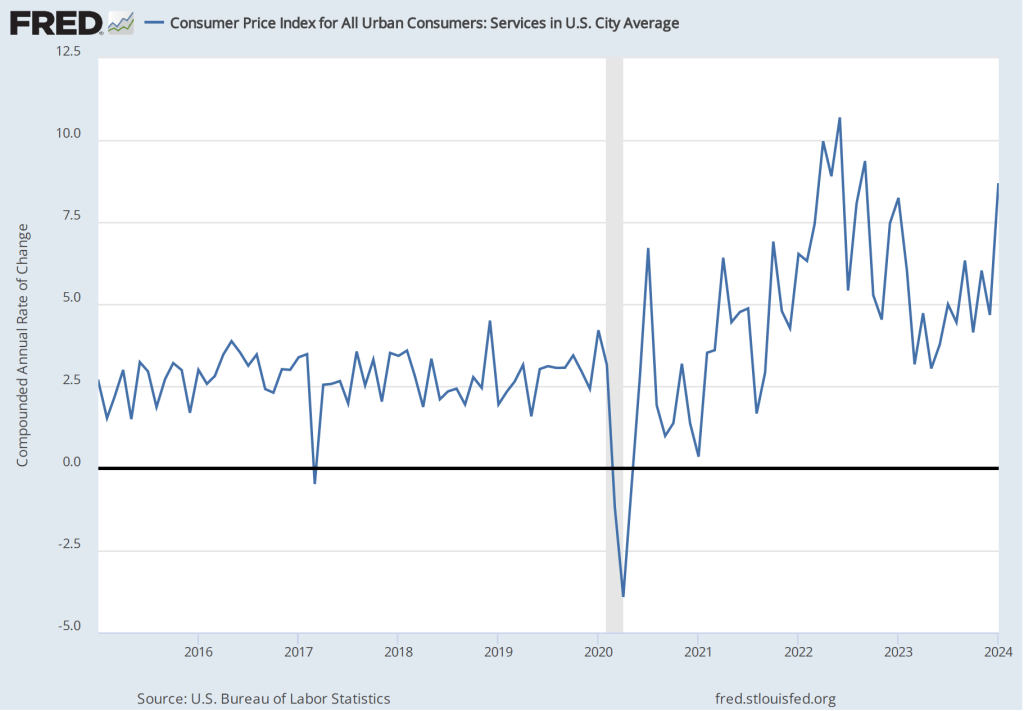Chair Jerome Powell and other members of the Federal Open Market Committee (Photo from federalreserve.gov)
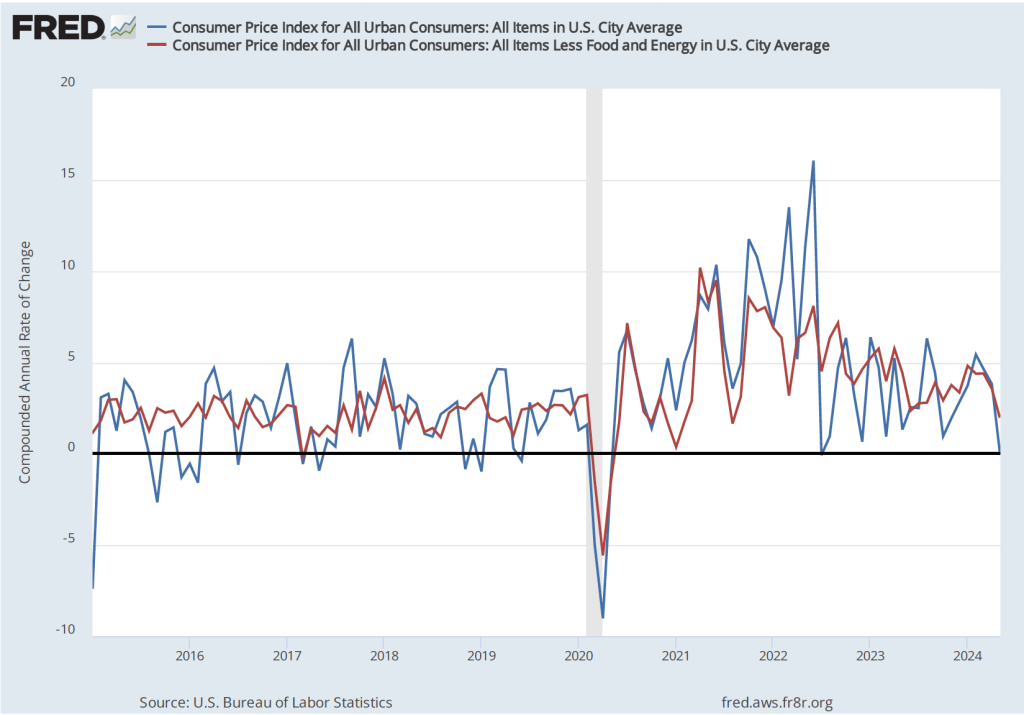
On Friday, June 28, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) released its “Personal Income and Outlays” report for April, which includes monthly data on the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index. Inflation as measured