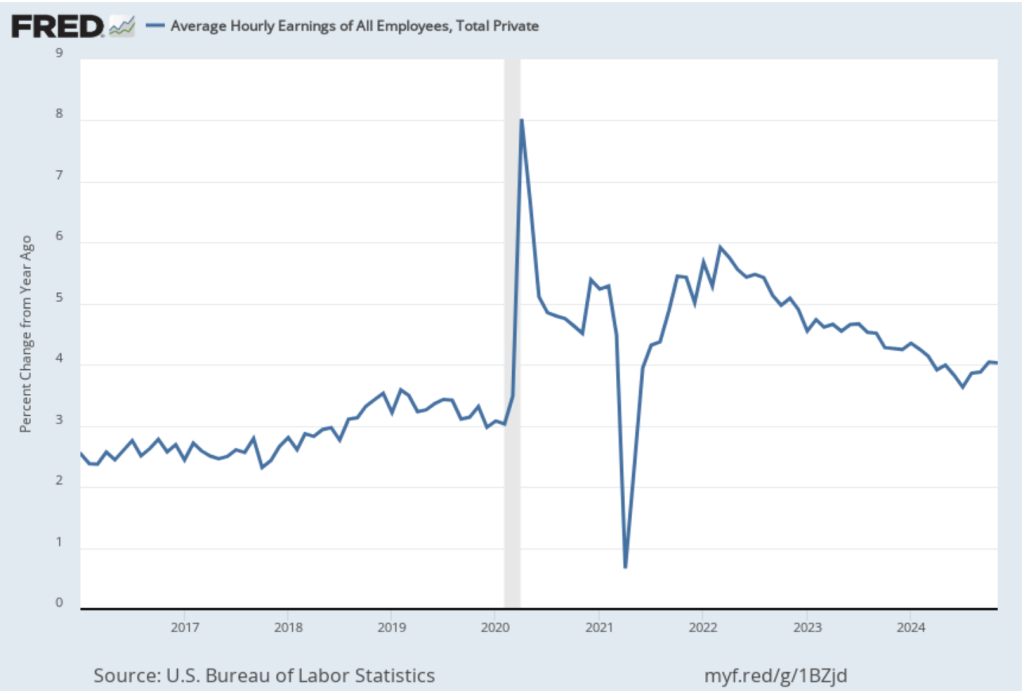
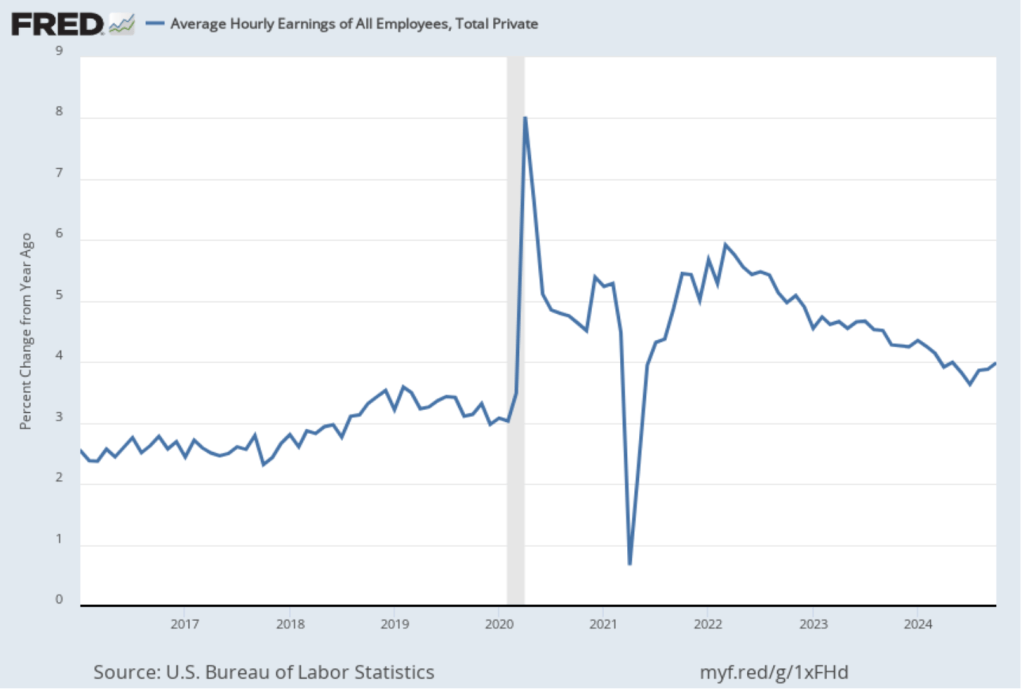
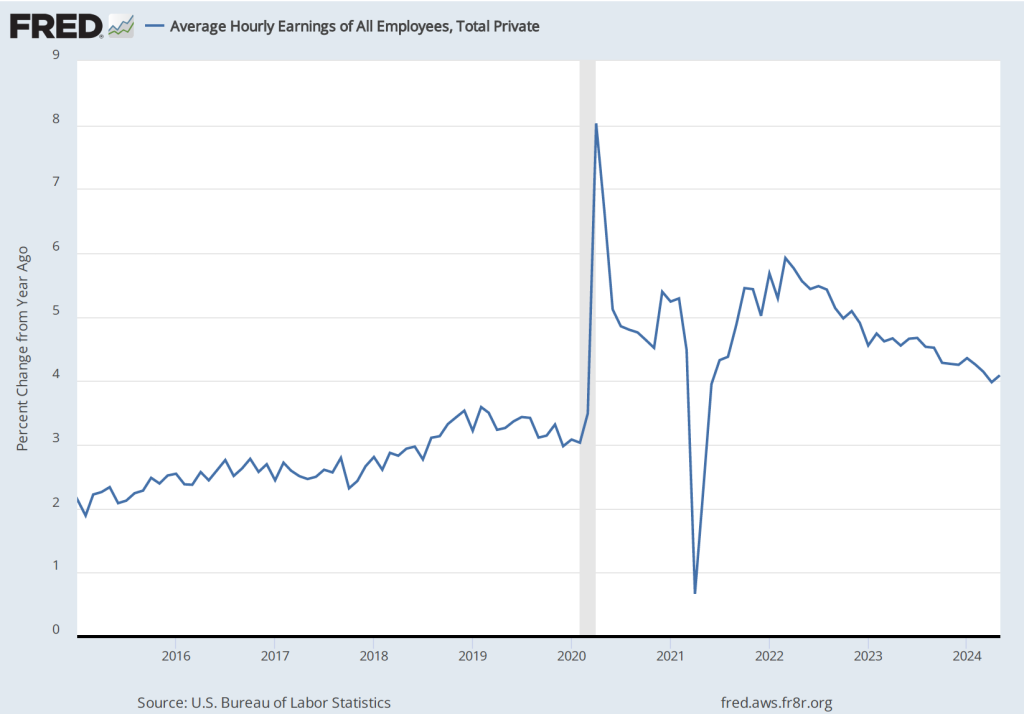
The establishment survey also includes data on average hourly earnings (AHE). As we noted in this post, many economists and policymakers believe the employment cost index (ECI) is a better measure of wage pressures in the economy than is the AHE. The AHE does have the important advantage of being available monthly, whereas the ECI is only available quarterly. The following figure shows the percentage change in the AHE from the same month in the previous year. The AHE increased 3.8 percent in March, down from 4.0 percent in February.

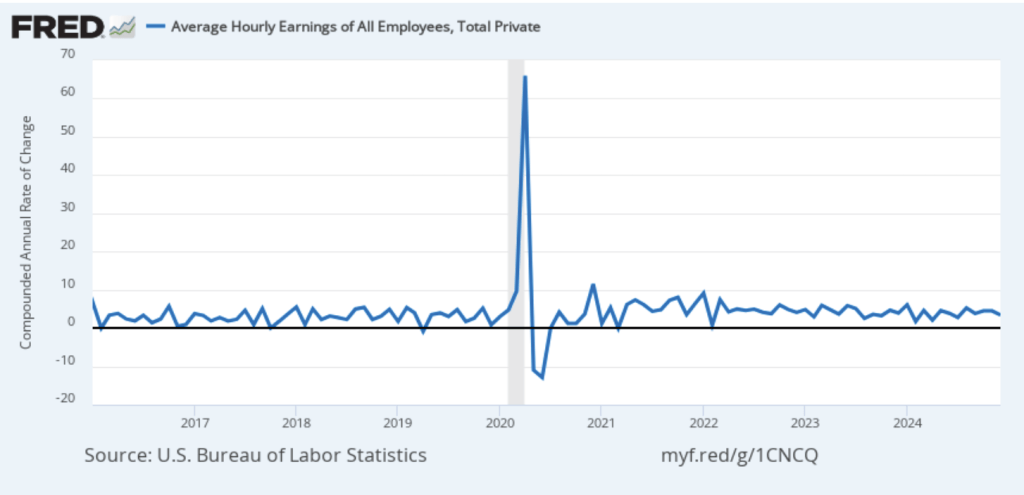
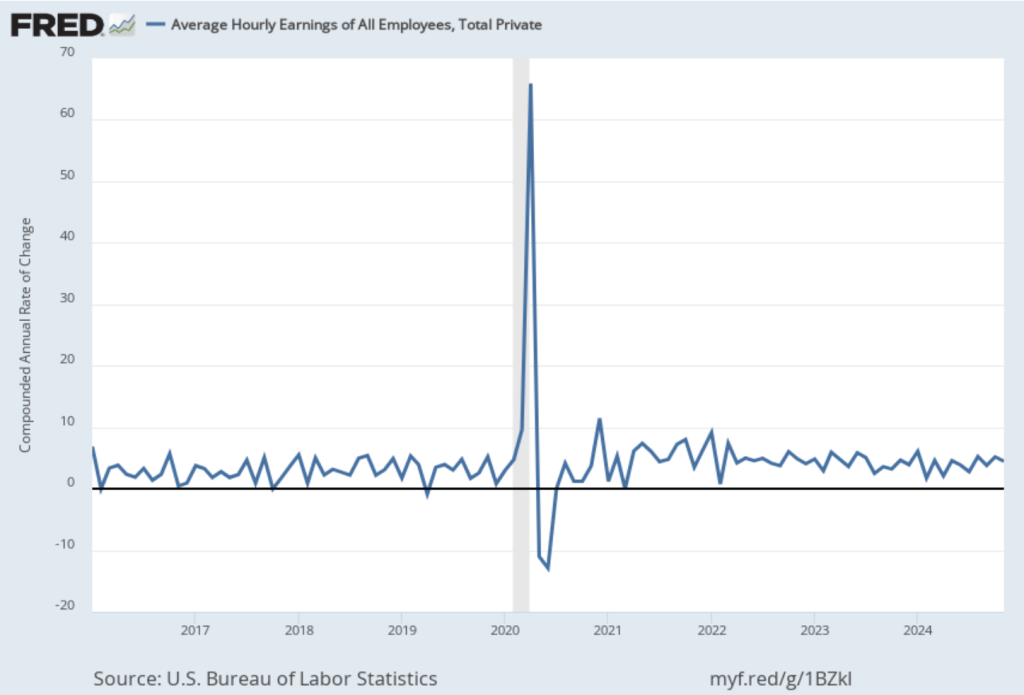
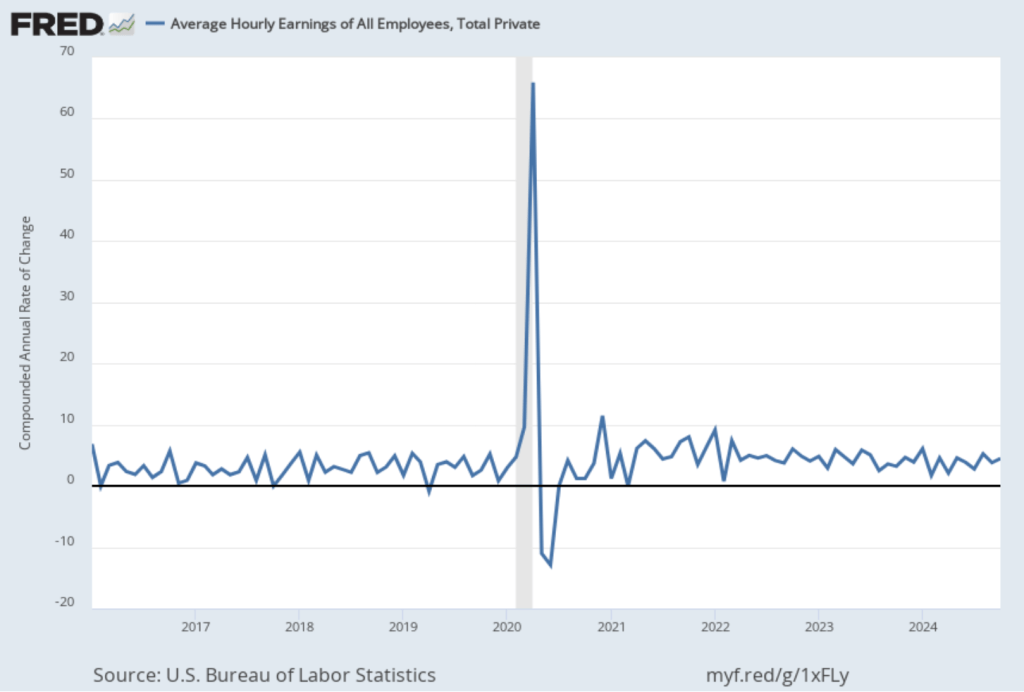
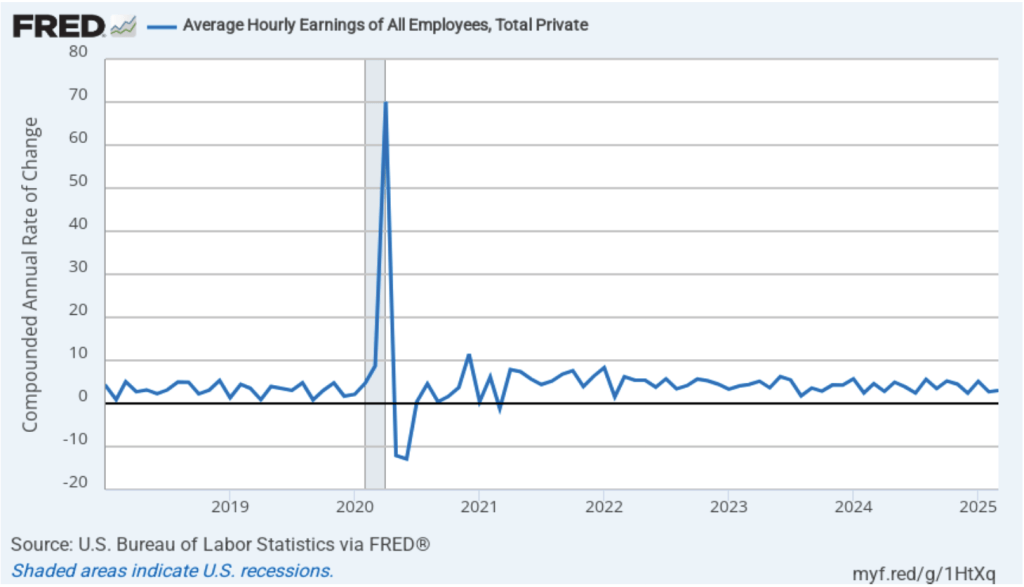
The following figure shows wage inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month wage inflation, whereas this figure shows 1-month wage inflation.) One-month wage inflation is much more volatile than 12-month wage inflation—note