
The result when asking GTP-4o to generate “an image illustrating inflation.”
Inflation, as measured by changes in the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, continued a slow decline that began in March. (The Fed uses annual changes in the PCE price index to evaluate whether it’s meeting its 2 percent annual inflation target.) On August 30, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) released its “Personal Income and Outlays” report for July, which contains monthly PCE data.
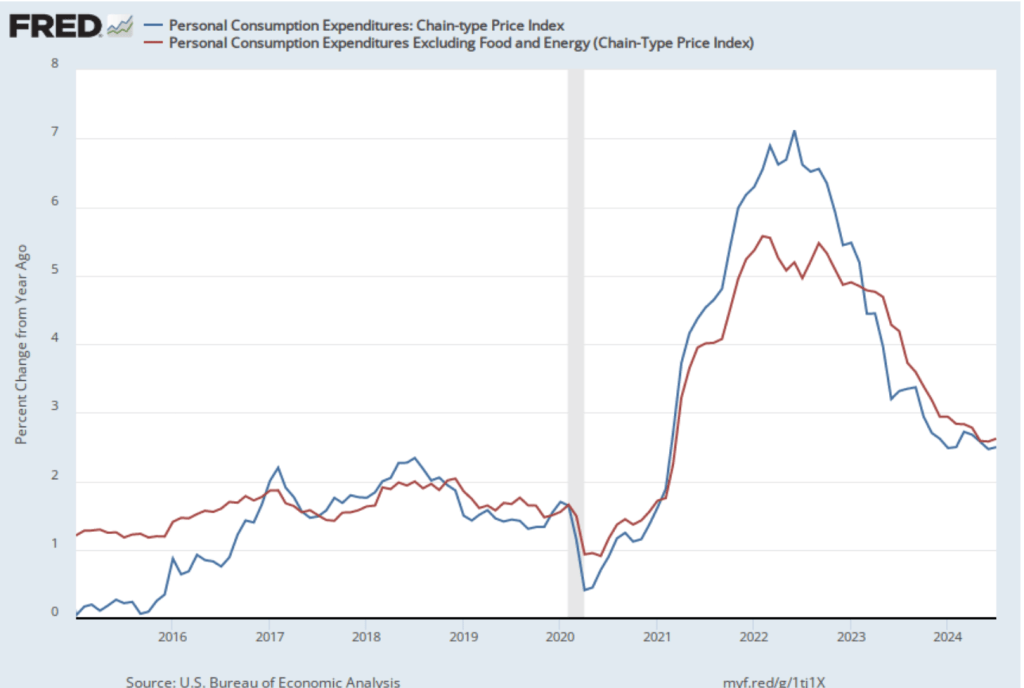
The following figure shows PCE inflation (blue line) and core PCE inflation (red line)—which excludes energy and food prices—for the period since January 2015 with inflation measured as the percentage change in the PCE from the same month in the previous year. Measured this way, in July PCE inflation (the blue line) was 2.5 percent, the same as in June. Core PCE inflation (the red line) in July was 2.6 percent, which was also unchanged from June.
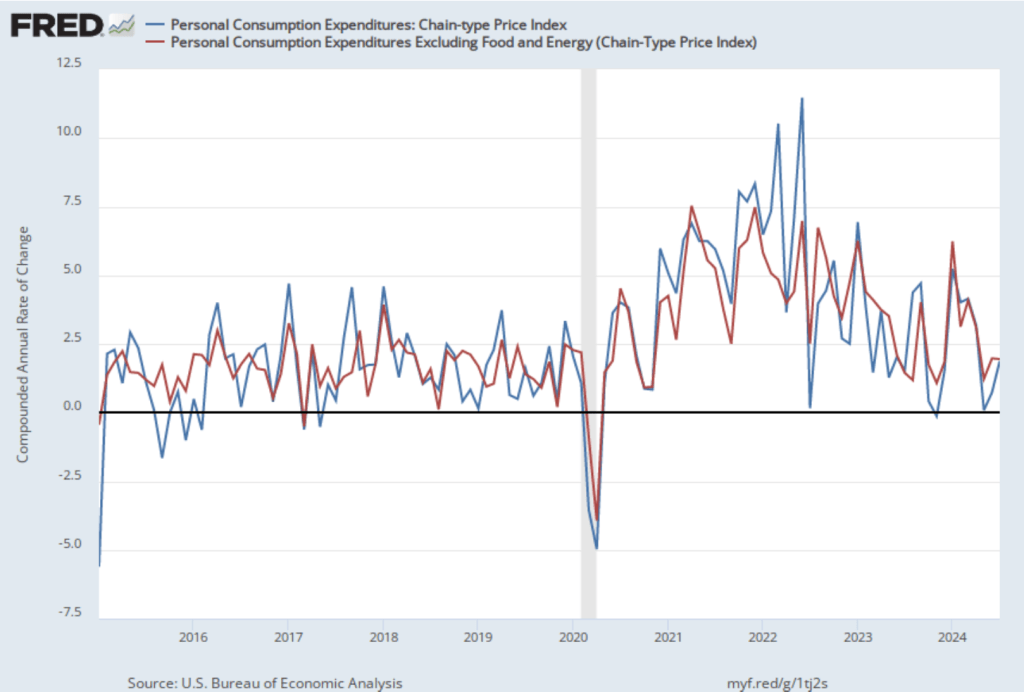
The following figure shows PCE inflation and core PCE inflation calculated by compounding the current month’s rate over an entire year. (The figure above shows what is sometimes called 12-month inflation, while this figure shows 1-month inflation.) Measured this way, PCE inflation rose in July to 1.7 percent from 0.7 percent in July—although higher in July, inflation was below the Fed’s 2 percent target in both months. Core PCE inflation was 2.0 percent in July, which was unchanged from June. These data indicate that inflation has been at or below the Fed’s target for the last three months.
