Supports: Microeconomics and Economics, Chapter 11, Section 11.5, and Essentials of Economics, Chapter 8, Section 8.5
Image generated by ChatGTP-4o showing the costs of inputs to a factory.
Mickey, the Econ Pup, sometimes struggles with drawing and interpreting cost curves. Examine the cost curves shown in images a. and b. and let Mickey know if you find any errors.
a.
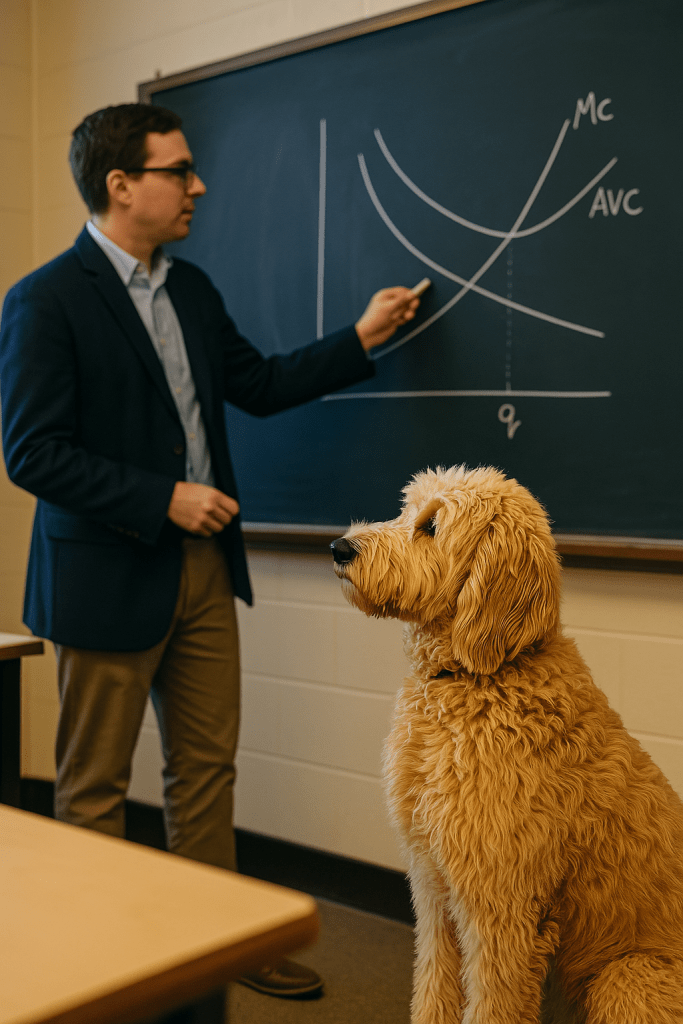

b.
Solving the Problem
Step 1: Review the chapter material. This problem is about drawing and interpreting cost curves, so you may want to review Chapter 11, Section 11.5, “Graphing Cost Curves.”
Step 2: Answer part a. by explaining whether there are any errors in the cost curves shown in the image in a. No wonder Mickey is confused! This figure has multiple errors:
- It’s an error to have the ATC and AVC curves cross. The unlabeled curve at the bottom is supposed to be AFC. We know that if a firm has fixed costs, then the ATC and AVC curves will get closer and closer as the quantity increases and AFC becomes smaller and smaller. But because AFC will never decline to zero, ATC and AVC can’t be equal at any quantity.
- The second error is related to the first error. We know that the MC and ATC curves should intersect at the quantity at which ATC is at a minimum. In this figure, the MC curve intersects the ATC curve at a quantity that is larger than the quantity at which ATC recaches a minimum.
- The third error is related to the first two errors. The relationship between the three average cost curves should be ATC = AVC + AFC at every quantity. In this figure the relationship doesn’t hold at any quantity.
- Finally, there is a dotted line from the point where the (unlabeled) AFC curve intersects with the MC curve down to the Q-axis. But that point has no economic significance.
Step 3: Answer part b. by explaining whether there are any errors in the cost curves shown in image b. Mickey can rest easy with these cost curve because, although the figure seems to be only partially finished, all of the cost curves are correctly drawn. The MC curve correctly intersects the AVC curve at the quantity at which the AVC curve is at a minimum. The instructor could finish the figure by labeling the bottom curve as AFC and by drawing an ATC curve above the AVC curve, with the ATC curve intersecting the MC curve at the quantity at which the ATC curve is at a minimum.