the very large swings in 1-month wage inflation in April and May 2020 during the business closures caused by the Covid pandemic. The March 1-month rate of wage inflation was 3.0 percent, up from 2.7 percent in February. Whether measured as a 12-month increase or as a 1-month increase, AHE is still increasing somewhat more rapidly than is consistent with the Fed achieving its 2 percent target rate of price inflation.
Taken by itself, today’s jobs report leaves the situation facing the Federal Reserve’s policy-making Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) largely unchanged. There are some indications that the economy may be weakening, as shown by some of the data in the jobs report and by some of the data incorporated by the Atlanta Fed in its pessimistic nowcast of first quarter real GDP. But the Fed hasn’t yet brought inflation down to its 2 percent annual target.
Looming over monetary policy is the fallout from the Trump Administration’s implementation of unexpectedly large tariff increases. As we note in this blog post, a large unexpected increase in tariffs results in an aggregate supply shock to the economy. In terms of the basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model that we discuss in Macroeconomics, Chapter 13 (Economics, Chapter 23), an unexpected increase in tariffs shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) to the left, increasing the price level and reducing the level of real GDP.
The effect of the tariffs poses a dilemma for the Fed. With inflation still running above the 2 percent annual target, additional upward pressure on the price level is unwelcome news. The dramatic decline in both stock prices and in the interest rate on the 10-Treasury note indicate that investors are concerned that the tariffs increases may push the U.S. economy into a recession. The FOMC can respond to the threat of a recession by cutting its target for the federal funds rate, but doing so runs the risk of pushing inflation higher.
In a speech today, Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated the following:
“We have stressed that it will be very difficult to assess the likely economic effects of higher tariffs until there is greater certainty about the details, such as what will be tariffed, at what level and for what duration, and the extent of retaliation from our trading partners. While uncertainty remains elevated, it is now becoming clear that the tariff increases will be significantly larger than expected. The same is likely to be true of the economic effects, which will include higher inflation and slower growth. The size and duration of these effects remain uncertain. While tariffs are highly likely to generate at least a temporary rise in inflation, it is also possible that the effects could be more persistent. Avoiding that outcome would depend on keeping longer-term inflation expectations well anchored, on the size of the effects, and on how long it takes for them to pass through fully to prices. Our obligation is to keep longer-term inflation expectations well anchored and to make certain that a one-time increase in the price level does not become an ongoing inflation problem.”