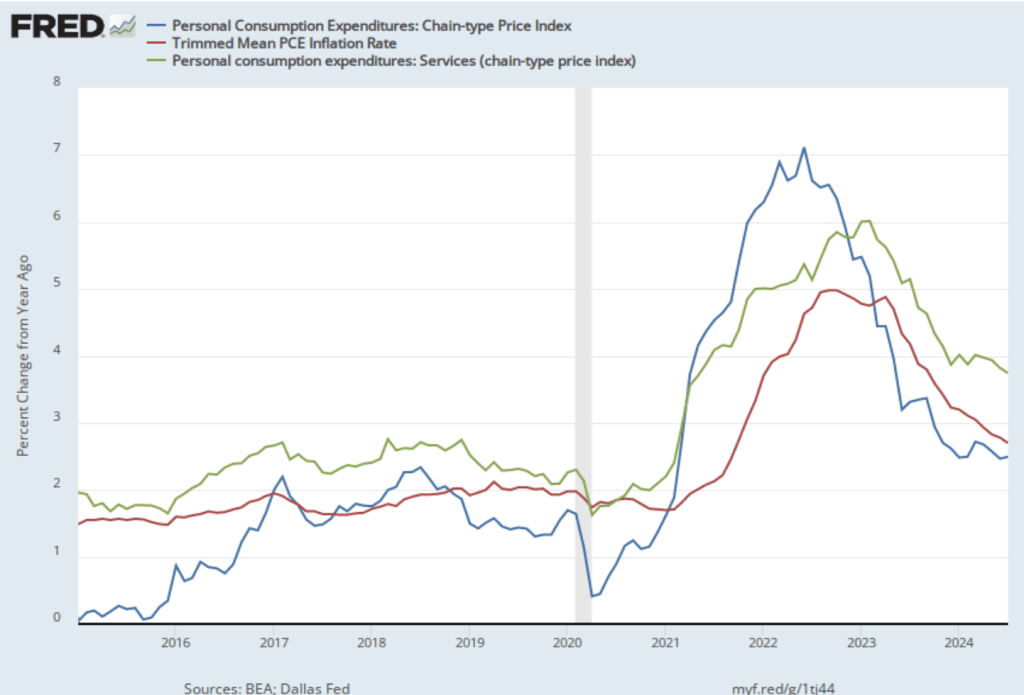
The following figure shows another way of gauging inflation by including the 12-month inflation rate in the PCE (the same as shown in the figure above), inflation measured using only the prices of the services included in the PCE (the green line), and the trimmed mean rate of PCE inflation (the red line). Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) have said that they are concerned by the persistence of elevated rates of inflation in services. The trimmed mean measure is compiled by economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas by dropping from the PCE the goods and services that have the highest and lowest rates of inflation. It can be thought of as another way of looking at core inflation by excluding the prices of goods and services that had particularly high or particularly low rates of inflation during the month.
Inflation using the trimmed mean measure was 2.7 percent in July (calculated as a 12-month inflation rate), down only slightly from 2.8 percent in June—and still above the Fed’s target inflation rate of 2 percent. Inflation in services remained high in July at 3.7 percent, although down from 3.9 percent in June.
On balance, taking together these various measures, inflation seems on track to return to the Fed’s 2 percent target. As we noted in this earlier post, last week in a speech at the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta’s monetary policy symposium in Jackson Hole, Wyoming , Fed Chair Jerome Powell all but confirmed that the the Fed’s policy-maiking Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) will cut its target for the federal funds rate at its next meeting on September 17-18. There was nothing in this latest PCE report to reduce the likelihood of the FOMC cutting its target at that meeting by an expected 0.25 percent point from a range of 5.25 percent to 5.50 percent to a range of 5.00 percent to 5.25 percent. There also is nothing in the report that would increase likelihood that the committee will cut its target by 0.50 percentage point, as many investors expected following the weak employment report released by the Bureau of labor Statistics (BLS) at the beginning of August. (We discuss this report and the reaction among investors in this post.)