by annual changes in the consumer price index (CPI) receives the most attention in the media, but the Federal Reserve looks instead to inflation as measured by annual changes in the PCE price index to evaluate whether it’s meeting its 2 percent annual inflation target.
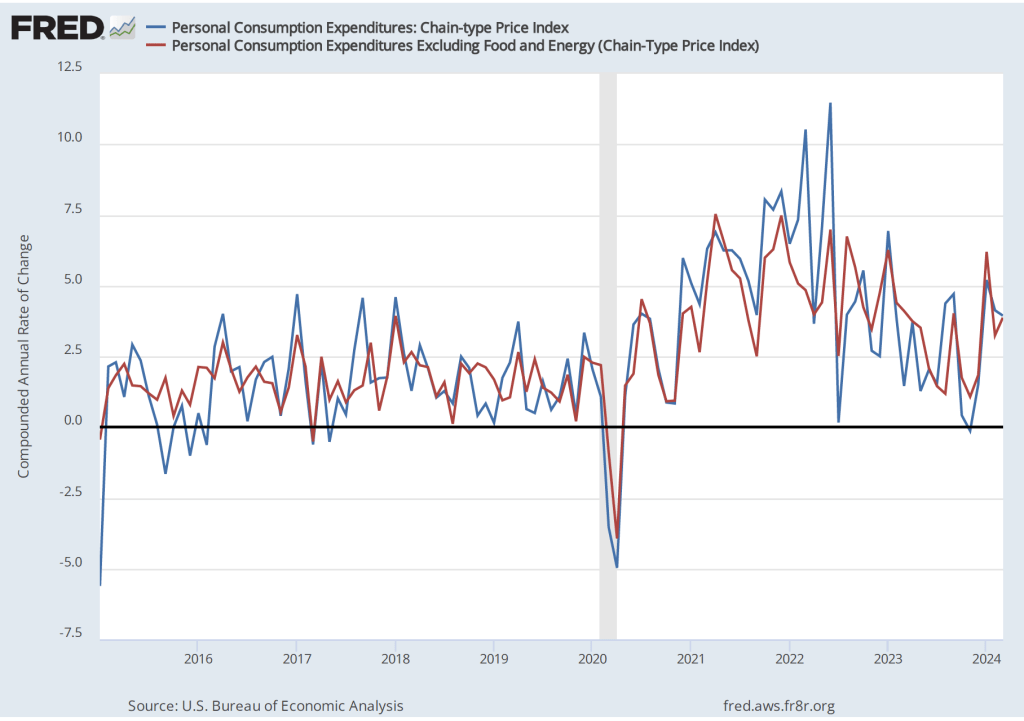
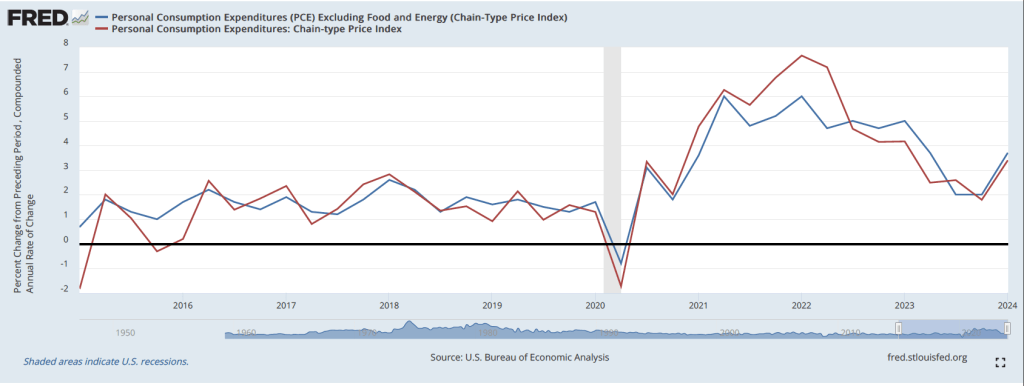
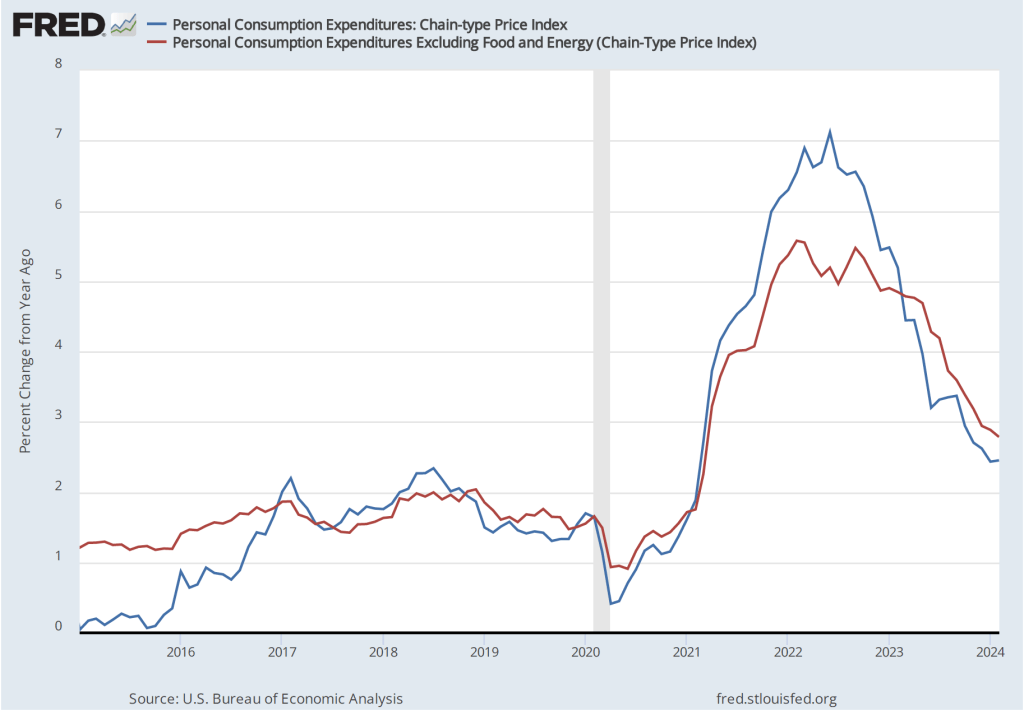
The following figure shows PCE inflation (blue line) and core PCE inflation (red line)—which excludes energy and food prices—for the period since January 2015 with inflation measured as the change in the PCE from the same month in the previous year. Measured this way, in May PCE inflation (the blue line) was 2.6 percent in May, down slightly from PCE inflation of 2.7 percent in April. Core PCE inflation (the red line) in May was also 2.6 percent, down from 2.8 percent in April.