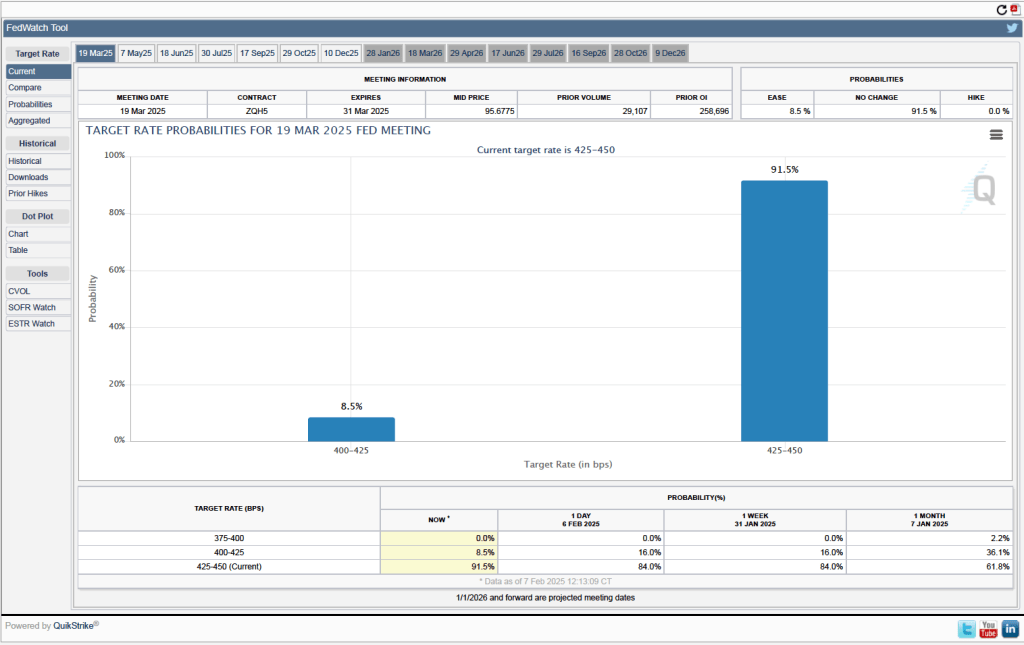
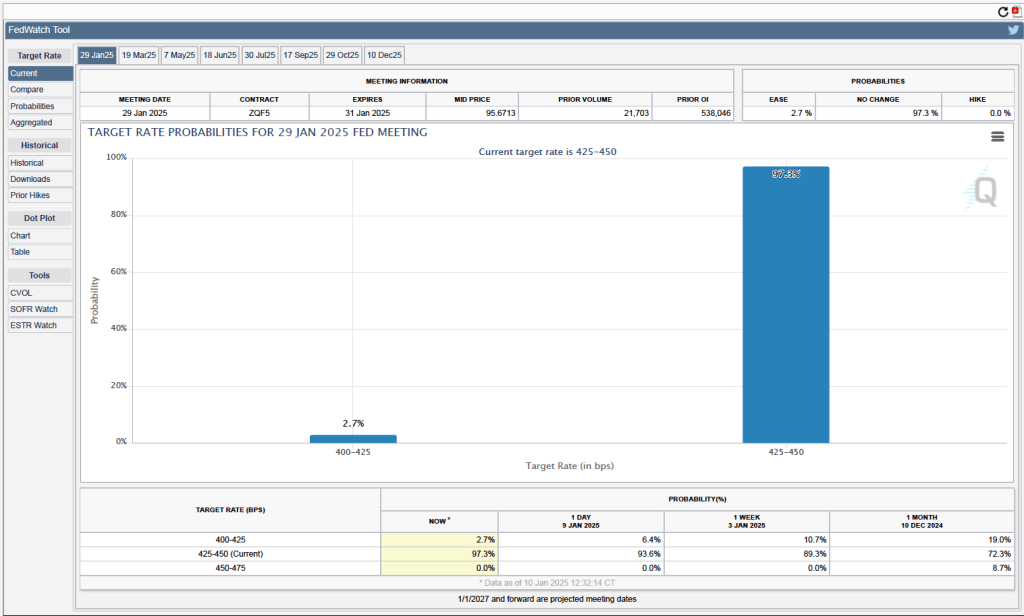
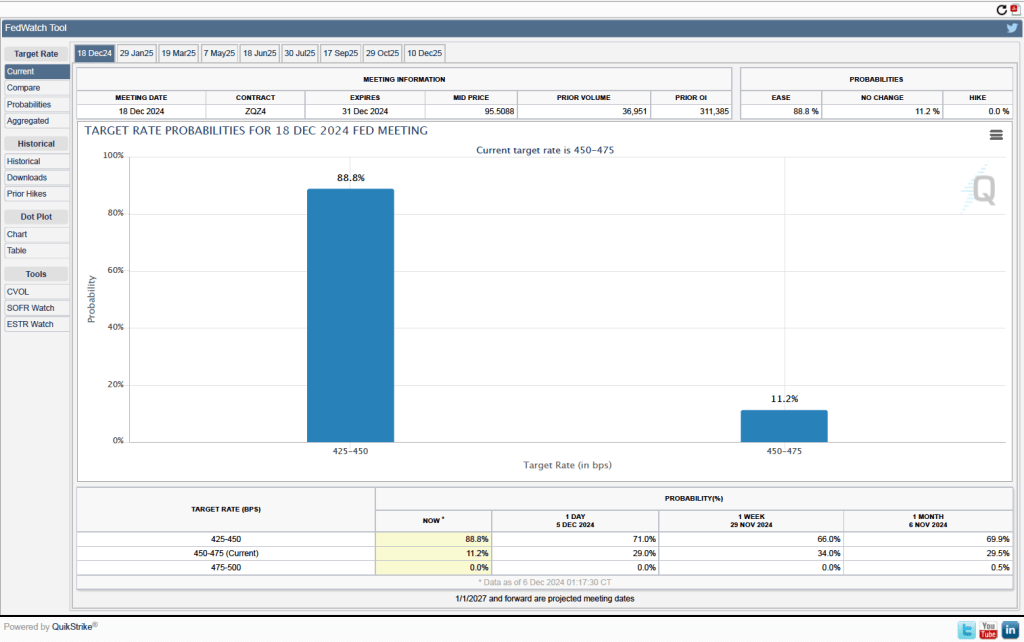
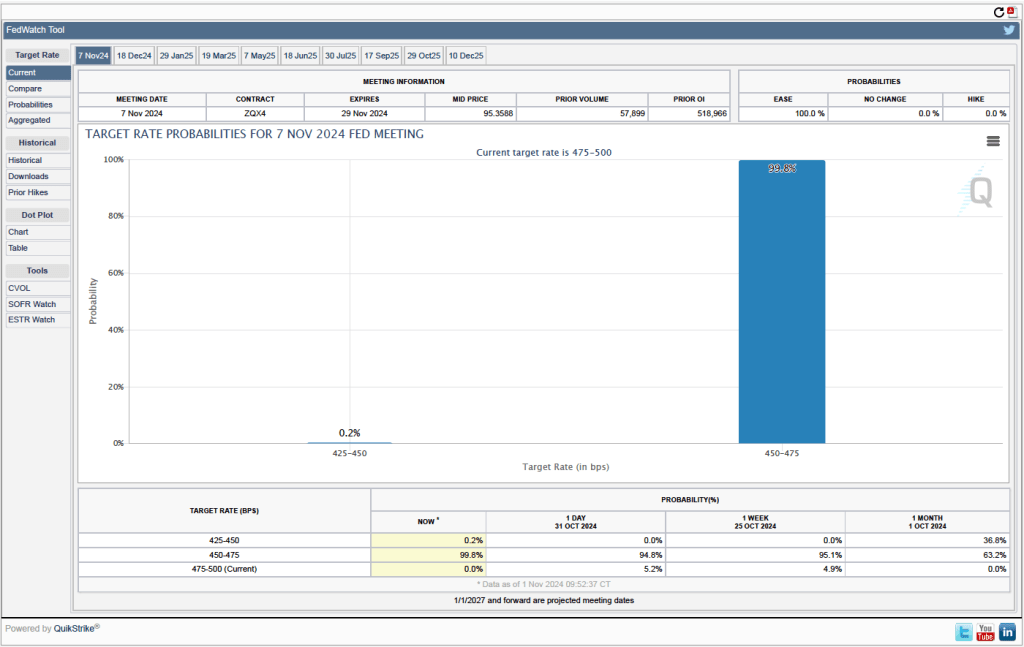
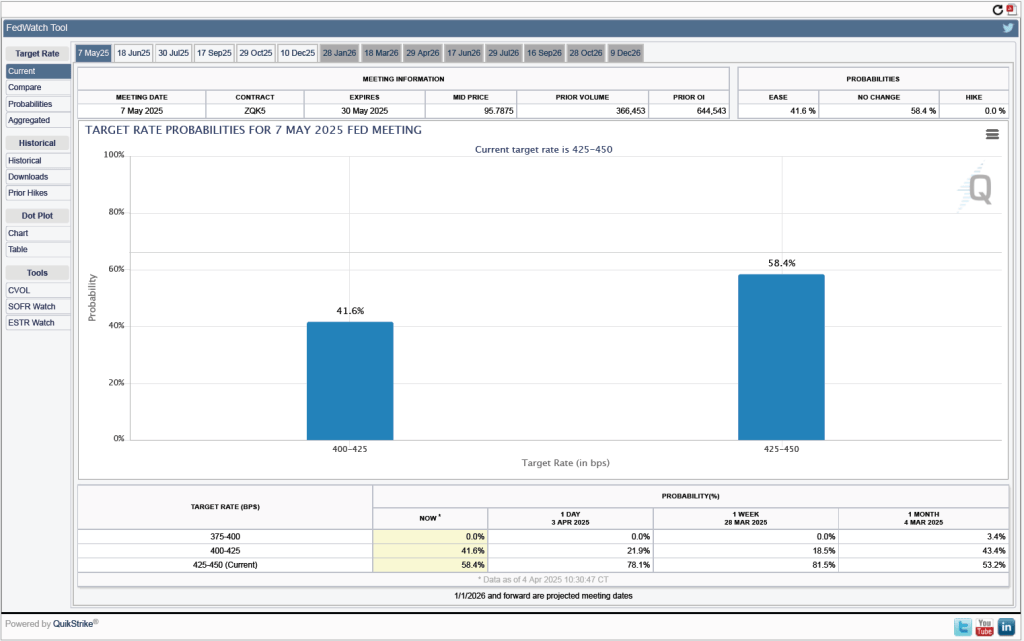
One indication of expectations of future cuts in the target for the federal funds rate comes from investors who buy and sell federal funds futures contracts. (We discuss the futures market for