
Image generated by ChatGTP-4o.
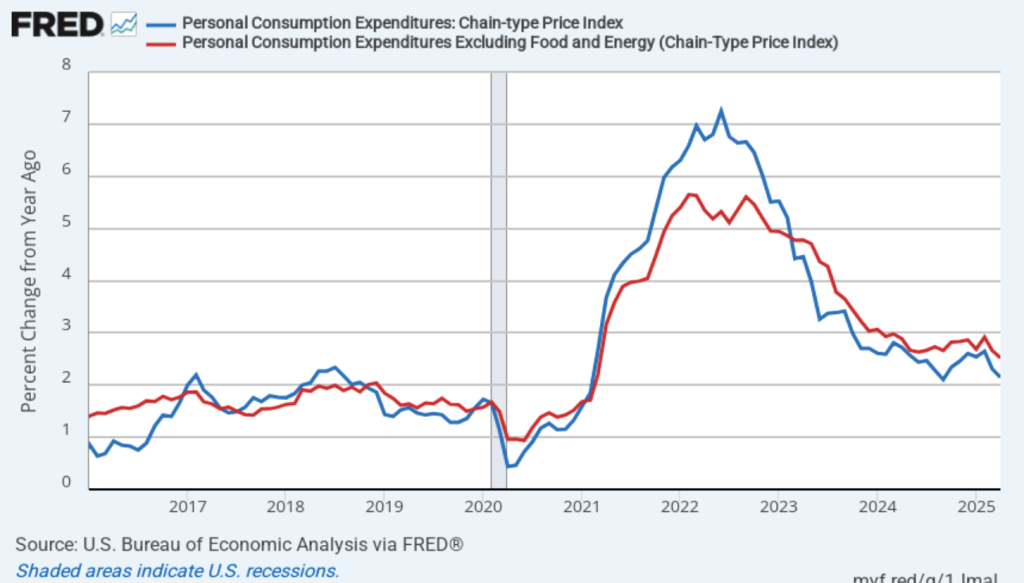
Today (May 30), the BEA released monthly data on the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index as part of its “Personal Income and Outlays” report. The Fed relies on annual changes in the PCE price index to evaluate whether it’s meeting its 2 percent annual inflation target. The following figure shows PCE inflation (the blue line) and core PCE inflation (the red line)—which excludes energy and food prices—for the period since January 2016, with inflation measured as the percentage change in the PCE from the same month in the previous year. In April, PCE inflation was 2.1 percent, down from 2.3 percent in March. Core PCE inflation in April was 2.5 percent, down from 2.7 percent in March. Headline PCE inflation was below the forecast of economists surveyed, while core PCE inflation was consistent with the forecast.
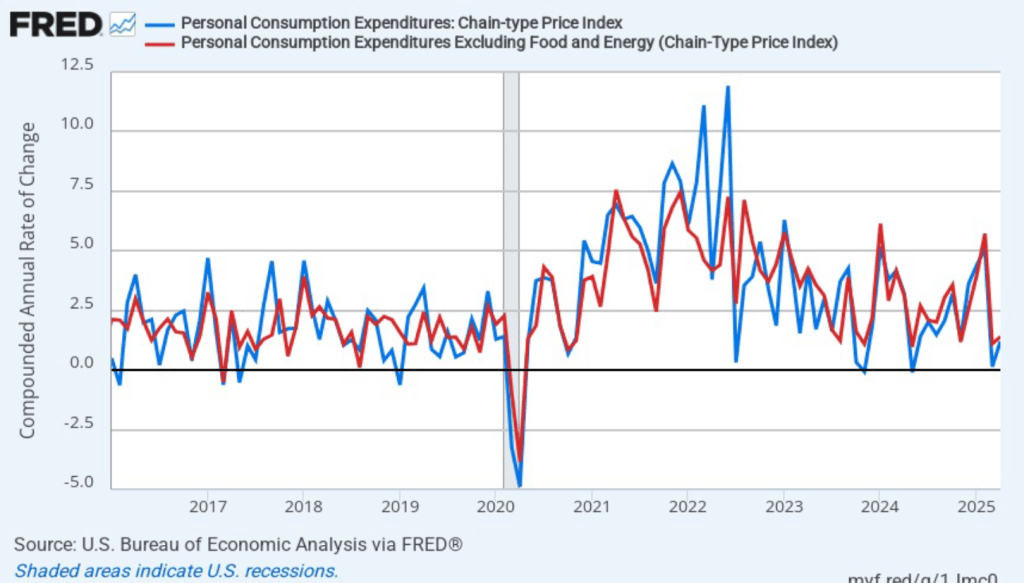
The following figure shows PCE inflation and core PCE inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month inflation, while this figure shows 1-month inflation.) Measured this way, PCE inflation increased in April to 1.2 percent from 0.1 percent in March. Core PCE inflation also increased from 1.1 percent in March to 1.4 percent in April. So, both 1-month PCE inflation estimates are well below the Fed’s 2 percent target. The usual caution applies that 1-month inflation figures are volatile (as can be seen in the figure), so we shouldn’t attempt to draw wider conclusions from one month’s data. In addition, because these data are for April, they don’t capture fully the price increases resulting from the tariff increases the Trump administration announced on April 2.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell has noted that inflation in non-market services has been high. Non-market services are services whose prices the BEA imputes rather than measures directly. For instance, the BEA assumes that prices of financial services—such as brokerage fees—vary with the prices of financial assets. So that if stock prices fall, the prices of financial services included in the PCE price index also fall. Powell has argued that these imputed prices “don’t really tell us much about … tightness in the economy. They don’t really reflect that.” The following figure shows 12-month headline inflation (the blue line) and 12-month core inflation (the red line) for market-based PCE. (The BEA explains the market-based PCE measure here.)