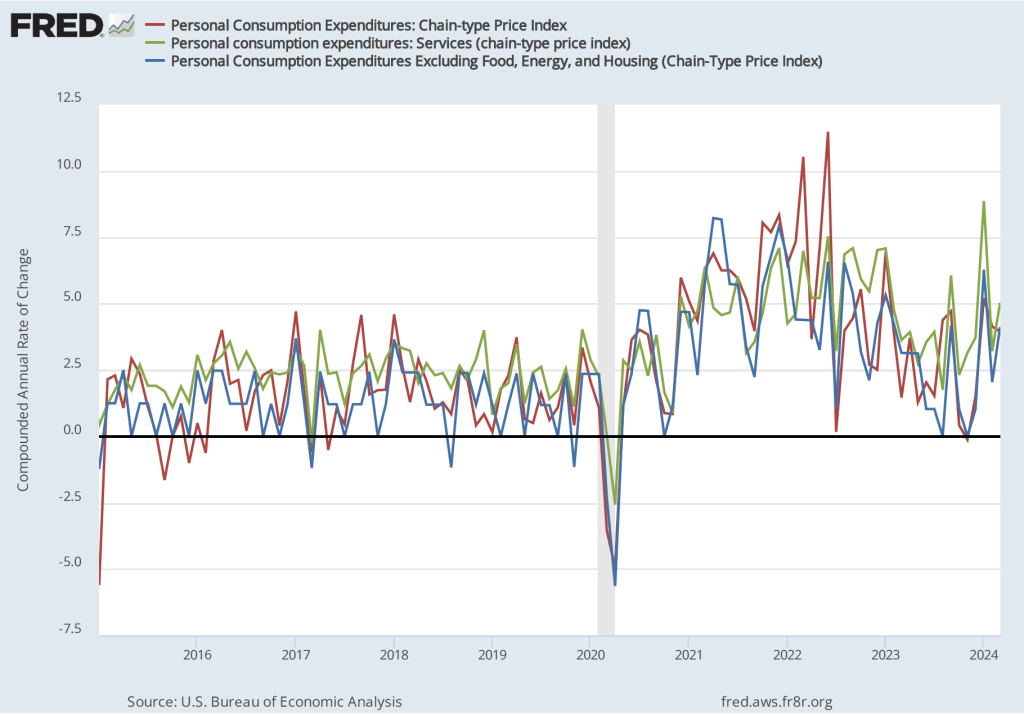
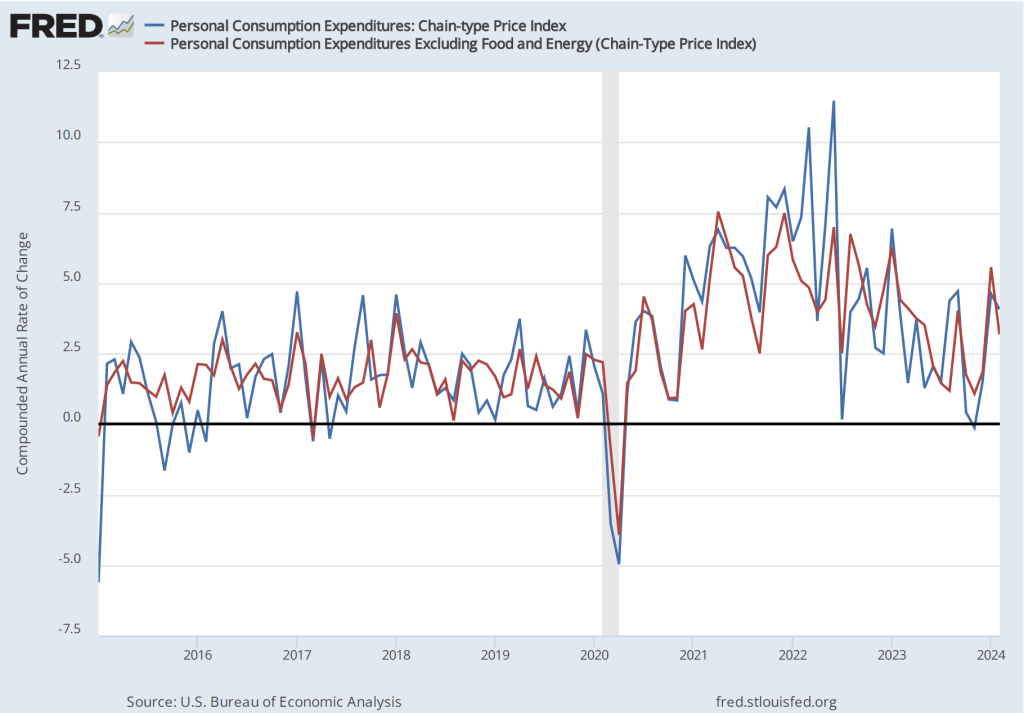
The following figure shows PCE inflation and core PCE inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month inflation, while this figure shows 1-month inflation.) Measured this way, PCE inflation sharply declined from 3.2 percent in April to -0.1 percent in in May—meaning that consumer prices actually fell during May. Core PCE inflation declined from 3.2 percent in April to 1.0 percent in May. This decline indicates that inflation by either meansure slowed substantially in May, but data for a single month should be interpreted with caution.

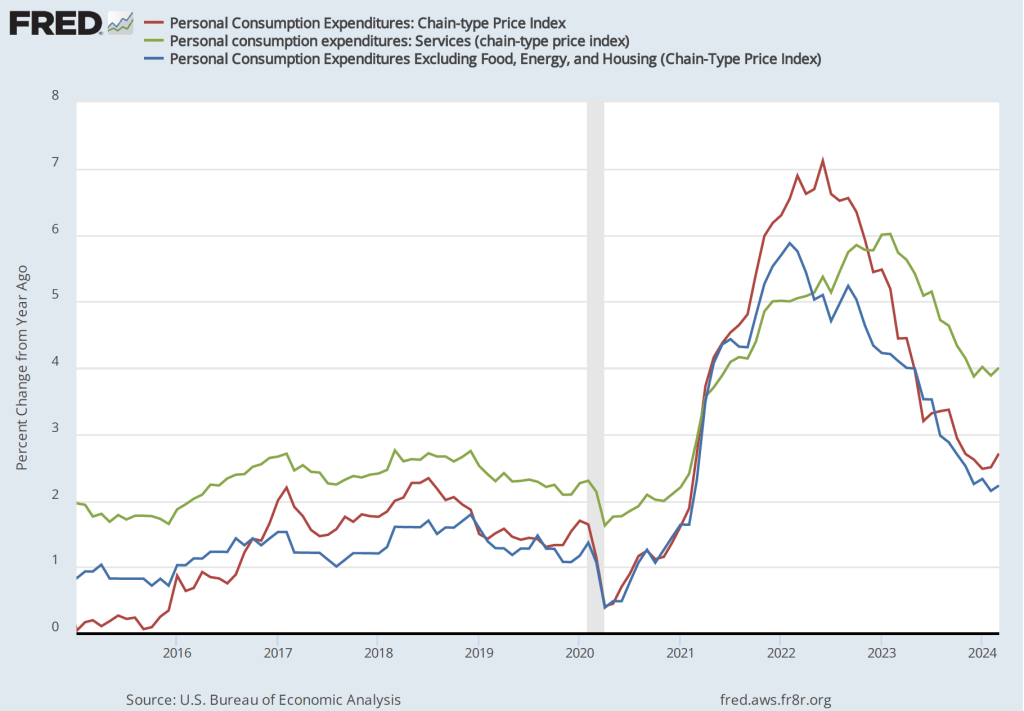
The following figure shows another way of gauging inflation by including the 12-month inflation rate in the PCE (the same as shown in the figure above—although note that PCE inflation is now the red line rather than the blue line), inflation as measured using only the prices of the services included in the PCE (the green line), and the trimmed mean rate of PCE inflation (the blue line). Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) have said that they are concerned by the persistence of elevated rates of inflation in services. The trimmed mean measure is compiled by economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas by dropping from the PCE the goods and services that have the highest and lowest rates of inflation. It can be thought of as another way of looking at core inflation by excluding the prices of goods and services that had particularly high or particularly low rates of inflation during the month.