federal funds in this blog post.) The data from the futures market indicate that, despite the potential effects of the surprisingly large tariff increases, investors don’t expect that the FOMC will cut its target for the federal funds rate at its May 6–7 meeting. As shown in the following figure, investors assign a 58.4 percent probability to the committee keeping its target unchanged at 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent at that meeting.
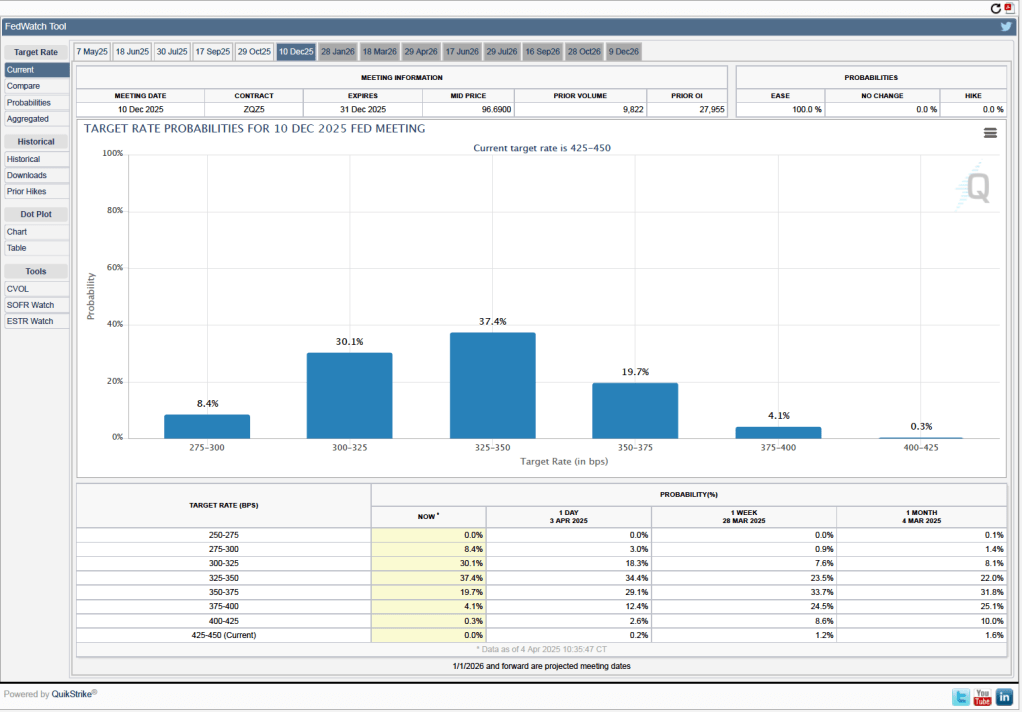
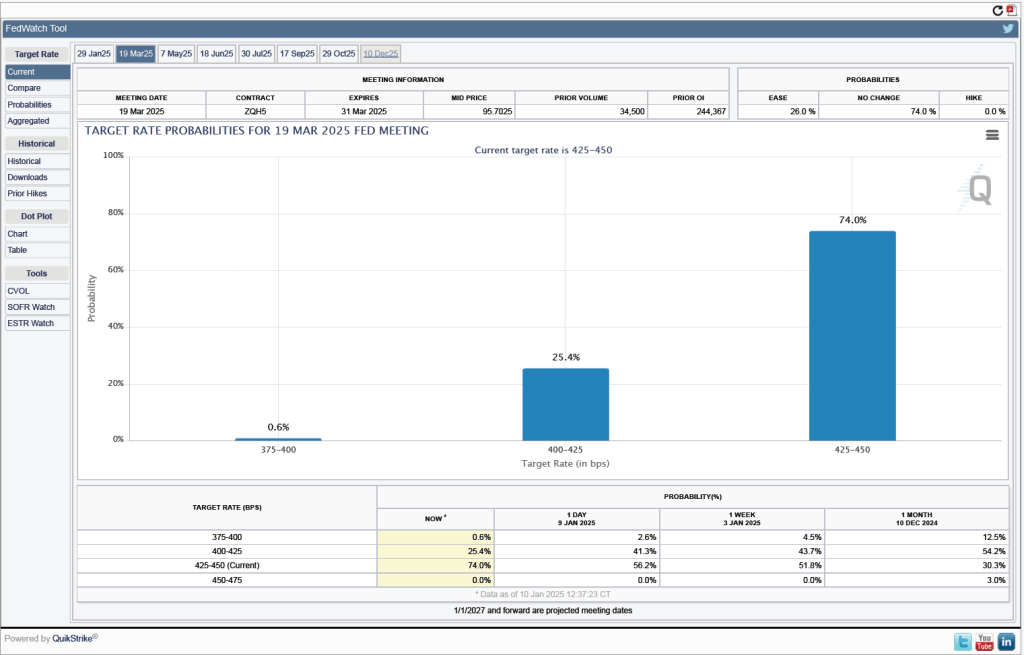
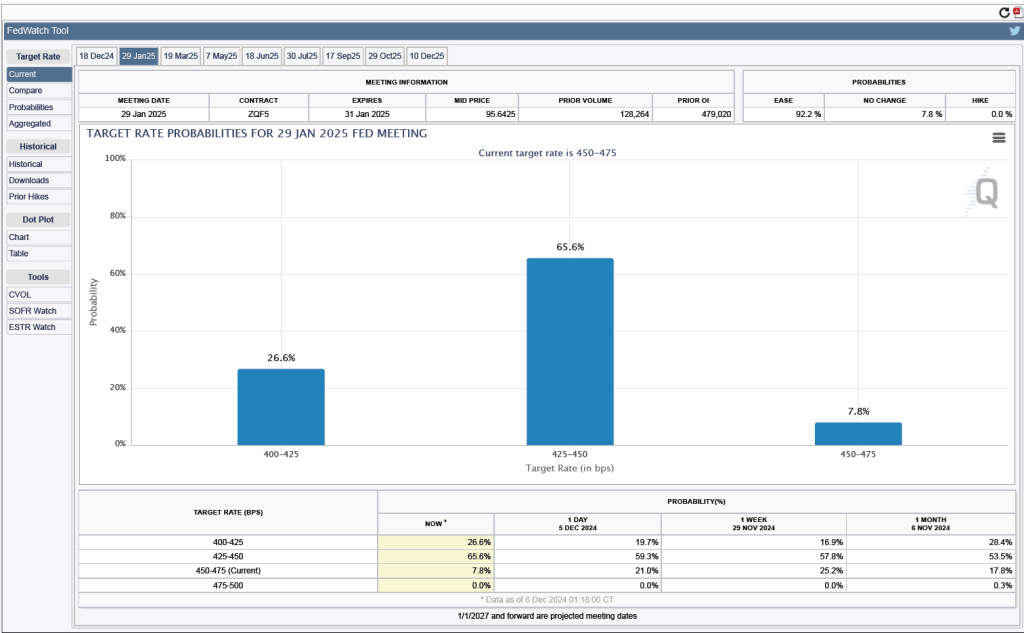
It’s a different story if we look at the end of the year. As the following figure shows, investors now expect that by the end of the FOMC’s meeting on December 9-10, the committee will have implemented at least four 0.25 percentage point (25 basis points) cuts in its target range for the federal funds rate. Investors assign a probability of 75.8 percent that the target range will end the year 3.25 percent to 3.50 percent or lower. At their March meeting, FOMC members projected only two 25 basis point cuts this year—but that was before the announcement of the unexpectedly large tariff increases.