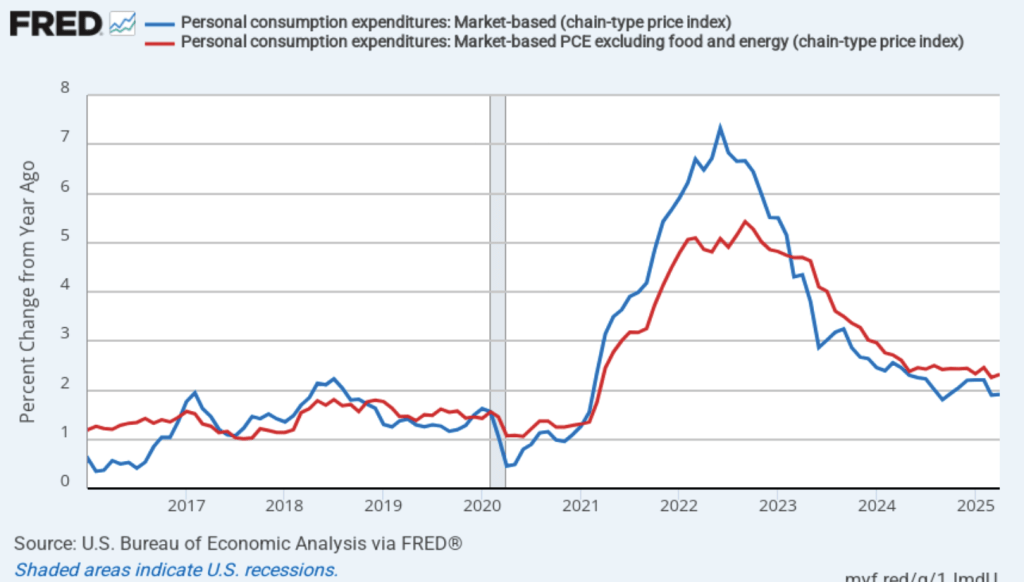
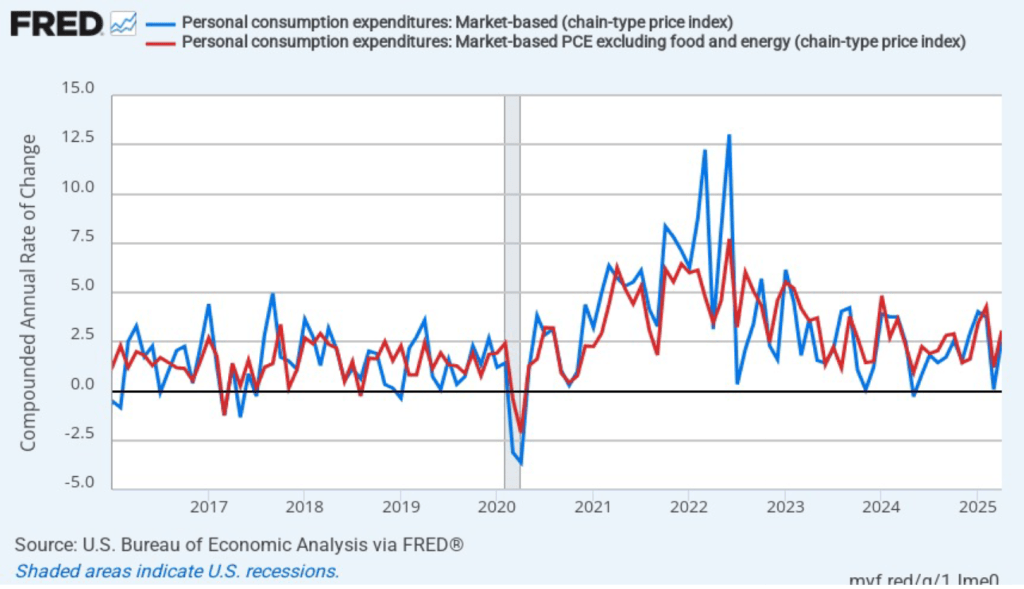
Headline market-based PCE inflation was 1.9 percent in April, unchanged from March. Core market-based PCE inflation was 2.3 percent in April, which was also unchanged from March. So, both market-based measures show about the same rate of inflation in April as the total measures do. In the following figure, we look at 1-month inflation using these measures. The 1-month inflation rates are both higher than the 12-month rates. Headline market-based inflation was 2.6 percent in April, up from 0.1 percent in March. Core market-based inflation was 3.1 percent in April, up from 1.2 percent in March. As the figure shows, the 1-month inflation rates are more volatile than the 12-month rates, which is why the Fed relies on the 12-month rates when gauging how close it is coming to hitting its target inflation rate.
In summary, today’s data provide some evidence that the inflation rate is getting closer to the Fed’s 2 percent annual target. Improving inflation combined with some indications that output growth is slowing—the BEA release indicated that growth in real consumption expenditures slowed in April—might make it more likely that the Fed’s policymaking Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) will cut its target for the federal funds rate relatively soon.
However, investors who buy and sell federal funds futures contracts expect that the FOMC will leave its federal funds rate target unchanged at its next meetings on June 17–18 and July 29–30. (We discuss the futures market for federal funds in this blog post.) Investors assign a probability 0f 72.6 percent to the FOMC cutting its target at its September 29–30 meeting. Investor expectations reflect the recent statements from Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other members of the FOMC that they intend to wait until the effects of the tariff increases on the economy are clearer before changing the target for the federal funds rate.