Inflation using the trimmed mean measure was 2.8 percent in May (calculated as a 12-month inflation rate), down only slightly from 2.9 percent in April—and still well above the Fed’s target inflation rate of 2 percent. Inflation in services remained high in May at 3.9 percent, down only slightly from 4.0 percent in April.
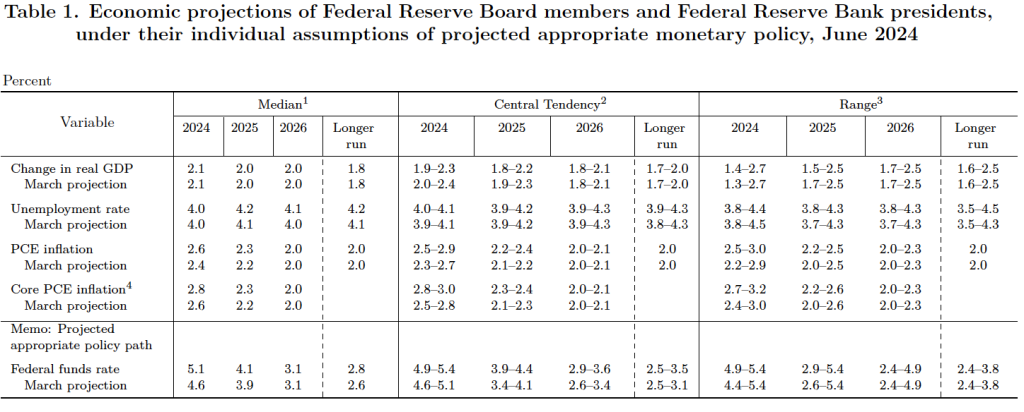
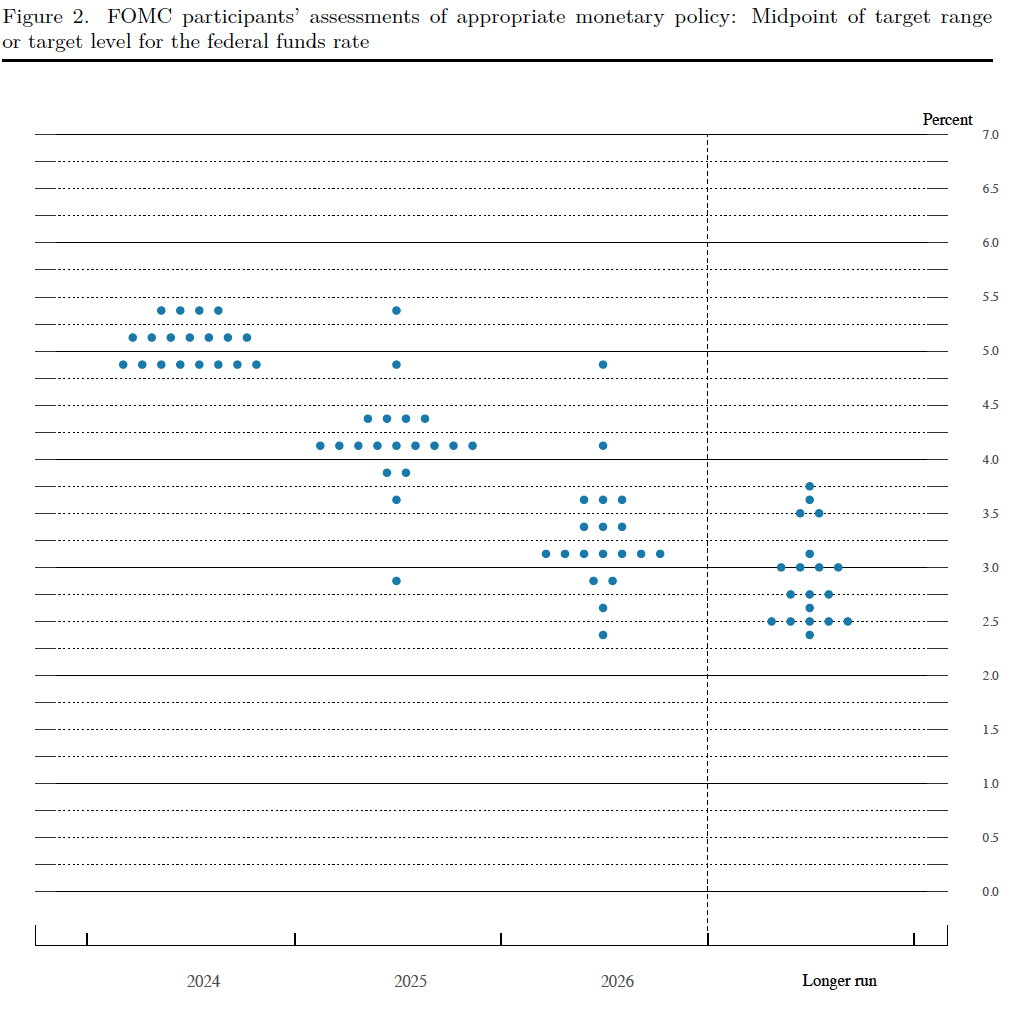
This month’s PCE inflation data indicate that the inflation rate is still declining towards the Fed’s target, with the low 1-month inflation rates being particularly encouraging. But the FOMC will likely need additional data before deciding to lower the committee’s target for the federal funds rate, which is currently 5.25 percent to 5.50 percent. The next meeting of the FOMC is July 30-31. What do financial markets think the FOMC will decide at that meeting?
Futures markets allow investors to buy and sell futures contracts on commodities–such as wheat and oil–and on financial assets. Investors can use futures contracts both to hedge against risk—such as a sudden increase in oil prices or in interest rates—and to speculate by, in effect, betting on whether the price of a commodity or financial asset is likely to rise or fall. (We discuss the mechanics of futures markets in Chapter 7, Section 7.3 of Money, Banking, and the Financial System.) The CME Group was formed from several futures markets, including the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, and allows investors to trade federal funds futures contracts. The data that result from trading on the CME indicate what investors in financial markets expect future values of the federal funds rate to be. The following chart from the CME’s FedWatch Tool shows the current values from trading of federal funds futures.

The probabilities in the chart reflect investors’ predictions of what the FOMC’s target for the federal funds rate will be after the committee’s July meeting. The chart indicates that investors assign a probability of only 10.3 percent to the FOMC cutting its federal funds rate target by 0.25 percentage point at that meeting and an 89.7 percent probability of the commitee leaving the target unchanged.
In contrast, the following figure shows that investors expect that the FOMC will cut its federal funds rate at the meeting scheduled for September 17-18. Investors assign a 57.9 percent probability of a 0.25 percentage point cut and a 6.2 percent probability of a 0.50 percentage point cut. The committee deciding to leave the target unchanged at 5.25 percent to 5.50 percent is assigned a probability of only 35.9 percent.